Question: Done in python. Also CANNOT use for loops, lists, or the sum() function node ADT: class node(object): def __init__(self, data, next=None): Create a new
Done in python. Also CANNOT use for loops, lists, or the sum() function
node ADT:
class node(object): def __init__(self, data, next=None): """ Create a new node for the given data. Pre-conditions: data: Any data value to be stored in the node next: Another node (or None, by default) """ self.__data = data self.__next = next def get_data(self): """ Retrieve the contents of the data field. Return the data value stored previously in the node """ return self.__data def get_next(self): """ Retrieve the contents of the next field. Return the value stored previously in the next field """ return self.__next def set_data(self, val): """ Set the contents of the data field to val. Pre-conditions: val: a data value to be stored Post-conditions: stores a new data value, replacing existing value Return none """ self.__data = val def set_next(self, val): """ Set the contents of the next field to val. Pre-conditions: val: a node, or the value None Post-conditions: stores a new next value, replacing existing value Return none """ self.__next = val
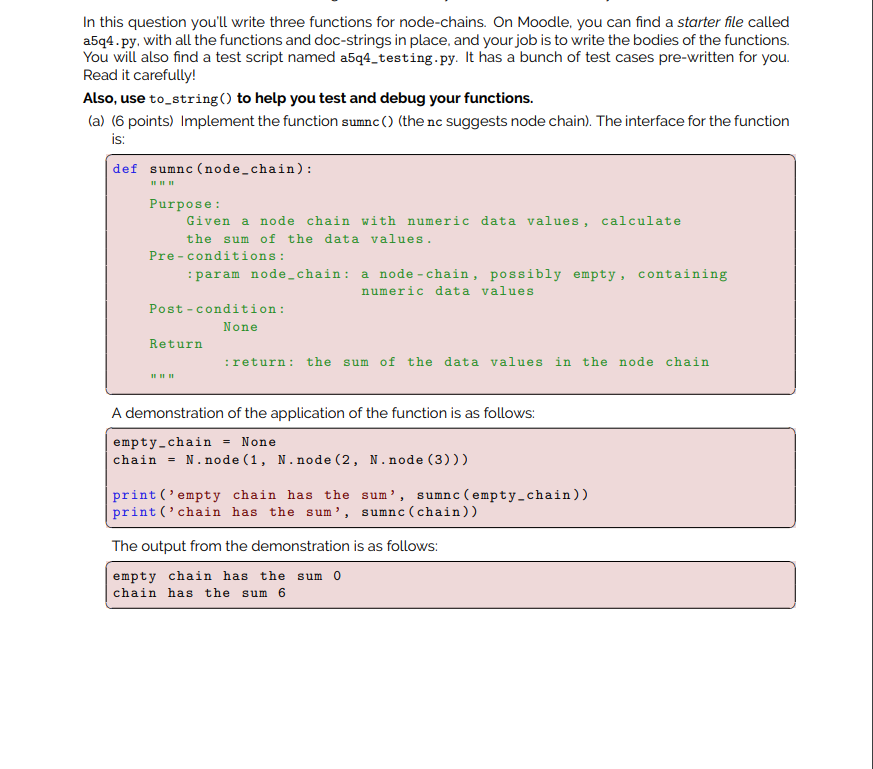
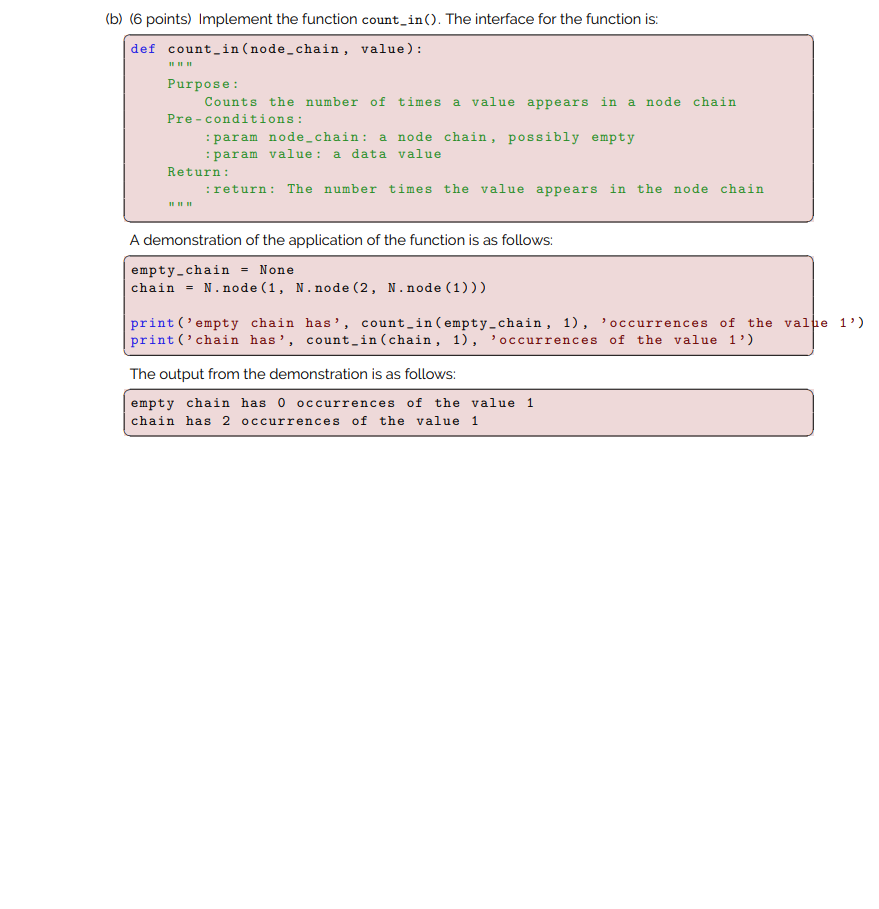
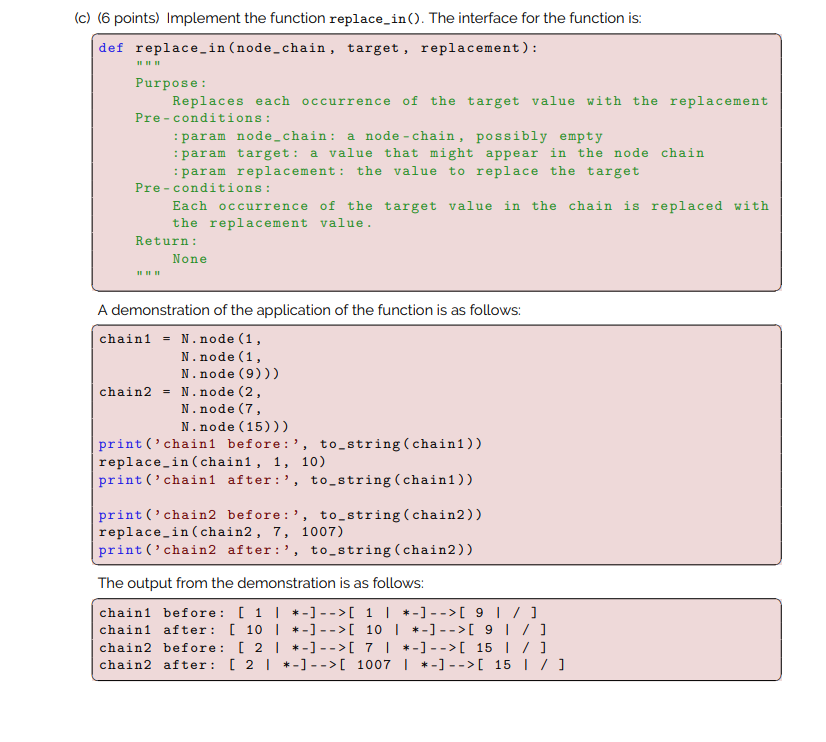
In this question you'll write three functions for node-chains. On Moodle, you can find a starter file called a5q4.py, with all the functions and doc-strings in place, and your job is to write the bodies of the functions. You will also find a test script named a5q4_testing.py. It has a bunch of test cases pre-written for you. Read it carefully! Also, use to_string() to help you test and debug your functions. (a) (6 points) Implement the function sumnc() (the nc suggests node chain). The interface for the function is: def sumnc (node_chain): Purpose: Given a node chain with numeric data values, calculate the sum of the data values. Pre-conditions: :param node_chain: a node-chain, possibly empty, containing numeric data values Post-condition: None Return :return: the sum of the data values in the node chain A demonstration of the application of the function is