Question: Develop the transfer function that relates h3 with F2 in deviation form. Find the steady-state gain and time constant. The level-flow system in the Figure

Develop the transfer function that relates h3 with F2 in deviation form. Find the steady-state gain and time constant.
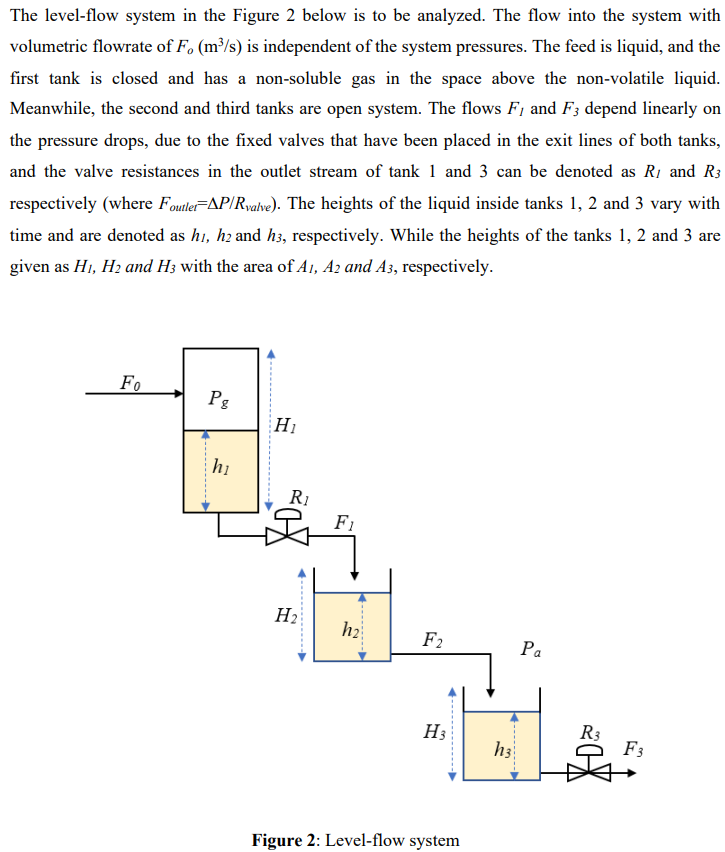
The level-flow system in the Figure 2 below is to be analyzed. The flow into the system with volumetric flowrate of F. (m/s) is independent of the system pressures. The feed is liquid, and the first tank is closed and has a non-soluble gas in the space above the non-volatile liquid. Meanwhile, the second and third tanks are open system. The flows F, and F3 depend linearly on the pressure drops, due to the fixed valves that have been placed in the exit lines of both tanks, and the valve resistances in the outlet stream of tank 1 and 3 can be denoted as R1 and R3 respectively (where Foutler=AP/Rvalve). The heights of the liquid inside tanks 1, 2 and 3 vary with time and are denoted as hi, he and h3, respectively. While the heights of the tanks 1, 2 and 3 are given as H1, H2 and Hz with the area of A1, A2 and A3, respectively. FO Pg H hi Ri X2 F1 H2 h2 F2 Pa H R3 h3 F3 Figure 2: Level-flow system The gas in the tank 1 obeys the ideal gas law, PgVg = nRT. The pressure (Pg) and volume (V3) of the gas in the tank vary with time. n, R and T are mole, gas constant and temperature of the gas, respectively, and constant throughout the time
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


