Question: Detailed question attached Problem 2: In this problem we explore the problem of hypothesis testing. The basic concept is to define the null hypothesis, Ho,
Detailed question attached
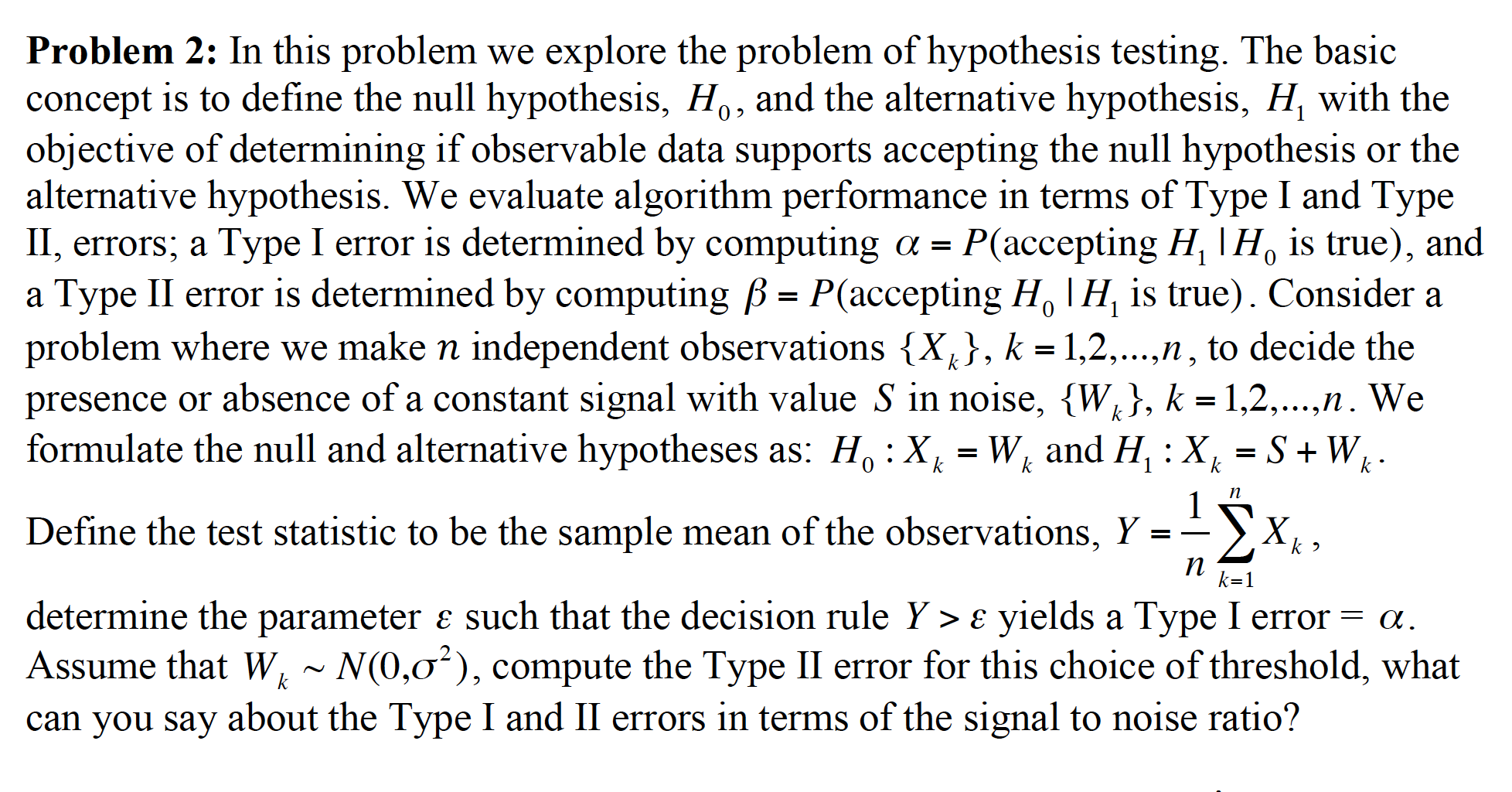
Problem 2: In this problem we explore the problem of hypothesis testing. The basic concept is to define the null hypothesis, Ho, and the alternative hypothesis, H, with the objective of determining if observable data supports accepting the null hypothesis or the alternative hypothesis. We evaluate algorithm performance in terms of Type I and Type II, errors; a Type I error is determined by computing a = P(accepting H, IH, is true), and a Type II error is determined by computing B = P(accepting H, I H, is true) . Consider a problem where we make n independent observations {X,}, k = 1,2,...,n, to decide the presence or absence of a constant signal with value S in noise, {W,}, k = 1,2,...,n. We formulate the null and alternative hypotheses as: H. : X, = W, and H, : X, = S + Wk. n Define the test statistic to be the sample mean of the observations, Y = - k ? n k=1 determine the parameter & such that the decision rule Y > & yields a Type I error = a. Assume that W, ~ N(0,o'), compute the Type II error for this choice of threshold, what can you say about the Type I and II errors in terms of the signal to noise ratio
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


