Question: Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not
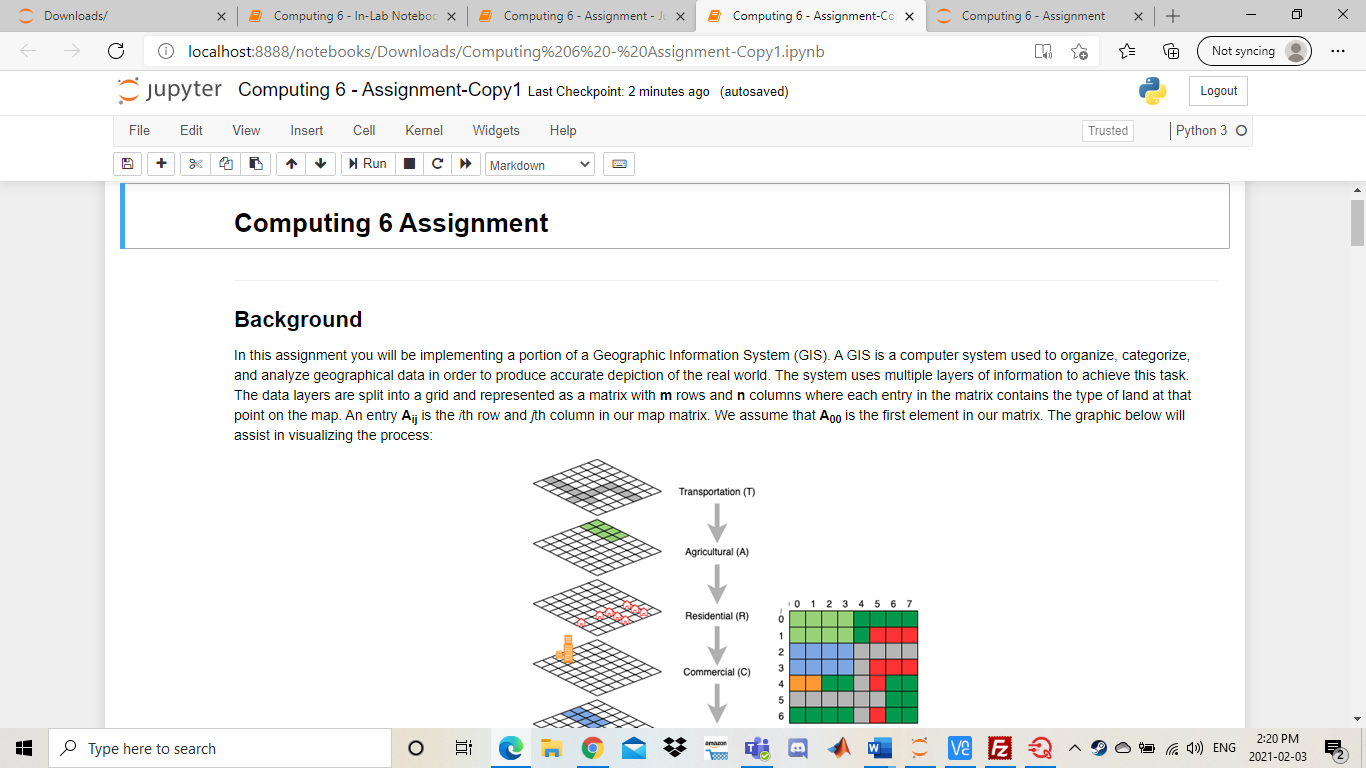
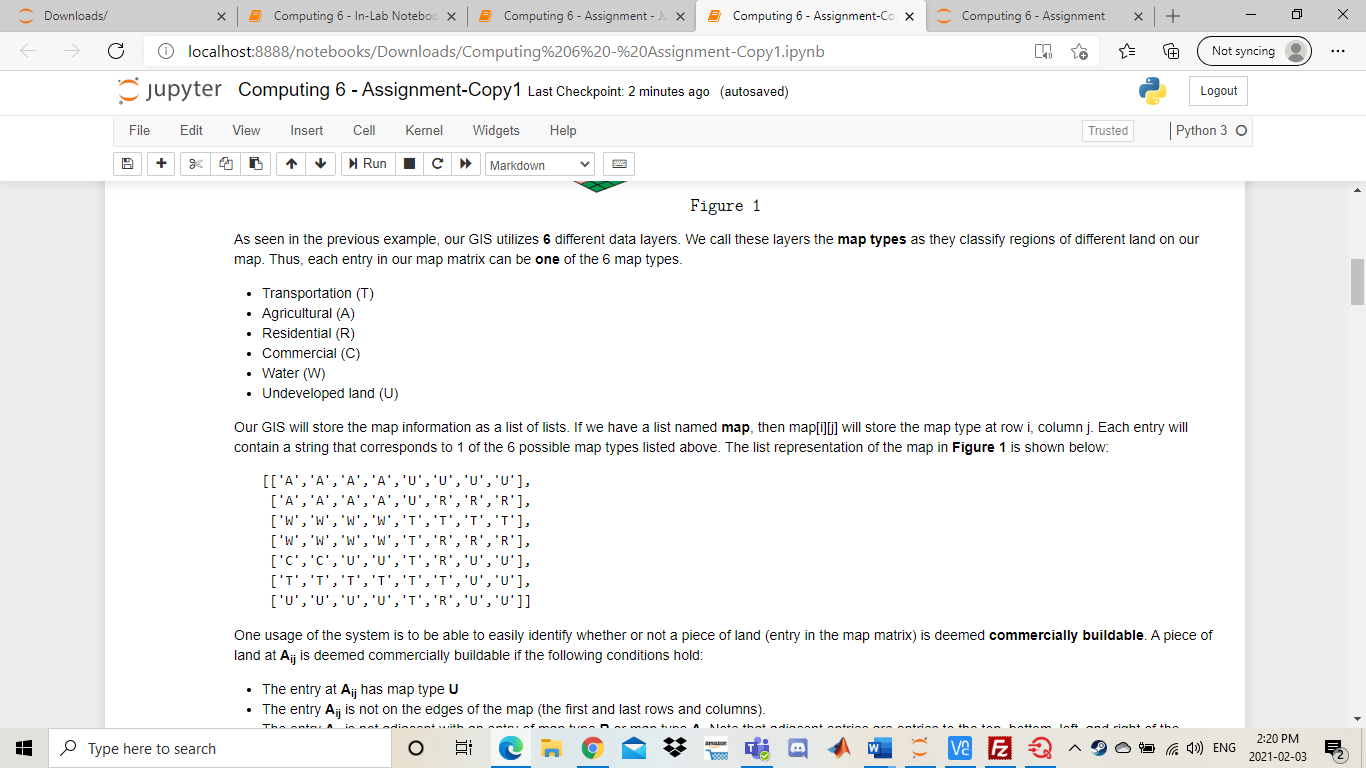
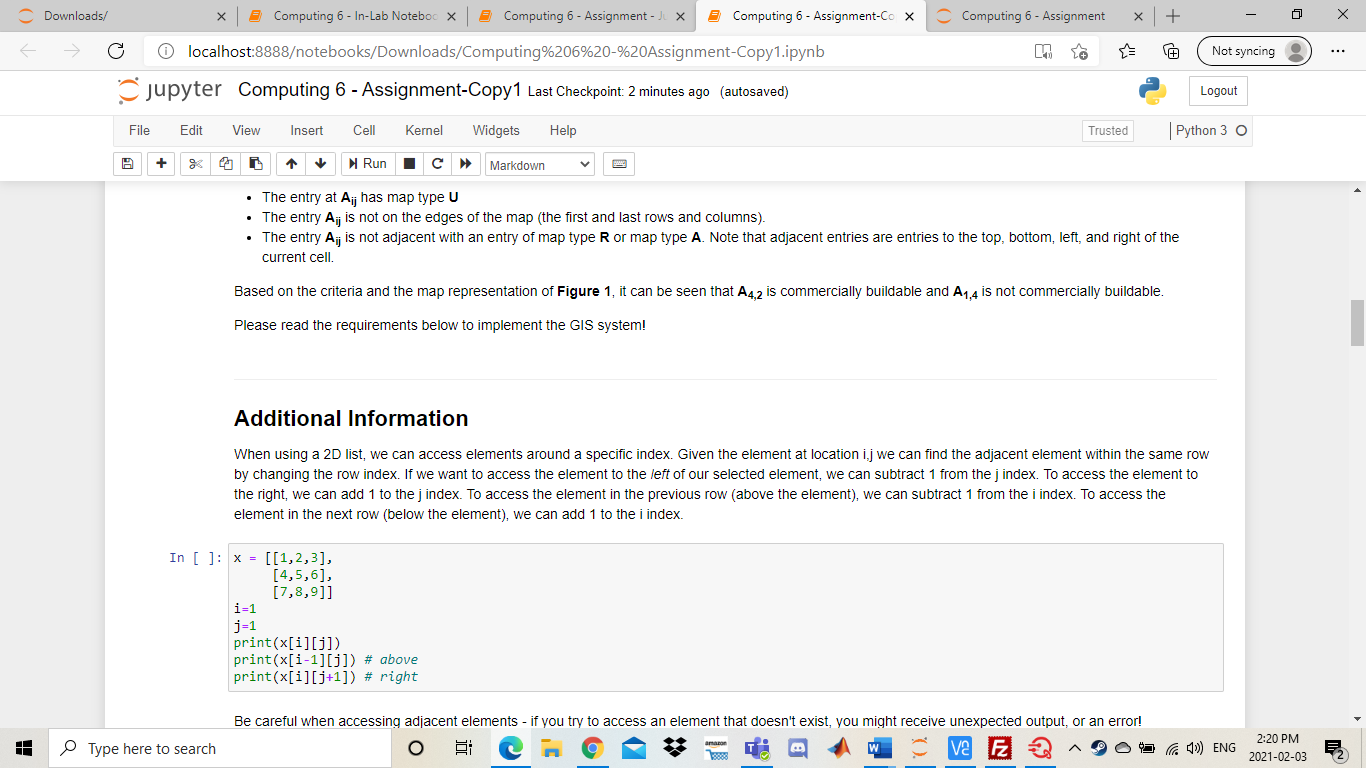
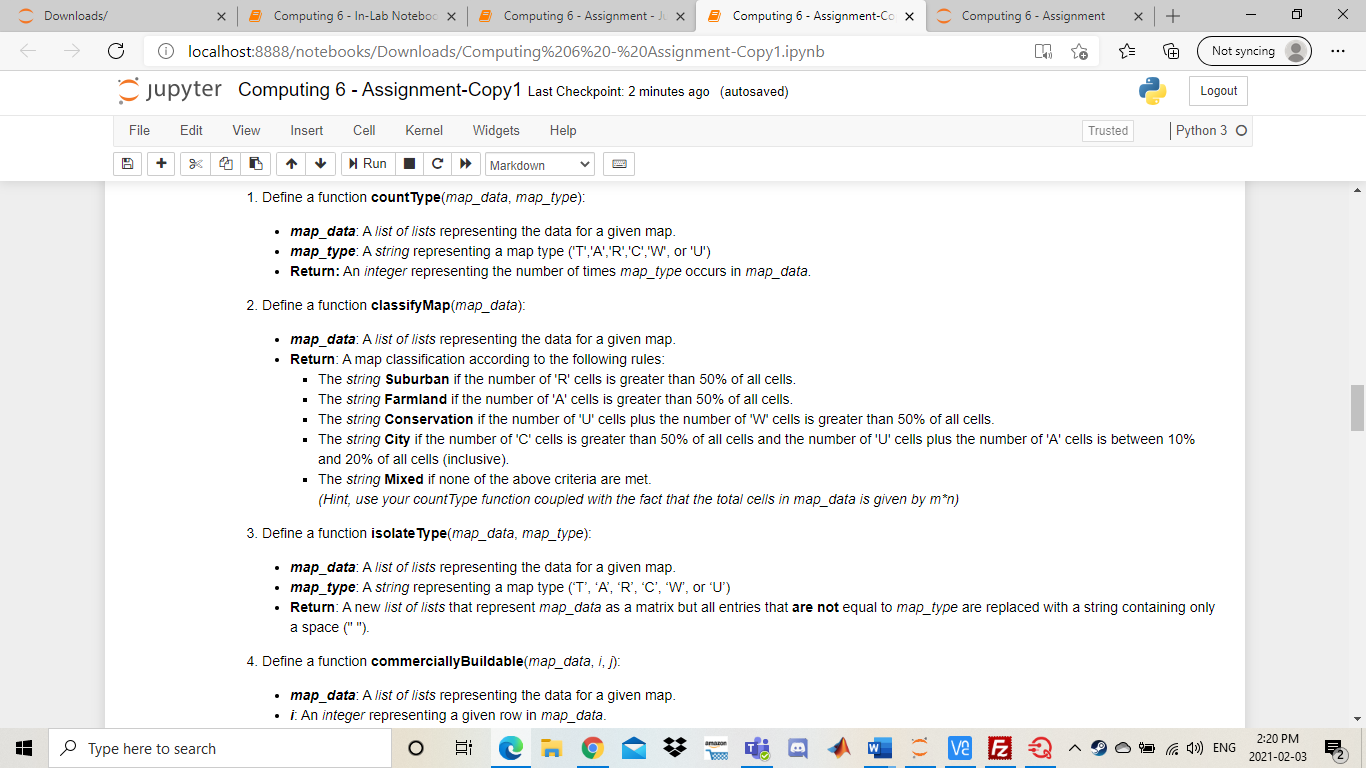
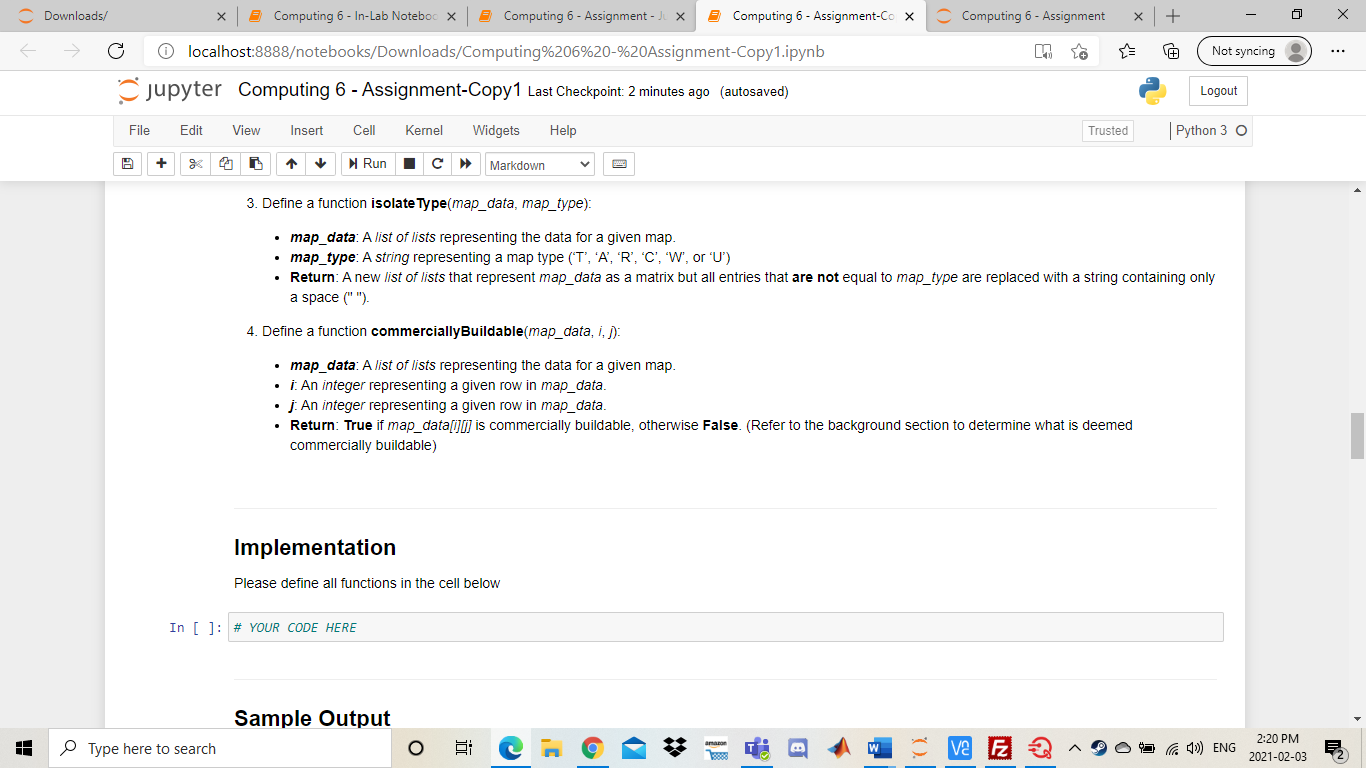
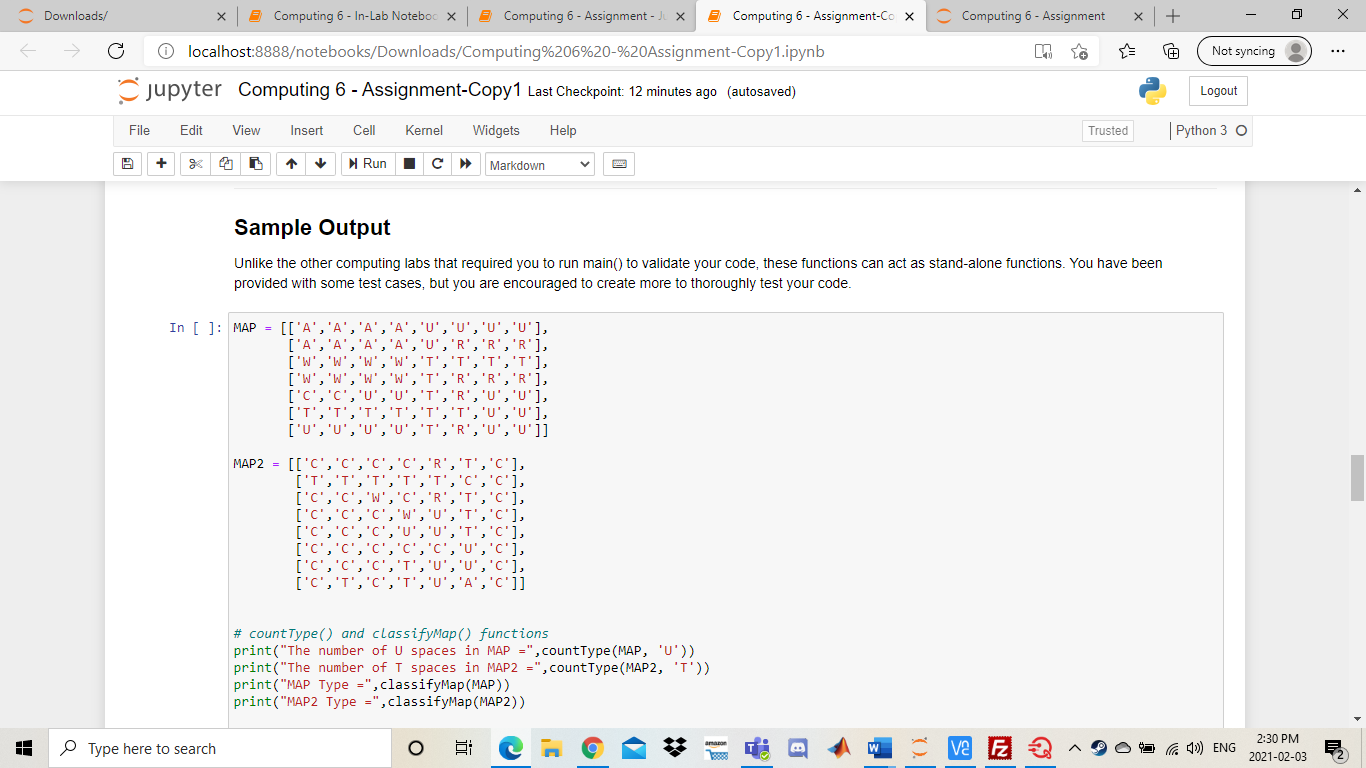
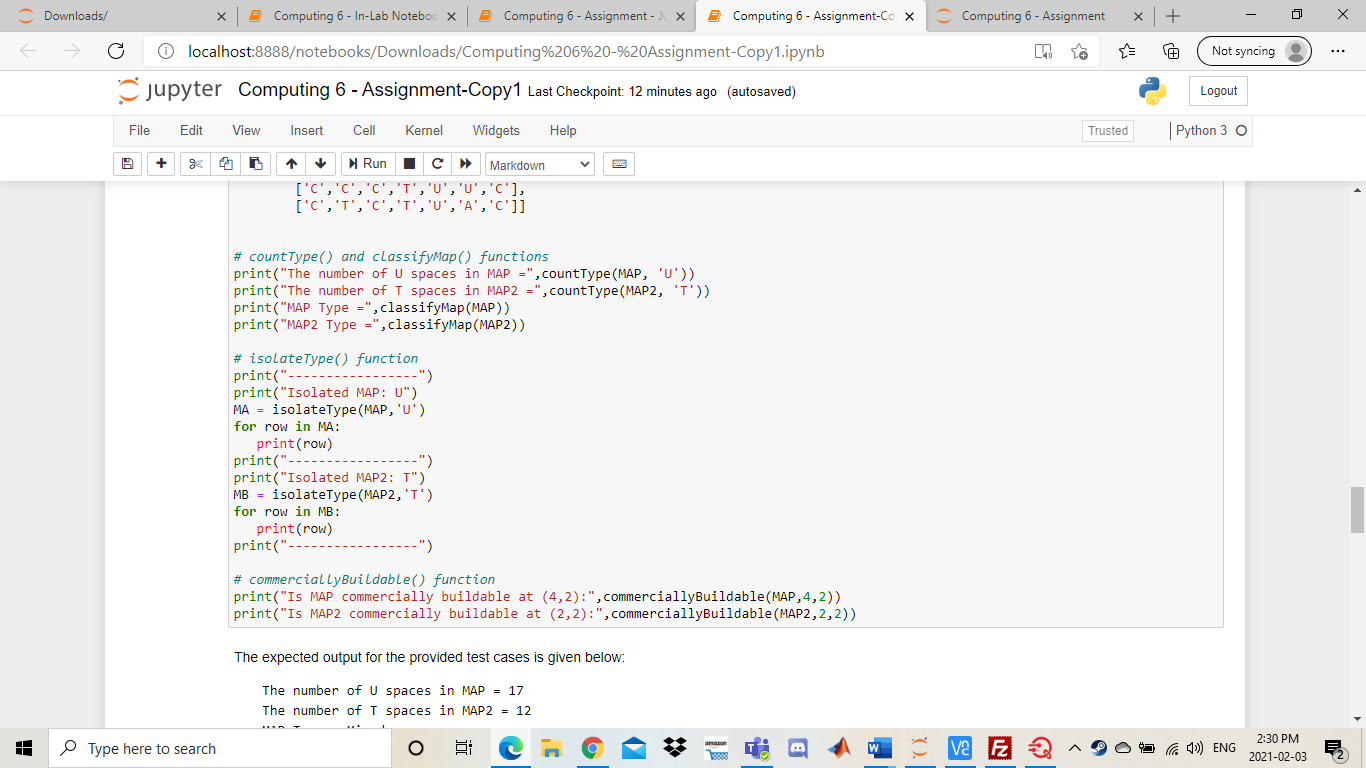
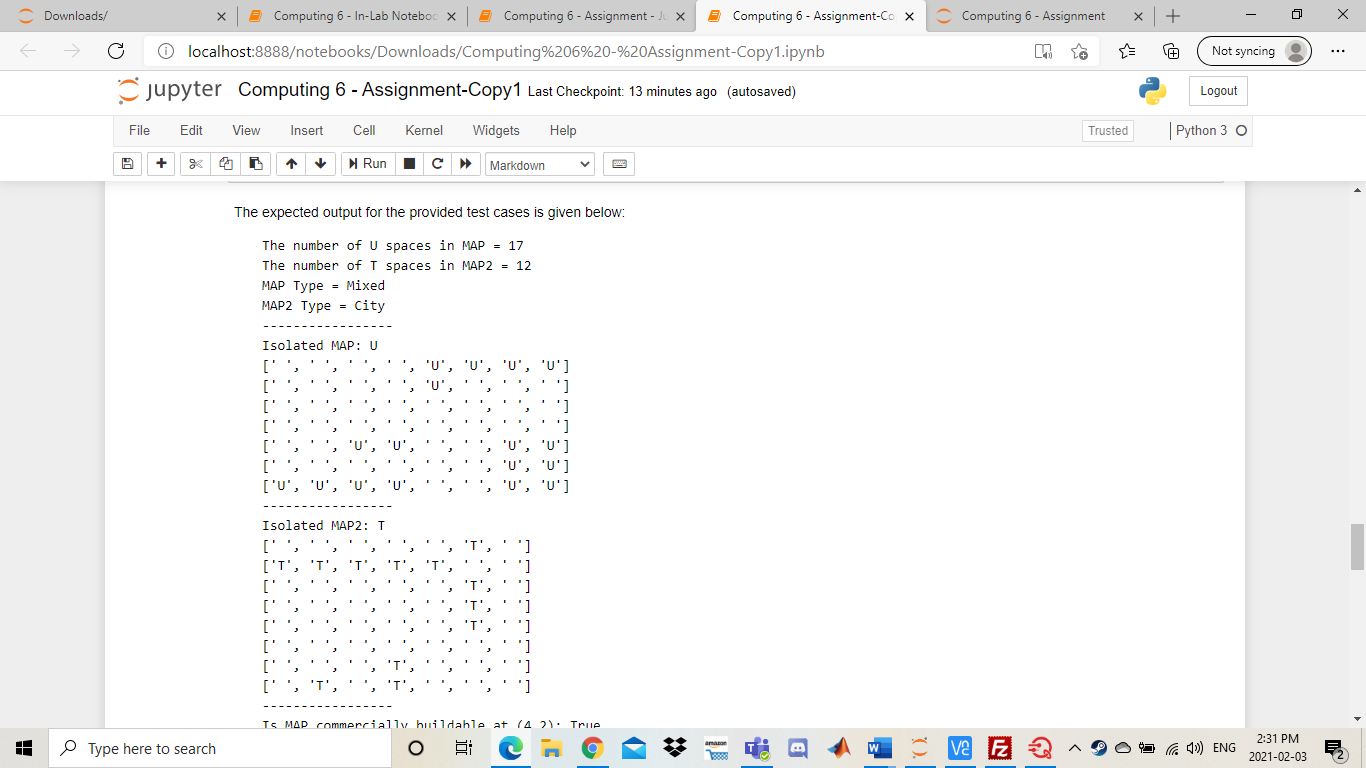
Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown Computing 6 Assignment Background In this assignment you will be implementing a portion of a Geographic Information System (GIS). A GIS is a computer system used to organize, categorize, and analyze geographical data in order to produce accurate depiction of the real world. The system uses multiple layers of information to achieve this task. The data layers are split into a grid and represented as a matrix with mrows and n columns where each entry in the matrix contains the type of land at that point on the map. An entry Ajj is the ith row and th column in our map matrix. We assume that App is the first element in our matrix. The graphic below will assist in visualizing the process: Transportation (1) Agricultural (A) 0 1 2 3 4 5 Residential (R) 1 2 Commercial (C) 5 j amazon Type here to search VE E D Ca 4)) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown Figure 1 As seen in the previous example, our GIS utilizes 6 different data layers. We call these layers the map types as they classify regions of different land on our map. Thus, each entry in our map matrix can be one of the 6 map types. Transportation (T) Agricultural (A) Residential (R) Commercial (C) Water (W) Undeveloped land (U) Our GIS will store the map information as a list of lists. If we have a list named map, then map[i][j] will store the map type at row i, column j. Each entry will contain a string that corresponds to 1 of the 6 possible map types listed above. The list representation of the map in Figure 1 shown below: [['A','A','A', 'A', 'U','U','U','U'], ('A','A',' ','R', 'R', 'R'], ['w', 'W', 'T','T','T', 'T'], ['W', 'W', ','R', 'R','R'], ['c','C', 'R','U','U'], ['T ['0', 'U'. ,'R', 'U','U']] One usage of the system is to be able to easily identify whether or not a piece of land (entry in the map matrix) is deemed commercially buildable. A piece of land at Ajj is deemed commercially buildable if the following conditions hold: The entry at Aij has map type U The entry Aj is not on the edges of the map (the first and last rows and columns). amazon Type here to search V2 E 2 C) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy 1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown The entry at Ajj has map type U The entry Aj is not on the edges of the map (the first and last rows and columns). The entry Aj is not adjacent with an entry of map type R or map type A. Note that adjacent entries are entries to the top, bottom, left and right