as follows: empty-chain = None chain = N.node(1, N.node (2, N.node (3))) print('empty chain has the sum', sumnc (empty-chain)) print('chain has the sum', sumnc (chain)) The output from the demonstration is as follows: empty chain has the sum o chain has the sum 6 (b) (6 points) Implement the function count_in(). The interface for the function is: def count_in(node_chain, value): Purpose: Counts the number of times a value appears in a node chain Pre-conditions: :param node_chain: a node chain, possibly empty :param value: a data value Return: :return: The number times the value appears in the node chain A demonstration of the application of the function is as follows: empty-chain None chain = N.node(1, N.node (2, N.node (1))) print('empty chain has', count_in(empty-chain, 1), occurrences of the valpe 1') print('chain has', count_in(chain, 1), 'occurrences of the value 1') The output from the demonstration is as follows: empty chain has 0 occurrences of the value 1 chain has 2 occurrences of the value 1 (c) (6 points) Implement the function replace_in(). The interface for the function is: def replace_in(node_chain, target, replacement): Purpose: Replaces each occurrence of the target value with the replacement Pre-conditions: :param node_chain: a node-chain, possibly empty :param target: a value that might appear in the node chain :param replacement: the value to replace the target Pre-conditions: Each occurrence of the target value in the chain is replaced with the replacement value. Return: None A demonstration of the application of the function is as follows: chain1 = N.node (1, N.node (1 N.node (9))) chain2 = N.node (2, N.node (7, N.node (15))) print('chain1 before:', to_string(chaini)) replace_in(chain1, 1, 10) print('chain1 after:', to_string(chain1)) print('chain2 before:', to_string(chain2)) replace_in(chain2, 7, 1007) print('chain2 after:', to_string (chain2)) The output from the demonstration is as follows: chaini before: [ 1 | *- ] -->[ 1 | + -]-->[ 9 / ] chain after: [ 10 | *- ] -->[ 10 | *-]-->[ 9 /] chain2 before: [ 2 | *-]-->[ 7 | *-]-->[ 15 | /] chain2 after: [ 2 | *-]-->[ 1007 | *-]-->[ 15 ]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


