Question: determine the optimal specific surface area in a full-scale reactor = Granules type Internal diameter expansion column Height expansion column Particle size (smallest) Particle size

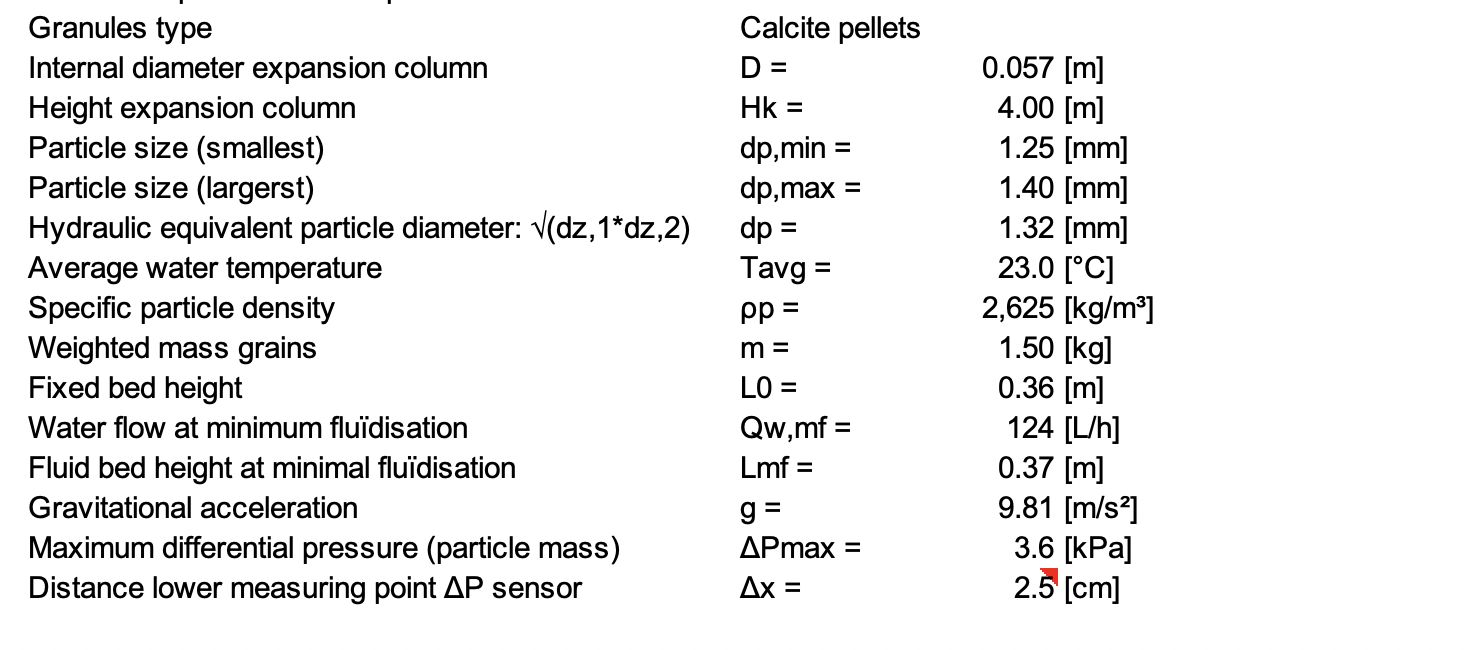
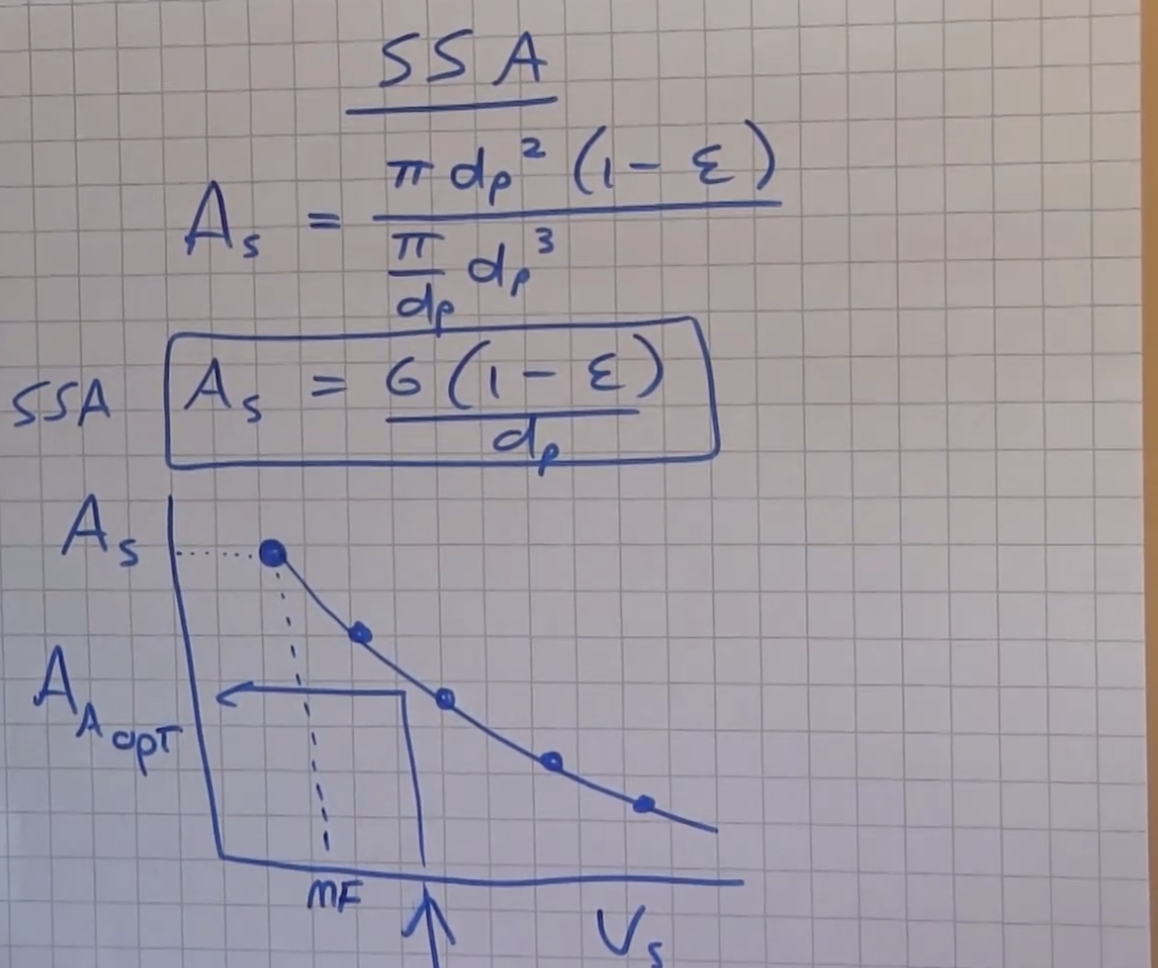
determine the optimal specific surface area in a full-scale reactor = Granules type Internal diameter expansion column Height expansion column Particle size (smallest) Particle size (largerst) Hydraulic equivalent particle diameter: V(dz,1*dz,2) Average water temperature Specific particle density Weighted mass grains Fixed bed height Water flow at minimum fludisation Fluid bed height at minimal fludisation Gravitational acceleration Maximum differential pressure (particle mass) Distance lower measuring point AP sensor Calcite pellets D = Hk = dp,min = dp,max dp = Tavg = pp = m = LO = Qw,mf = Lmf = g= APmax = Ax = = 0.057 [m] 4.00 [m] 1.25 [mm] 1.40 [mm] 1.32 [mm] 23.0 [C] 2,625 [kg/m] 1.50 [kg] 0.36 [m] 124 [L/h] 0.37 [m] 9.81 [m/s] 3.6 [kPa] 2.5 [cm] = 2 SSA To dp (1-) des de As = 6 (1- ) de As = T 3 SSA A A, Ance opt ME N . Us determine the optimal specific surface area in a full-scale reactor = Granules type Internal diameter expansion column Height expansion column Particle size (smallest) Particle size (largerst) Hydraulic equivalent particle diameter: V(dz,1*dz,2) Average water temperature Specific particle density Weighted mass grains Fixed bed height Water flow at minimum fludisation Fluid bed height at minimal fludisation Gravitational acceleration Maximum differential pressure (particle mass) Distance lower measuring point AP sensor Calcite pellets D = Hk = dp,min = dp,max dp = Tavg = pp = m = LO = Qw,mf = Lmf = g= APmax = Ax = = 0.057 [m] 4.00 [m] 1.25 [mm] 1.40 [mm] 1.32 [mm] 23.0 [C] 2,625 [kg/m] 1.50 [kg] 0.36 [m] 124 [L/h] 0.37 [m] 9.81 [m/s] 3.6 [kPa] 2.5 [cm] = 2 SSA To dp (1-) des de As = 6 (1- ) de As = T 3 SSA A A, Ance opt ME N . Us
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