of the current cell. Based on the criteria and the map representation of Figure 1, it can be seen that A4,2 is commercially buildable and A1,4 is not commercially buildable. Please read the requirements below to implement the GIS system! Additional Information When using a 2D list, we can access elements around a specific index. Given the element at location ij we can find the adjacent element within the same row by changing the row index. If we want to access the element to the left of our selected element, we can subtract 1 from the j index. To access the element to the right, we can add 1 to the j index. To access the element in the previous row (above the element), we can subtract 1 from the i index. To access the element in the next row (below the element), we can add 1 to the i index. In [ ]: x = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6), [7,8,9]] i=1 j-1 print(x[i][j]) print(x[i-1][j]) # above print(x[i][j+1]) # right Be careful when accessing adjacent elements - if you try to access an element that doesn't exist, you might receive unexpected output, or an error! O VE E ' Type here to search Ca 1)) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy 1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + > Markdown Run print(x[i]j+1]) # right Be careful when accessing adjacent elements - if you try to access an element that doesn't exist, you might receive unexpected output, or an error! In [ ]: print(x[i-2][j]) # 2 above - actually wraps around and gives us the element in row -1 (which is the last row) print(x[i][j+2]) # 2 right - tries to access value in column 3 (which doesn't exist) NOTE THAT YOU WILL BE MARKED ON MULTIPLE ITEMS IN THIS LAB IN ADDITION TO THE FUNCTIONALITY OF YOUR CODE Variable Names Commenting . General Legibility Reflective Questions Program Requirements (12 Marks) Your GIS system will be comprised of a set of functions used to analyze the information of any given map. In addition, you will be creating a function used to determine whether or not a piece of land is commercially buildable. The requirements of the system are given below. Please ensure that your functions have the EXACT naming as specified! Failure to do so will result in lost marks. 1. Define a function countType(map_data, map_type): amon Type here to search VE E Ca 1)) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 30 + Run Markdown 1. Define a function countType(map_data, map_type) map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. map_type: A string representing a map type ('T','A', 'R','C','W', or 'U') Return: An integer representing the number of times map_type occurs in map_data. 2. Define a function classify Map(map_data): map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. Return: A map classification according to the following rules: The string Suburban if the number of 'R' cells is greater than 50% of all cells. The string