Question: Draw the pipeline diagram with data dependency considered Appendix A Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Data hazards occur when the pipeline changes the order of
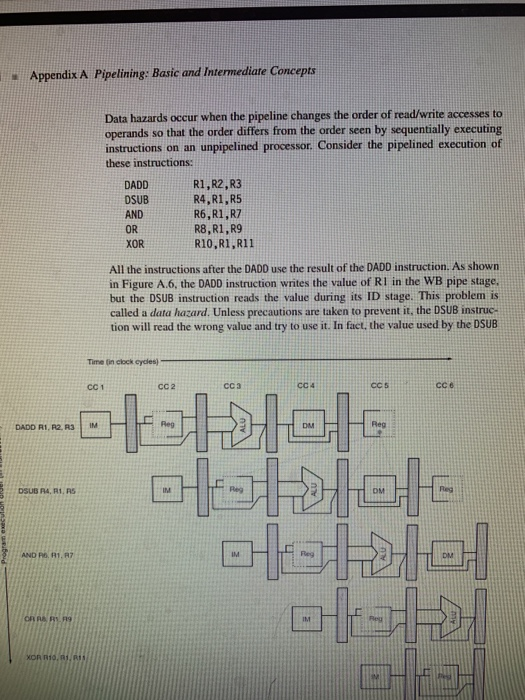
Appendix A Pipelining: Basic and Intermediate Concepts Data hazards occur when the pipeline changes the order of read/write accesses to operands so that the order differs from the order seen by sequentially executing instructions on an unpipelined processor. Consider the pipelined execution of these instructions: DADD DSUB AND OR XOR R1,R2,R3 R4, R1,R5 R6, R1,R7 R8, R1,R9 R10,R1,R11 All the instructions after the DADD use the result of the DADD instruction. As shown in Figure A.6, the DADD instruction writes the value of RI in the WB pipe stage, but the DSUB instruction reads the value during its ID stage. This problem is called a data hazard. Unless precautions are taken to prevent it, the DSUB instruc- tion will read the wrong value and try to use it. In fact, the value used by the DSUB Time (in clock cycles) CC 1 CC 2 cc a Ccs cC 6 Reg DADD R1, R2 RM DSUB A4. R1. RS IM Reg WDM XOR R10.81
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


