Question: Don't do it on an Excel sheet, solve it by hand PLEASE! Thank you in advance 11-18 Erika Entrepreneur assembles laptop com- puter systems in
Don't do it on an Excel sheet, solve it by hand PLEASE!
Thank you in advance
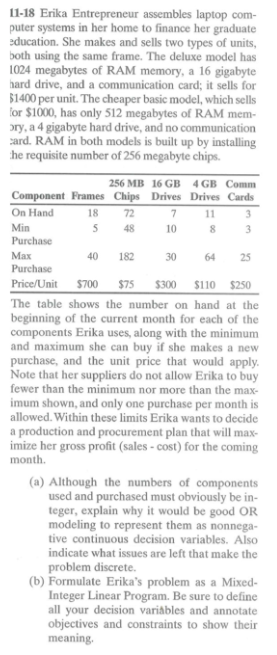
11-18 Erika Entrepreneur assembles laptop com- puter systems in her home to finance her graduate education. She makes and sells two types of units, both using the same frame. The deluxe model has 1024 megabytes of RAM memory, a 16 gigabyte hard drive, and a communication card; it sells for $1400 per unit. The cheaper basic model, which sells for $1000, has only 512 megabytes of RAM mem- ory, a 4 gigabyte hard drive, and no communication ard. RAM in both models is built up by installing he requisite number of 256 megabyte chips. Max 256 MB 16 GB 4 GB Comm Component Frames Chips Drives Drives Cards On Hand 18 727 113 Min 5 48 10 8 3 Purchase 40182 30 64 25 Purchase Price/Unit $700 $75 $300 $110 $250 The table shows the number on hand at the beginning of the current month for each of the components Erika uses, along with the minimum and maximum she can buy if she makes a new purchase, and the unit price that would apply. Note that her suppliers do not allow Erika to buy fewer than the minimum nor more than the max- imum shown, and only one purchase per month is allowed. Within these limits Erika wants to decide a production and procurement plan that will max- imize her gross profit (sales - cost) for the coming month. (a) Although the numbers of components used and purchased must obviously be in- teger, explain why it would be good OR modeling to represent them as nonnega- tive continuous decision variables. Also indicate what issues are left that make the problem discrete. (b) Formulate Erika's problem as a Mixed- Integer Linear Program. Be sure to define all your decision variables and annotate objectives and constraints to show their meaning. 11-18 Erika Entrepreneur assembles laptop com- puter systems in her home to finance her graduate education. She makes and sells two types of units, both using the same frame. The deluxe model has 1024 megabytes of RAM memory, a 16 gigabyte hard drive, and a communication card; it sells for $1400 per unit. The cheaper basic model, which sells for $1000, has only 512 megabytes of RAM mem- ory, a 4 gigabyte hard drive, and no communication ard. RAM in both models is built up by installing he requisite number of 256 megabyte chips. Max 256 MB 16 GB 4 GB Comm Component Frames Chips Drives Drives Cards On Hand 18 727 113 Min 5 48 10 8 3 Purchase 40182 30 64 25 Purchase Price/Unit $700 $75 $300 $110 $250 The table shows the number on hand at the beginning of the current month for each of the components Erika uses, along with the minimum and maximum she can buy if she makes a new purchase, and the unit price that would apply. Note that her suppliers do not allow Erika to buy fewer than the minimum nor more than the max- imum shown, and only one purchase per month is allowed. Within these limits Erika wants to decide a production and procurement plan that will max- imize her gross profit (sales - cost) for the coming month. (a) Although the numbers of components used and purchased must obviously be in- teger, explain why it would be good OR modeling to represent them as nonnega- tive continuous decision variables. Also indicate what issues are left that make the problem discrete. (b) Formulate Erika's problem as a Mixed- Integer Linear Program. Be sure to define all your decision variables and annotate objectives and constraints to show their meaningStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


