Question: Details: To allow your Queue classes to be flexible you will make them generic, utilizing a type parameter. Specifically, your classes will both implement the
Details:
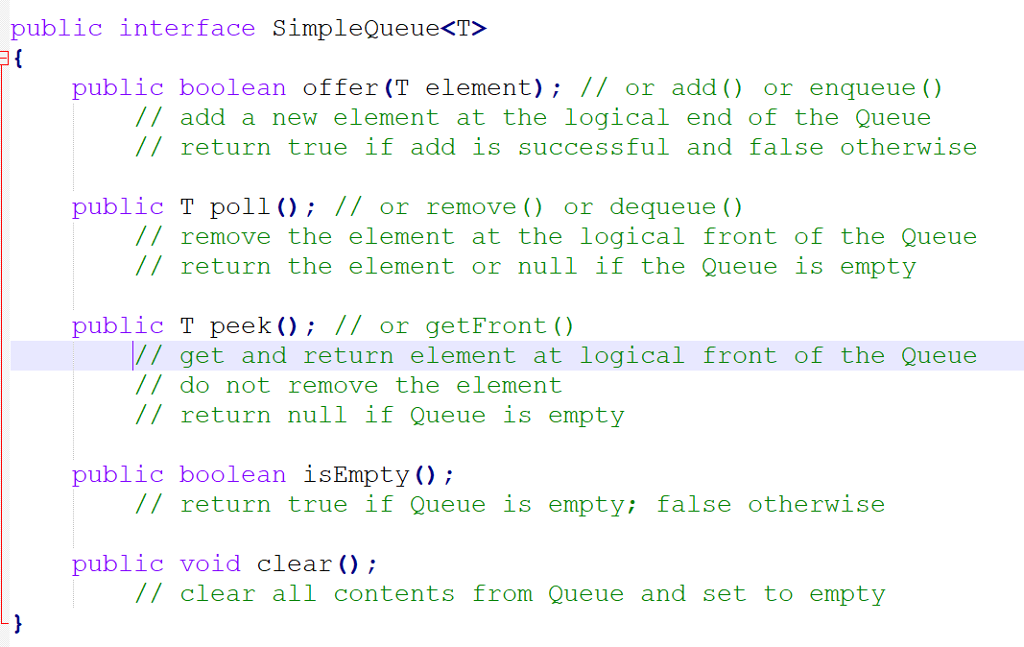
To allow your Queue classes to be flexible you will make them generic, utilizing a type parameter. Specifically, your classes will both implement the SimpleQueue interface. This interface contains the 5 methods above and is provided for you in file SimpleQueue.java.
In order to enable the bookkeeping to determine the efficiency of your Queue operations, your Queue classes will also implement a second interface, Moves. This interface is provided for you in file Moves.java and contains the following two methods:
public int getMoves(); // return the value of the moves variable
public void setMoves(int val); // initialize the moves variable to val
This interface will allow you to set and obtain the information in a moves variable within your Queue classes. The moves variable will be updated during your offer() and poll() methods such that each assignment to a location in the array causes an increment of the variable. For example, given the first Queue implementation above, an offer() to an empty queue will require 1 move (put item in location 0). However, the next offer() will require a shift of the first item down (1 move) plus the assignment of the new item (1 move) for a total of 2 moves.
Call your classes PrimQ1 (add at beginning, remove from end) and PrimQ2 (add at end, remove from beginning). Below are the class headers that are required for these:
public class PrimQ1 implements SimpleQueue, Moves
public class PrimQ2 implements SimpleQueue, Moves
Once you have completed your PrimQ1 and PrimQ2 classes, you will test them with the program CS445Rec1.java, which is also provided for you. Read over this program carefully your classes should work with the program as it is written if CS445Rec1.java will not compile or run correctly then you must fix your classes do not change CS445Rec1.java.
After everything is working, look at the output to your program and compare the results for PrimQ1 and PrimQ2. Later I will be posting my results and you can compare yours to mine (they should be the same). Also later we will discuss the results overall and why neither is actually desirable.
Note: When creating a dynamic array in a generic class, you cannot actually allocate an array of type T. Rather, you must create an array of Object, then cast it to (T []).
SimpleQueue.java
Moves.java

CS445Rec1.java
public interface SimpleQueue public boolean offer (T element); I/ or add) or enqueue // add a new element at the logical end of the Queue // return true if add is successful and false otherwise public T poll ; 1/ or remove() or dequeue // remove the element at the logical front of the Queue // return the element or null if the Queue is empty public T peek ; // or getFront () // get and return element at logical front of the Queue // do not remove the element // return null if Queue is empty public boolean isEmpty // return true if Queue is empty: false otherwise public void clear // clear all contents from Queue and set to empty public interface Moves public int getMoves ) //return the value of the moves variable public void setMoves (int val) 1I initialize the noves variable to val mport java.util.*; public class CS445Rec1 public static void main(string [1 args) // Create ArrayLists of interface types ArrayList> kyews-new ArrayList> ArrayList moonew ArrayList Add an instance of each Q type to each ArrayList Note that we only I create two objects here each object is being accessed (in turn) as // a SimpleQueue (1))moo.add ( (Move kyews.get (0)); kyews.add (new Prim@2 (1)m.add (Moves) kyews.get ()) / set moves for each object to o for (Moves m: moo) m.setMoves (0) System.out.print ("Adding to oueues: ") for (int i-0: i : kyews) Q.offer (X) System.out..println) for (intj-0; j and removing all items from each / SimpleQueuecInteger> therein. This could also have been done using the "toreach" version of the for loop or in other ways as well. Java 8 has many ways of iterating through a collection Integer temp for (int j-0 j