Farmland if the number of 'A' cells is greater than 50% of all cells. The string Conservation if the number of 'U' cells plus the number of 'W' cells is greater than 50% of all cells. The string City if the number of 'C' cells is greater than 50% of all cells and the number of 'U' cells plus the number of 'A' cells is between 10% and 20% of all cells (inclusive) The string Mixed if none of the above criteria are met. (Hint, use your countType function coupled with the fact that the total cells in map_data is given by m*n) 3. Define a function isolate Type(map_data, map_type) map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. map_type: A string representing a map type (T', 'A', 'R', 'C', 'W', or 'U') Return: A new list of lists that represent map_data as a matrix but all entries that are not equal to map_type are replaced with a string containing only a space (""). 4. Define a function commerciallyBuildable(map_data, 1, 1) map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. i An integer representing a given row in map_data. Type here to search > VE E VE E 3 Markdown Sample Output Unlike the other computing labs that required you to run main() to validate your code, these functions can act as stand-alone functions. You have been provided with some test cases, but you are encouraged to create more to thoroughly test your code. "U','0','U','U'], In [ ]: MAP = [['a','A'. ['a',' ['w ['W' ['c',' ['t ['U', "] 'R','R','R'), 'R','U','U'] 'U','U ]] MAP2 = [['C' 1. '], ['c ['C ['c', ['c','T 'U','C'], 'A','C']] # countType() and classifyMap() functions print("The number of U spaces in MAP =", countType(MAP, 'U')) print("The number of I spaces in MAP2 =", countType(MAP2, 'T')) print("MAP Type =", classifyMap (MAP)) print("MAP2 Type =", classifyMap(MAP2)) Type here to search > va E 2 > D Ca )) ENG 2:30 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 12 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown ['c','c','C' 'U', 'U', 'c'i ['c','T', 'c','T','U','A','C']] # countType() and classifyMap() functions print("The number of U spaces in MAP =", countType (MAP, 'U')) print("The number of I spaces in MAP2 =",countType(MAP2, 'T')) print("MAP Type =" classifyMap(MAP)) print("MAP2 Type =", classifyMap (MAP2)) # isolateType() function print(" print("Isolated MAP: U") MA = isolateType(MAP,'U') for row in MA: print (row) print(" print("Isolated MAP2: 1") MB = isolateType(MAP2, 'T') for row in MB: print(row) print("- -") # commercial LyBuildable() function print("Is MAP commercially buildable at (4,2):", commerciallyBuildable(MAP,4,2)) print("Is MAP2 commercially buildable at (2,2):", commerciallyBuildable (MAP2,2,2)) The expected output for the provided test cases is given below: The number of U spaces in MAP = 17 The number of I spaces in MAP2 = 12 Type here to search ve F D Ca )) ENG 2:30 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 13 