Question: Does anyone understand how to solve these questions? QUESTION 1 10 points Save Answer Use nominal GDP (GDP) and nominal GDI (GD/) to construct a
Does anyone understand how to solve these questions?
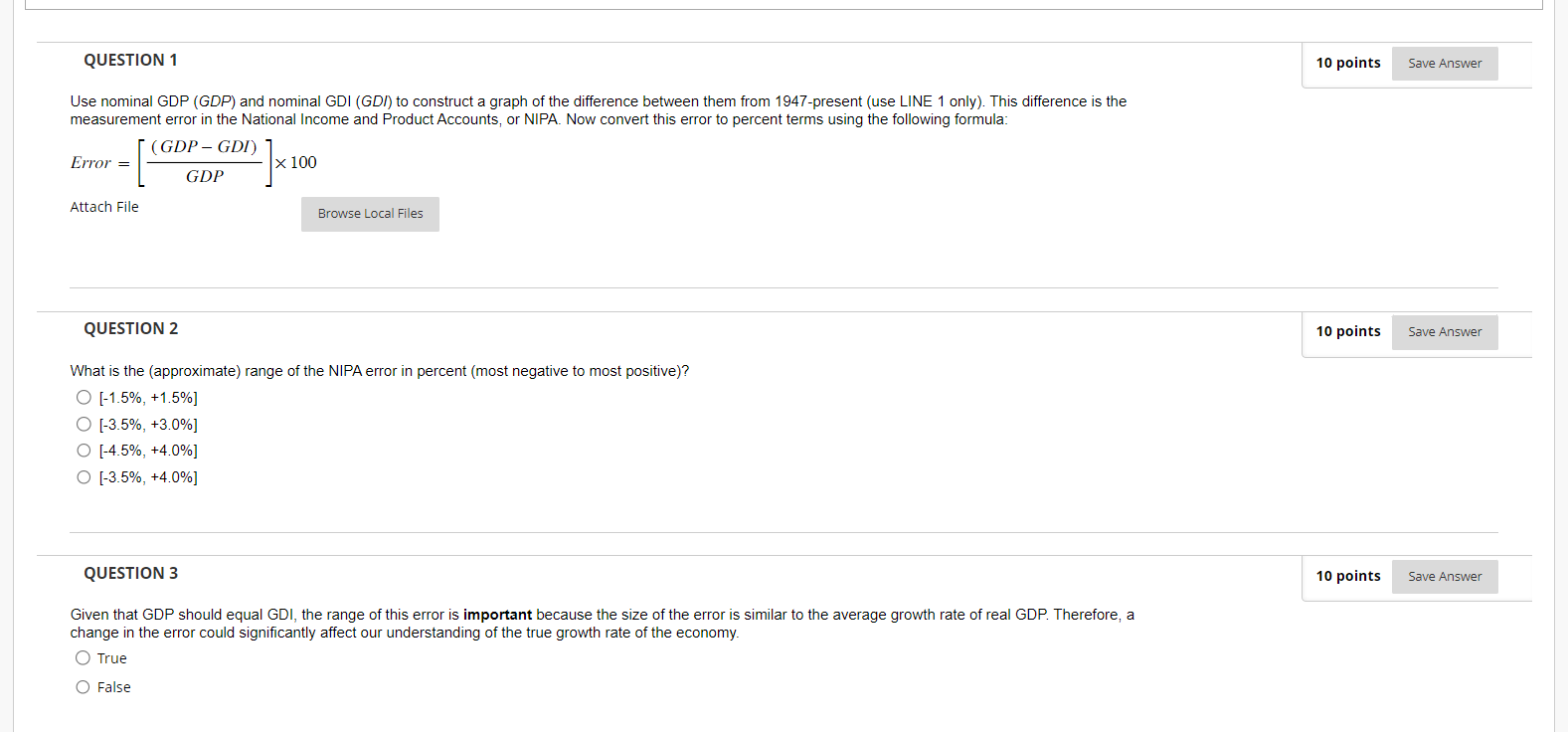
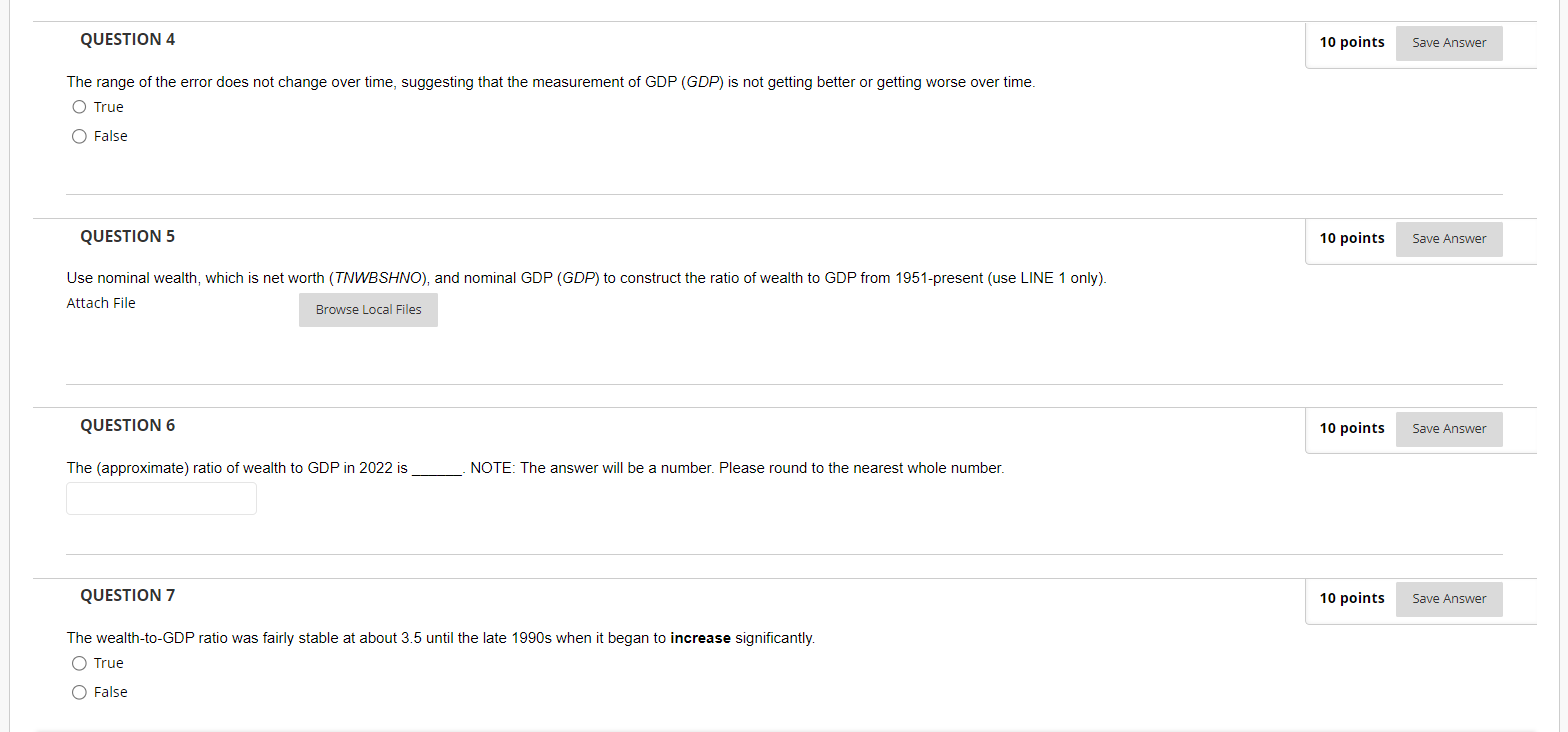
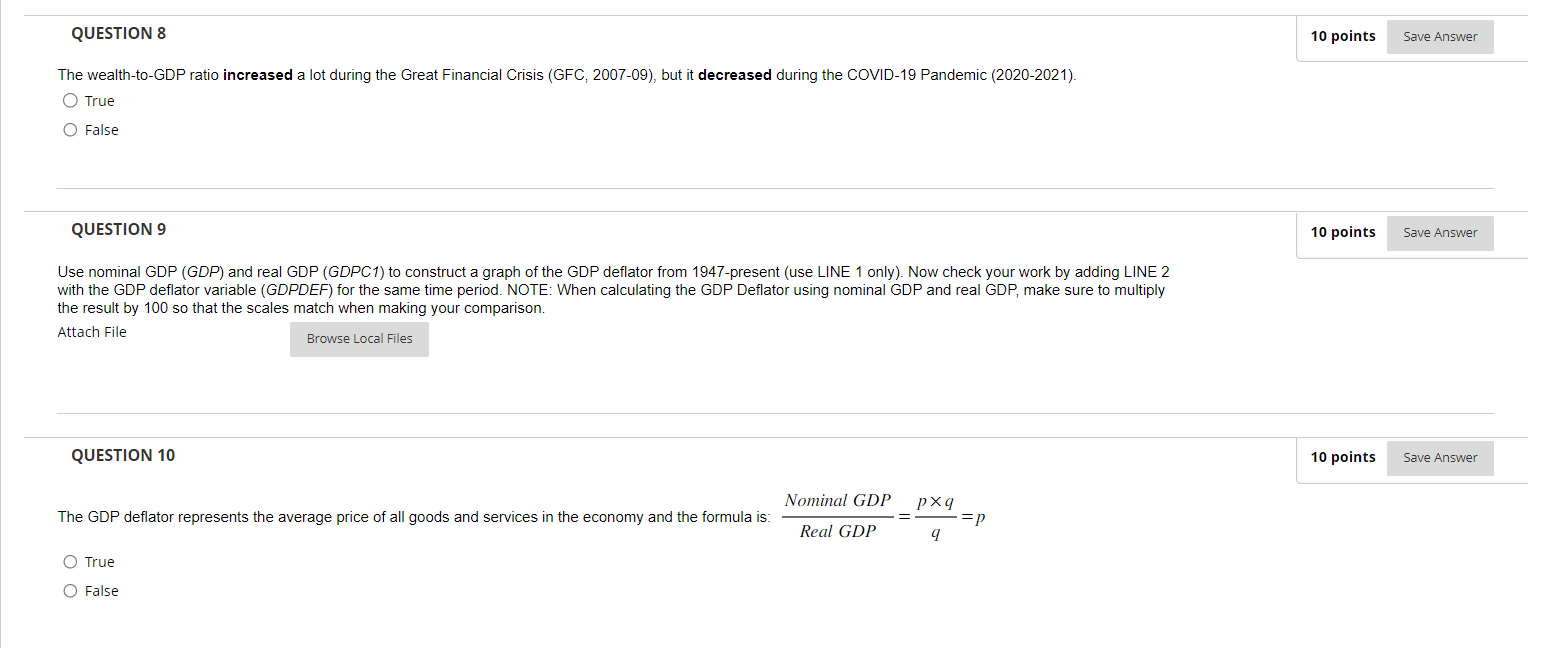
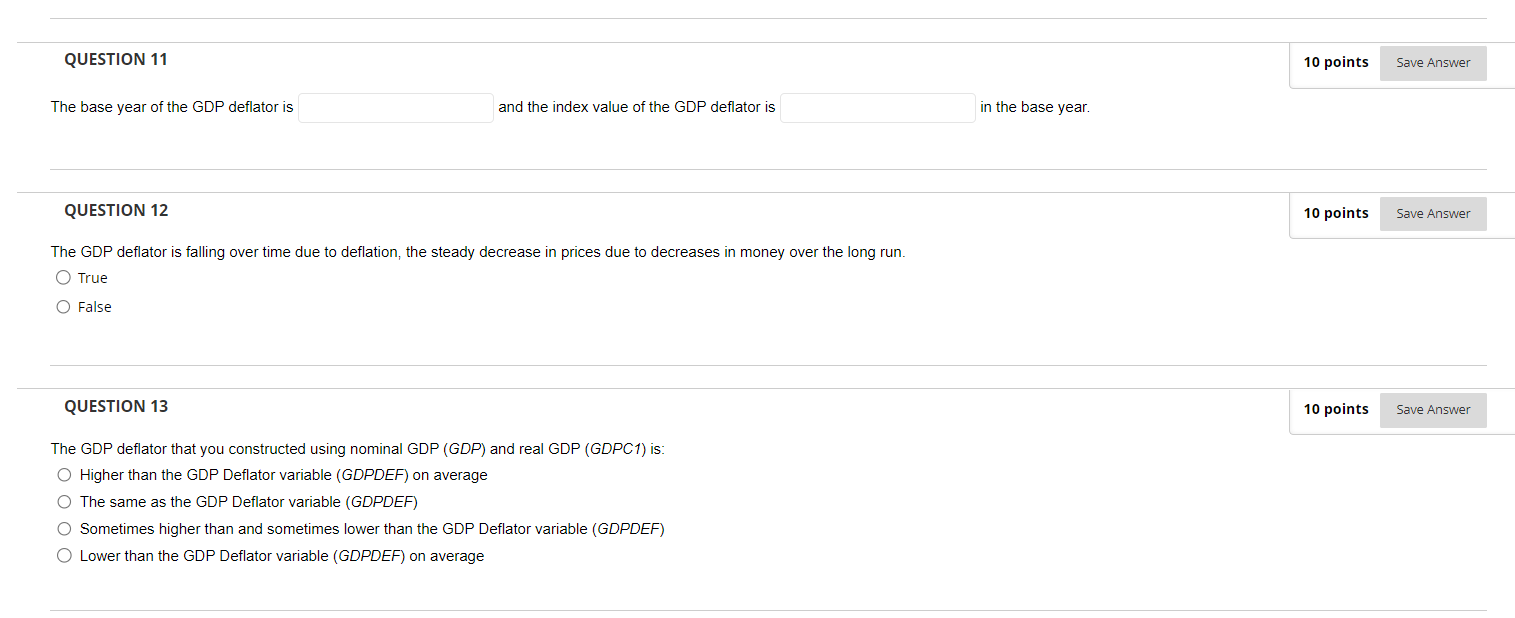
QUESTION 1 10 points Save Answer Use nominal GDP (GDP) and nominal GDI (GD/) to construct a graph of the difference between them from 1947-present (use LINE 1 only). This difference is the measurement error in the National Income and Product Accounts, or NIPA. Now convert this error to percent terms using the following formula: (GDP - GDI) Error = x 100 GDP Attach File Browse Local Files QUESTION 2 10 points Save Answer What is the (approximate) range of the NIPA error in percent (most negative to most positive)? O [-1.5%, +1.5%] O [-3.5%, +3.0%] O [-4.5%, +4.0%] O [-3.5%, +4.0%] QUESTION 3 10 points Save Answer Given that GDP should equal GDI, the range of this error is important because the size of the error is similar to the average growth rate of real GDP. Therefore, a change in the error could significantly affect our understanding of the true growth rate of the economy. O True O FalseQUESTION 4 10 points Save Answer The range of the error does not change over time, suggesting that the measurement of GDP (GDP) is not getting better or getting worse over time. O True O False QUESTION 5 10 points Save Answer Use nominal wealth, which is net worth (TNWBSHNO), and nominal GDP (GDP) to construct the ratio of wealth to GDP from 1951-present (use LINE 1 only). Attach File Browse Local Files QUESTION 6 10 points Save Answer The (approximate) ratio of wealth to GDP in 2022 is NOTE: The answer will be a number. Please round to the nearest whole number. QUESTION 7 10 points Save Answer The wealth-to-GDP ratio was fairly stable at about 3.5 until the late 1990s when it began to increase significantly. O True O FalseQUESTION 8 10 points Save Answer The wealth-to-GDP ratio increased a lot during the Great Financial Crisis (GFC, 2007-09), but it decreased during the COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-2021). O True O False QUESTION 9 10 points Save Answer Use nominal GDP (GDP) and real GDP (GDPC1) to construct a graph of the GDP deflator from 1947-present (use LINE 1 only). Now check your work by adding LINE 2 with the GDP deflator variable (GDPDEF) for the same time period. NOTE: When calculating the GDP Deflator using nominal GDP and real GDP, make sure to multiply the result by 100 so that the scales match when making your comparison. Attach File Browse Local Files QUESTION 10 10 points Save Answer Nominal GDP pxq The GDP deflator represents the average price of all goods and services in the economy and the formula is: - =p Real GDP q O True O FalseQUESTION 11 10 points Save Answer The base year of the GDP deflator is and the index value of the GDP deflator is in the base year. QUESTION 12 10 points Save Answer The GDP deflator is falling over time due to deflation, the steady decrease in prices due to decreases in money over the long run. O True O False QUESTION 13 10 points Save Answer The GDP deflator that you constructed using nominal GDP (GDP) and real GDP (GDPC1) is: O Higher than the GDP Deflator variable (GDPDEF) on average O The same as the GDP Deflator variable (GDPDEF) O Sometimes higher than and sometimes lower than the GDP Deflator variable (GDPDEF) O Lower than the GDP Deflator variable (GDPDEF) on average
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


