Question: Do not copy answer from other people. 1. Consider a biofilm of height H that contains cells distributed homogeneously throughout. The cells take up nutrient
Do not copy answer from other people.
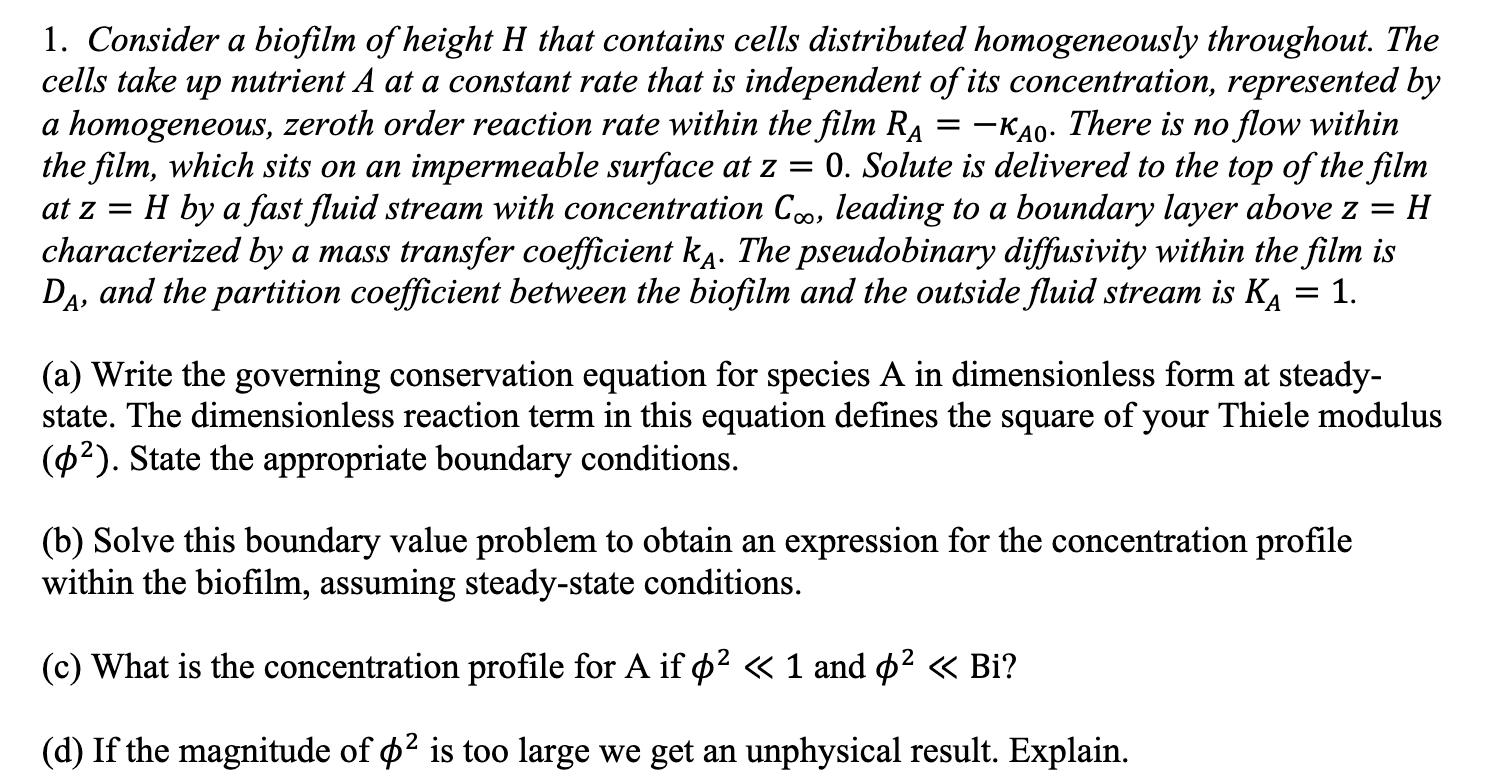
1. Consider a biofilm of height H that contains cells distributed homogeneously throughout. The cells take up nutrient A at a constant rate that is independent of its concentration, represented by a homogeneous, zeroth order reaction rate within the film RA=A0. There is no flow within the film, which sits on an impermeable surface at z=0. Solute is delivered to the top of the film at z=H by a fast fluid stream with concentration C, leading to a boundary layer above z=H characterized by a mass transfer coefficient kA. The pseudobinary diffusivity within the film is DA, and the partition coefficient between the biofilm and the outside fluid stream is KA=1. (a) Write the governing conservation equation for species A in dimensionless form at steadystate. The dimensionless reaction term in this equation defines the square of your Thiele modulus (2). State the appropriate boundary conditions. (b) Solve this boundary value problem to obtain an expression for the concentration profile within the biofilm, assuming steady-state conditions. (c) What is the concentration profile for A if 21 and 2Bi ? (d) If the magnitude of 2 is too large we get an unphysical result. Explain
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