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + 1 Run > Markdown The expected output for the provided test cases is given below: The number of U spaces in MAP = 17 The number of I spaces in MAP2 = 12 MAP Type = Mixed MAP2 Type - City 'U', '0', 'U'] 1 Isolated MAP: U [' [' [' [" [' "] 'U', 'U'] 'U', 'U'l "U', 'U'] ['U', '0', 'U', Isolated MAP2: T [' ['T', [ [' [' [' TS MAP commercially buildable at 14 2). True Type here to search T mi > ve F 2 D Ca )) ENG 2:31 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X 5 Computing 6 - Assignment - J x Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 13 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run c > Markdown Code Legibility (6 Marks) Your code will be marked on commenting and code legibility. The mark breakdown is as follows: 2 marks for using appropriate variable names that indicate what is being stored in that variable 2 marks for leaving comments on major parts of your code such as where you read the file or calculate a summation 2 marks for general legibility. The TA's should be able to understand your code without spending hours reading it. For example do not put your code in one very long line as this is hard for someone else reading your code to understand Test Plan Develop a test plan for your program. Your test plan should have at least three test cases: one normal case, one boundary case, and one abnormal case. You can test any function but you must test at least two different functions. Please use the following format for your test cases: Function: Input: Output: Excepted Output: Pass/Fail: An example test case is shown below: Type here to search T J' ve F 2 VE E 69 D Ca )) ENG 2:31 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 13 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 30 + Run Markdown Implement your testing plan in the cell below! DOUBLE CLICK TO EDIT THIS CELL. DO NOT DELETE QUOTATION MARKS Reflective Questions (6 Marks) 1. Which functions did you use a nested structure (nested loops, nested conditionals, etc) to implement the requirements? Would it have been possible to implement them without using a nested structure? Which functions did you not use i nested structure? Would it have been possible to implement them with a nested structure? 2. Suppose we wanted to create an additional map classification called 'Urban City' which is indicated by the number of 'R' cells plus the number of 'C' cells being between 60% and 80%. Can we do this? How might this affect our classifyMap() function? 