Question: Discuss your key findings: Did dimensionality reduction improve performance or interpretation? Which classifier performed best and why? What did the clusters reveal about your data?
Discuss your key findings:
- Did dimensionality reduction improve performance or interpretation?
- Which classifier performed best and why?
- What did the clusters reveal about your data?
- Were there any surprises or inconsistencies in the results?
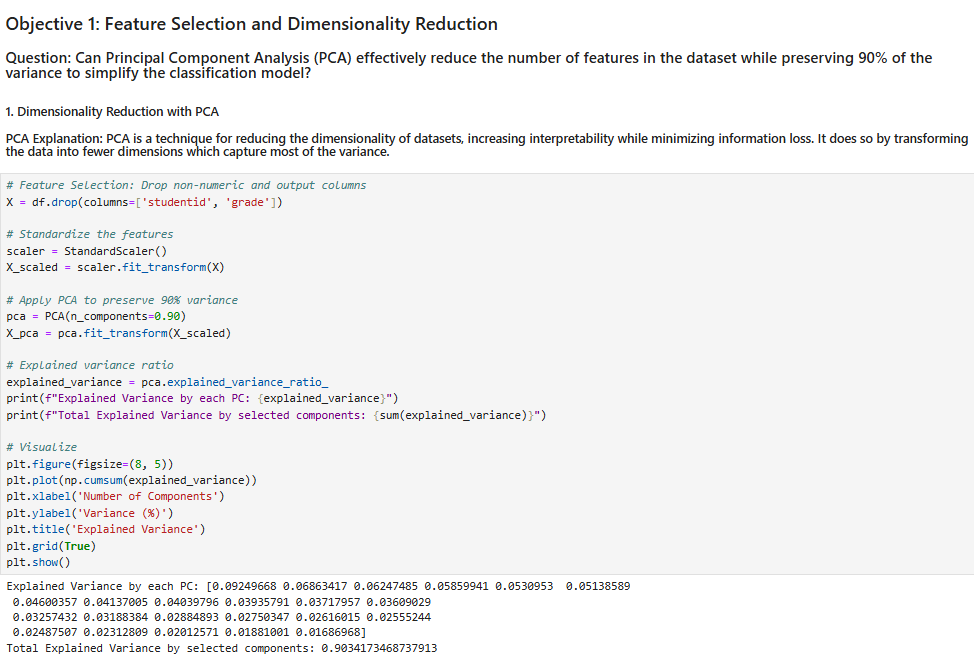
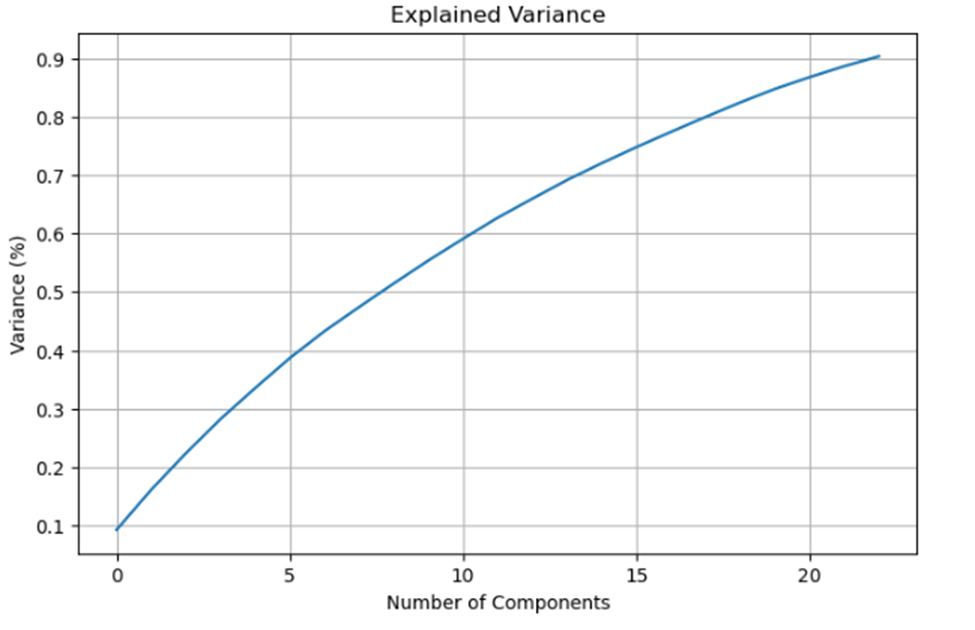
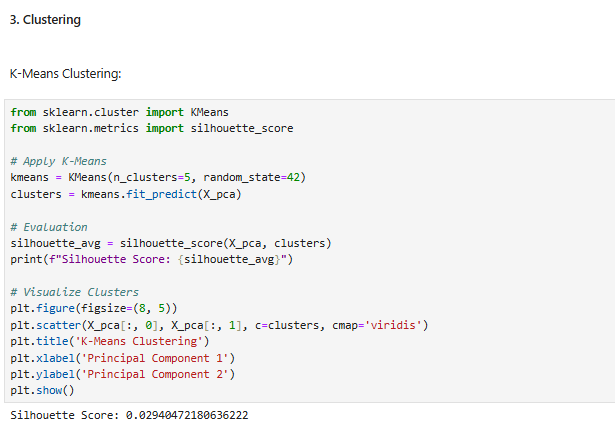
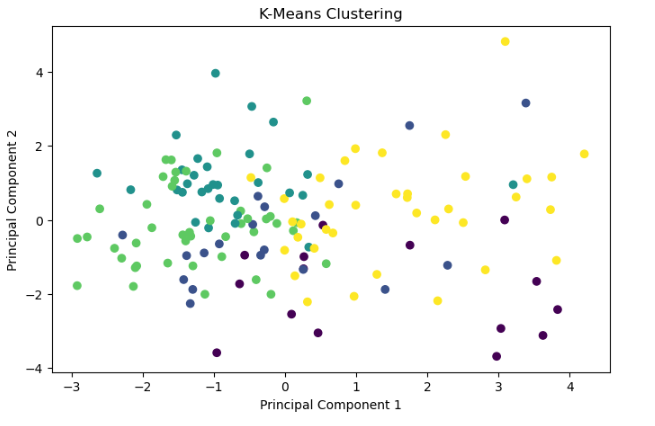
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


