Question: Draft an educational and thoughtful response to the post below: Instructional skill: Given a soil triangle and percentages of sand and clay in a soil
Draft an educational and thoughtful response to the post below:
Instructional skill: Given a soil triangle and percentages of sand and clay in a soil sample, students will identify the type of soil with 80% accuracy.
Audience: Students in this program will range from grades 9-12, and will vary in experience level, ability, and background. Students will have different goals upon graduation, so information should apply to learners with different interests (household gardening versus farm management).
Subordinate skills:
- Describe Soil Composition
1.1. Knowledge of soil components
- Define the particle sizes of the three article sizes of soil: sand, silt, and clay
- Diagram the differences between sand, silt, and clay in terms of particle size, texture, and water retention.
- Analyze how particle size impacts soil texture categories (e.g., sandy loam, clay loam).
- Examine Soil Texture Triangle
2.1. Familiarity with the soil texture triangle
- Explain how the soil texture triangle represents soil classification based on sand, silt, and clay content.
2.2. Identifying regions in the triangle
- Recognize and locate different soil types (e.g., loam, sandy clay loam) on the triangle.
- Examine the boundaries between soil types on the triangle represent threshold values of sand, silt, and clay percentages.
- Applying Percentages to the Soil Texture Triangle
3.1. Plotting a point on the triangle
- Use the given percentages of sand and clay to plot a point on the soil triangle.
- Use simple arithmetic to deduce the percentage of silt when given sand and clay.
3.2. Identifying soil type based on the plotted point
- Locate the region in which the plotted point falls to determine the corresponding soil type.
- Describe how slight differences in percentages may change the soil classification.
- Practice and Accuracy
4.1. Repeated practice with different soil samples
- Identify soil types from multiple sample percentages to build accuracy.
- Use feedback to improve precision in identifying the correct soil type.
4.2. Evaluating accuracy and making adjustments
- Reflect on mistakes or near misses (e.g., misclassifying loam vs. sandy loam).
- Implement strategies for improving accuracy, such as double-checking plotted points or reviewing triangle boundaries.
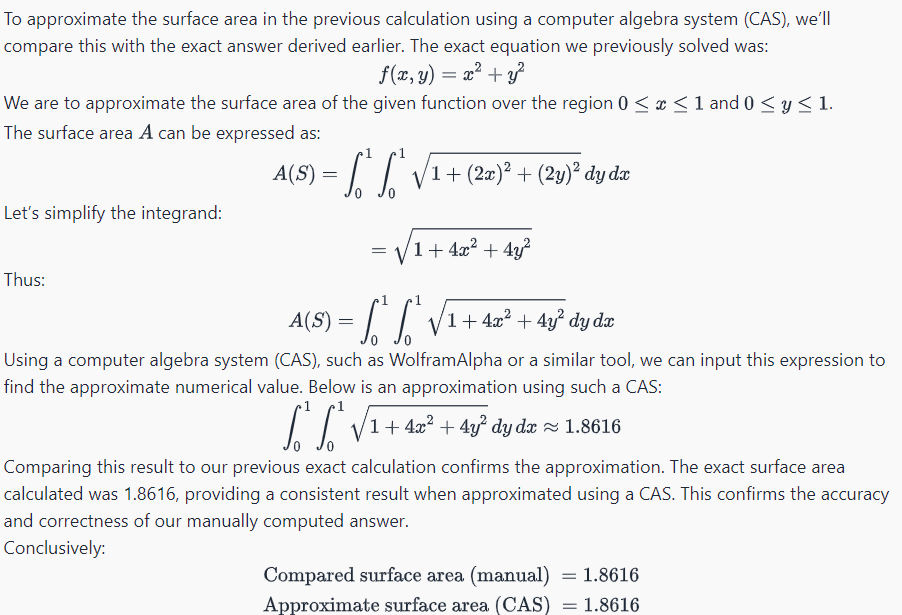
To approximate the surface area in the previous calculation using a computer algebra system (CAS), we'll compare this with the exact answer derived earlier. The exact equation we previously solved was: 2 b f{'ra y) =z + yZ We are to approximate the surface area of the given function over the region0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