3. How many test cases would you need to confirm that your classifyMap() function correctly identifies a "Farmland" map? Explain what your test cases would be DOUBLE CLICK TO EDIT THIS CELL. DO NOT DELETE QUOTATION MARKS - Type here to search j a > VE E Ca )) ENG 2:31 PM 2021-02-03 Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown Computing 6 Assignment Background In this assignment you will be implementing a portion of a Geographic Information System (GIS). A GIS is a computer system used to organize, categorize, and analyze geographical data in order to produce accurate depiction of the real world. The system uses multiple layers of information to achieve this task. The data layers are split into a grid and represented as a matrix with mrows and n columns where each entry in the matrix contains the type of land at that point on the map. An entry Ajj is the ith row and th column in our map matrix. We assume that App is the first element in our matrix. The graphic below will assist in visualizing the process: Transportation (1) Agricultural (A) 0 1 2 3 4 5 Residential (R) 1 2 Commercial (C) 5 j amazon Type here to search VE E D Ca 4)) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown Figure 1 As seen in the previous example, our GIS utilizes 6 different data layers. We call these layers the map types as they classify regions of different land on our map. Thus, each entry in our map matrix can be one of the 6 map types. Transportation (T) Agricultural (A) Residential (R) Commercial (C) Water (W) Undeveloped land (U) Our GIS will store the map information as a list of lists. If we have a list named map, then map[i][j] will store the map type at row i, column j. Each entry will contain a string that corresponds to 1 of the 6 possible map types listed above. The list representation of the map in Figure 1 shown below: [['A','A','A', 'A', 'U','U','U','U'], ('A','A',' ','R', 'R', 'R'], ['w', 'W', 'T','T','T', 'T'], ['W', 'W', ','R', 'R','R'], ['c','C', 'R','U','U'], ['T ['0', 'U'. ,'R', 'U','U']] One usage of the system is to be able to easily identify whether or not a piece of land (entry in the map matrix) is deemed commercially buildable. A piece of land at Ajj is deemed commercially buildable if the following conditions hold: The entry at Aij has map type U The entry Aj is not on the edges of the map (the first and last rows and columns). amazon Type here to search V2 E 2 C) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy 1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown The entry at Ajj has map type U The entry Aj is not on the edges of the map (the first and last rows and columns). The entry Aj is not adjacent with an entry of map type R or map type A. Note that adjacent entries are entries to the top, bottom, left and right of the current cell. Based on the criteria and the map representation of Figure 1, it can be seen that A4,2 is commercially buildable and A1,4 is not commercially buildable. Please read the requirements below to implement the GIS system! Additional Information When using a 2D list, we can access elements around a specific index. Given the element at location ij we can find the adjacent element within the same row by changing the row index. If we want to access the element to the left of our selected