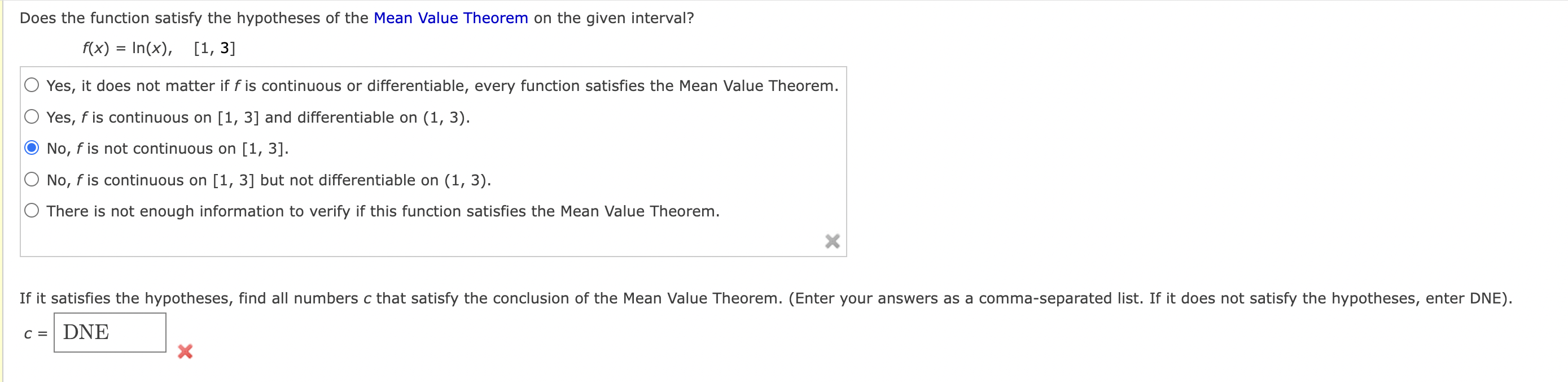
Question: Does the function satisfy the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval? f(x) = In(x), [1, 3] Yes, it does not matter
![on the given interval? f(x) = In(x), [1, 3] Yes, it does](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66654651369de_169666546510f1b5.jpg)
![Mean Value Theorem. Yes, f is continuous on [1, 3] and differentiable](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/666546522933b_1706665465206902.jpg)
![on (1, 3). O No, f is not continuous on [1, 3].](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66654652b7812_170666546528972b.jpg)
![O No, f is continuous on [1, 3] but not differentiable on](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66654653231f8_1716665465306cbc.jpg)
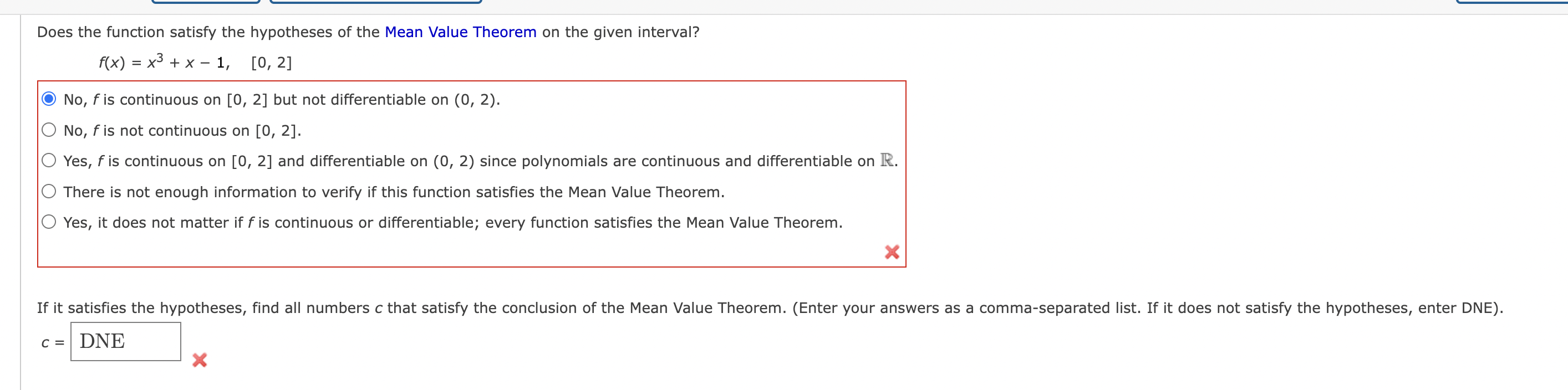
Does the function satisfy the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval? f(x) = In(x), [1, 3] Yes, it does not matter if f is continuous or differentiable, every function satisfies the Mean Value Theorem. Yes, f is continuous on [1, 3] and differentiable on (1, 3). O No, f is not continuous on [1, 3]. O No, f is continuous on [1, 3] but not differentiable on (1, 3). There is not enough information to verify if this function satisfies the Mean Value Theorem. X If it satisfies the hypotheses, find all numbers c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. If it does not satisfy the hypotheses, enter DNE). C = DNE XFind the number 6 that satisfies the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval. (Enter your answers as a comma~separated list. If an answer does not exist, enter DNE.) f(X) = \\/)_(, [0, 25] Graph the function, the secant line through the endpoints, and the tangent line at (c, f(c)). Y Y 25 25 20 20 15 15 10 10 S 5 -'*~ -''' '''' ' x '' X 1 2 3 4 5 6 O O 1 2 3 4 5 6 Y 5 6 5 s 4 4 3 3 7 7 Does the function satisfy the hypotheses of the Mean Value Theorem on the given interval? f(x) = x3 + x - 1, [0, 2] O No, f is continuous on [0, 2] but not differentiable on (0, 2). O No, f is not continuous on [0, 2]. Yes, f is continuous on [0, 2] and differentiable on (0, 2) since polynomials are continuous and differentiable on R. There is not enough information to verify if this function satisfies the Mean Value Theorem. Yes, it does not matter if f is continuous or differentiable; every function satisfies the Mean Value Theorem. X If it satisfies the hypotheses, find all numbers c that satisfy the conclusion of the Mean Value Theorem. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list. If it does not satisfy the hypotheses, enter DNE). C = DNE X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