element, we can subtract 1 from the j index. To access the element to the right, we can add 1 to the j index. To access the element in the previous row (above the element), we can subtract 1 from the i index. To access the element in the next row (below the element), we can add 1 to the i index. In [ ]: x = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6), [7,8,9]] i=1 j-1 print(x[i][j]) print(x[i-1][j]) # above print(x[i][j+1]) # right Be careful when accessing adjacent elements - if you try to access an element that doesn't exist, you might receive unexpected output, or an error! O VE E ' Type here to search Ca 1)) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy 1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + > Markdown Run print(x[i]j+1]) # right Be careful when accessing adjacent elements - if you try to access an element that doesn't exist, you might receive unexpected output, or an error! In [ ]: print(x[i-2][j]) # 2 above - actually wraps around and gives us the element in row -1 (which is the last row) print(x[i][j+2]) # 2 right - tries to access value in column 3 (which doesn't exist) NOTE THAT YOU WILL BE MARKED ON MULTIPLE ITEMS IN THIS LAB IN ADDITION TO THE FUNCTIONALITY OF YOUR CODE Variable Names Commenting . General Legibility Reflective Questions Program Requirements (12 Marks) Your GIS system will be comprised of a set of functions used to analyze the information of any given map. In addition, you will be creating a function used to determine whether or not a piece of land is commercially buildable. The requirements of the system are given below. Please ensure that your functions have the EXACT naming as specified! Failure to do so will result in lost marks. 1. Define a function countType(map_data, map_type): amon Type here to search VE E Ca 1)) ENG 2:20 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Co X Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 2 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 30 + Run Markdown 1. Define a function countType(map_data, map_type) map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. map_type: A string representing a map type ('T','A', 'R','C','W', or 'U') Return: An integer representing the number of times map_type occurs in map_data. 2. Define a function classify Map(map_data): map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. Return: A map classification according to the following rules: The string Suburban if the number of 'R' cells is greater than 50% of all cells. The string Farmland if the number of 'A' cells is greater than 50% of all cells. The string Conservation if the number of 'U' cells plus the number of 'W' cells is greater than 50% of all cells. The string City if the number of 'C' cells is greater than 50% of all cells and the number of 'U' cells plus the number of 'A' cells is between 10% and 20% of all cells (inclusive) The string Mixed if none of the above criteria are met. (Hint, use your countType function coupled with the fact that the total cells in map_data is given by m*n) 3. Define a function isolate Type(map_data, map_type) map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. map_type: A string representing a map type (T', 'A', 'R', 'C', 'W', or 'U') Return: A new list of lists that represent map_data as a matrix but all entries that are not equal to map_type are replaced with a string containing only a space (""). 4. Define a function commerciallyBuildable(map_data, 1, 1) map_data: A list of lists representing the data for a given map. i An integer representing a given row in map_data. Type here to search > VE E VE E 3 Markdown Sample Output Unlike the other computing labs that required you to run main() to validate your code, these functions can act as stand-alone functions. You have been provided with some test cases, but you are encouraged to create more to thoroughly test your code. "U','0','U','U'], In [ ]: MAP = [['a','A'. ['a',' ['w ['W' ['c',' ['t ['U', "] 'R','R','R'), 'R','U','U'] 'U','U ]] MAP2 = [['C' 1. '], ['c ['C ['c', ['c','T 'U','C'], 'A','C']] # countType() and classifyMap() functions print("The number of U spaces in MAP =", countType(MAP, 'U')) print("The number of I spaces in MAP2 =", countType(MAP2, 'T')) print("MAP Type =", classifyMap (MAP)) print("MAP2 Type =", classifyMap(MAP2)) Type here to search > va E 2 > D Ca )) ENG 2:30 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 12 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run Markdown ['c','c','C' 'U', 'U', 'c'i ['c','T', 'c','T','U','A','C']] # countType() and classifyMap() functions print("The number of U spaces in MAP =", countType (MAP, 'U')) print("The number of I spaces in MAP2 =",countType(MAP2, 'T')) print("MAP Type =" classifyMap(MAP)) print("MAP2 Type =", classifyMap (MAP2)) # isolateType() function print(" print("Isolated MAP: U") MA = isolateType(MAP,'U') for row in MA: print (row) print(" print("Isolated MAP2: 1") MB = isolateType(MAP2, 'T') for row in MB: print(row) print("- -") # commercial LyBuildable() function print("Is MAP commercially buildable at (4,2):", commerciallyBuildable(MAP,4,2)) print("Is MAP2 commercially buildable at (2,2):", commerciallyBuildable (MAP2,2,2)) The expected output for the provided test cases is given below: The number of U spaces in MAP = 17 The number of I spaces in MAP2 = 12 Type here to search ve F D Ca )) ENG 2:30 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ Computing 6 - In-Lab Noteboc X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + ta Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 13 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + 1 Run > Markdown The expected output for the provided test cases is given below: The number of U spaces in MAP = 17 The number of I spaces in MAP2 = 12 MAP Type = Mixed MAP2 Type - City 'U', '0', 'U'] 1 Isolated MAP: U [' [' [' [" [' "] 'U', 'U'] 'U', 'U'l "U', 'U'] ['U', '0', 'U', Isolated MAP2: T [' ['T', [ [' [' [' TS MAP commercially buildable at 14 2). True Type here to search T mi > ve F 2 D Ca )) ENG 2:31 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X 5 Computing 6 - Assignment - J x Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 13 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 3 O + Run c > Markdown Code Legibility (6 Marks) Your code will be marked on commenting and code legibility. The mark breakdown is as follows: 2 marks for using appropriate variable names that indicate what is being stored in that variable 2 marks for leaving comments on major parts of your code such as where you read the file or calculate a summation 2 marks for general legibility. The TA's should be able to understand your code without spending hours reading it. For example do not put your code in one very long line as this is hard for someone else reading your code to understand Test Plan Develop a test plan for your program. Your test plan should have at least three test cases: one normal case, one boundary case, and one abnormal case. You can test any function but you must test at least two different functions. Please use the following format for your test cases: Function: Input: Output: Excepted Output: Pass/Fail: An example test case is shown below: Type here to search T J' ve F 2 VE E 69 D Ca )) ENG 2:31 PM 2021-02-03 C Downloads/ 5 Computing 6- In-Lab Noteboo X Computing 6 - Assignment - X Computing 6 - Assignment-Cox Computing 6 - Assignment + Not syncing localhost:8888otebooks/Downloads/Computing%206%20-%20Assignment-Copy1.ipynb jupyter Computing 6 - Assignment-Copy1 Last Checkpoint: 13 minutes ago (autosaved) Logout File Edit View Insert Cell Kernel Widgets Help Trusted Python 30 + Run Markdown Implement your testing plan in the cell below! DOUBLE CLICK TO EDIT THIS CELL. DO NOT DELETE QUOTATION MARKS Reflective Questions (6 Marks) 1. Which functions did you use a nested structure (nested loops, nested conditionals, etc) to implement the requirements? Would it have been possible to implement them without using a nested structure? Which functions did you not use i nested structure? Would it have been possible to implement them with a nested structure? 2. Suppose we wanted to create an additional map classification called 'Urban City' which is indicated by the number of 'R' cells plus the number of 'C' cells being between 60% and 80%. Can we do this? How might this affect our classifyMap() function? 3. How many test cases would you need to confirm that your classifyMap() function correctly identifies a "Farmland" map? Explain what your test cases would be DOUBLE CLICK TO EDIT THIS CELL. DO NOT DELETE QUOTATION MARKS - Type here to search j a > VE E Ca )) ENG 2:31 PM 2021-02-03
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


