Question: Draw the tree-by-letter trees represented by the data tuples in the morse.py file. (You may draw them on paper or use the style shown below.)
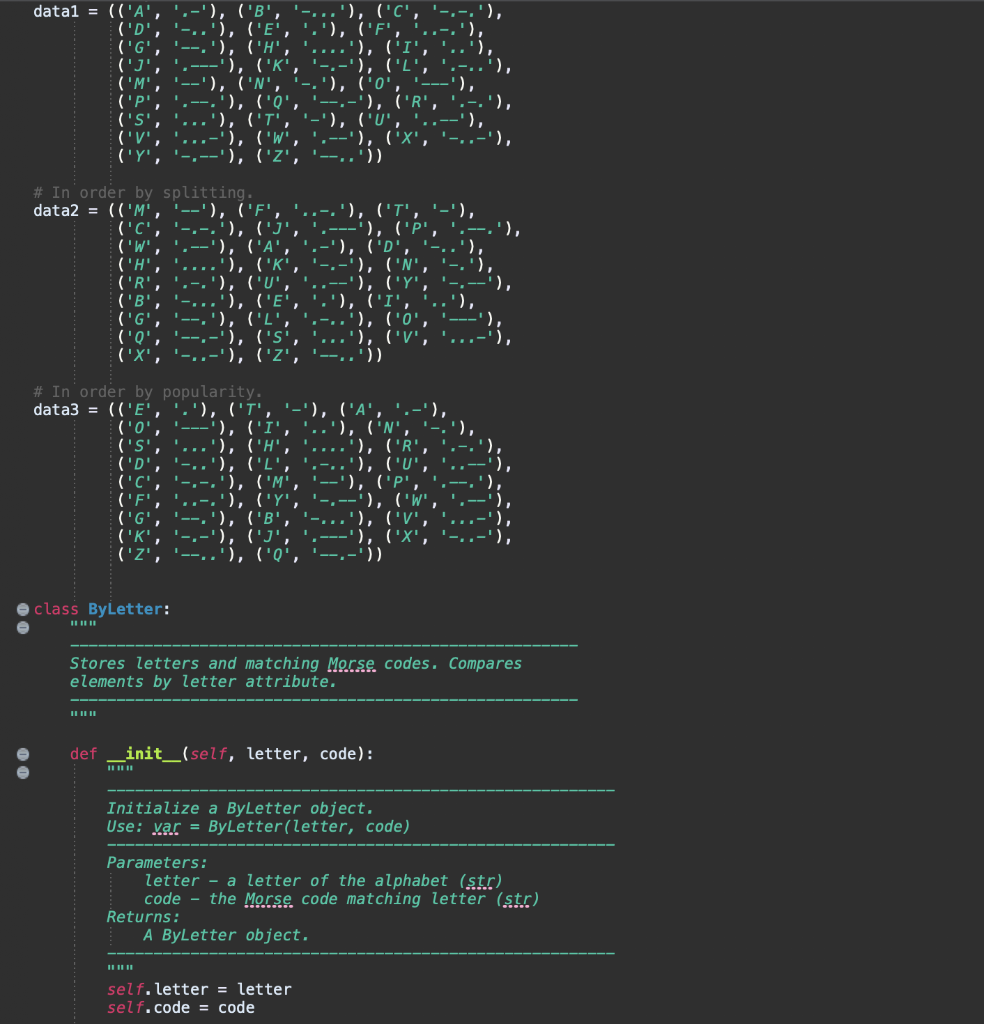
Draw the tree-by-letter trees represented by the data tuples in the morse.py file. (You may draw them on paper or use the style shown below.) Which of these three is the most inefficient tree? Why? Which of these is likely to be the most efficient tree? How could you (theoretically) figure that out?
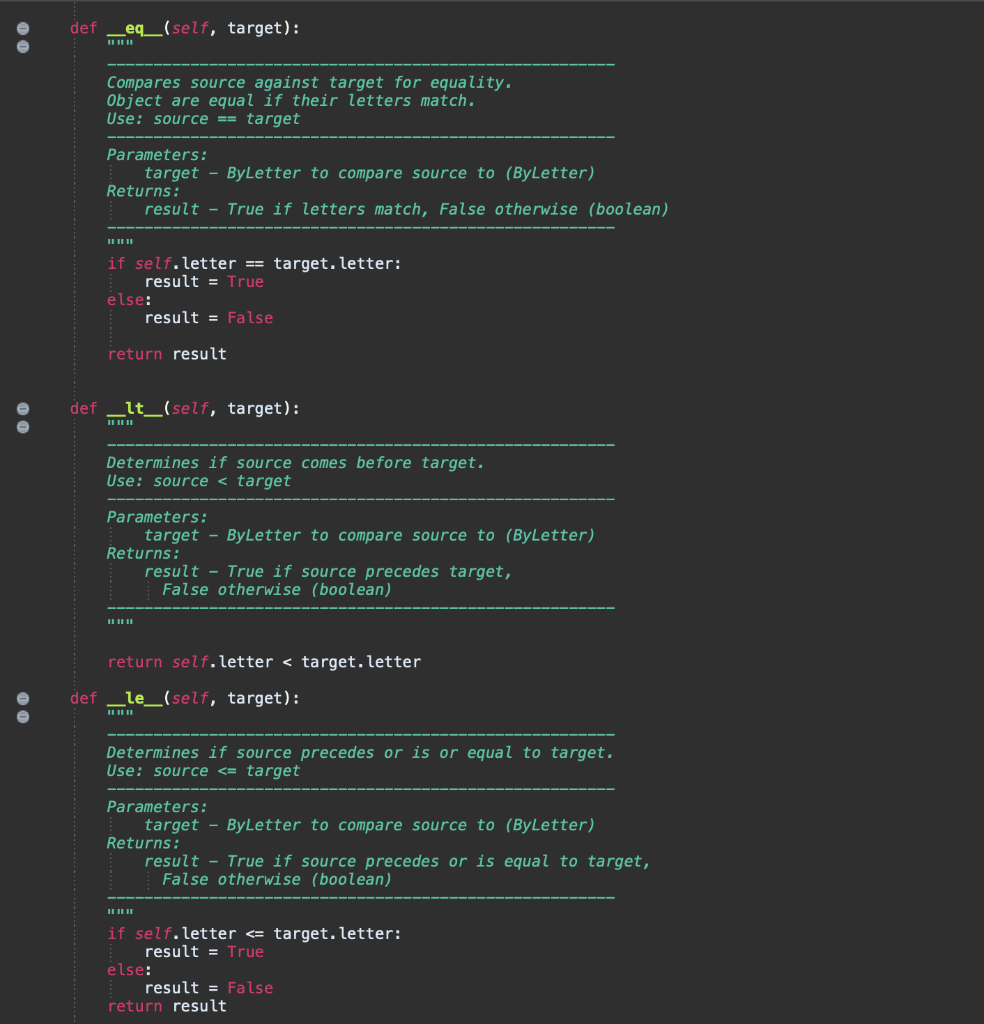
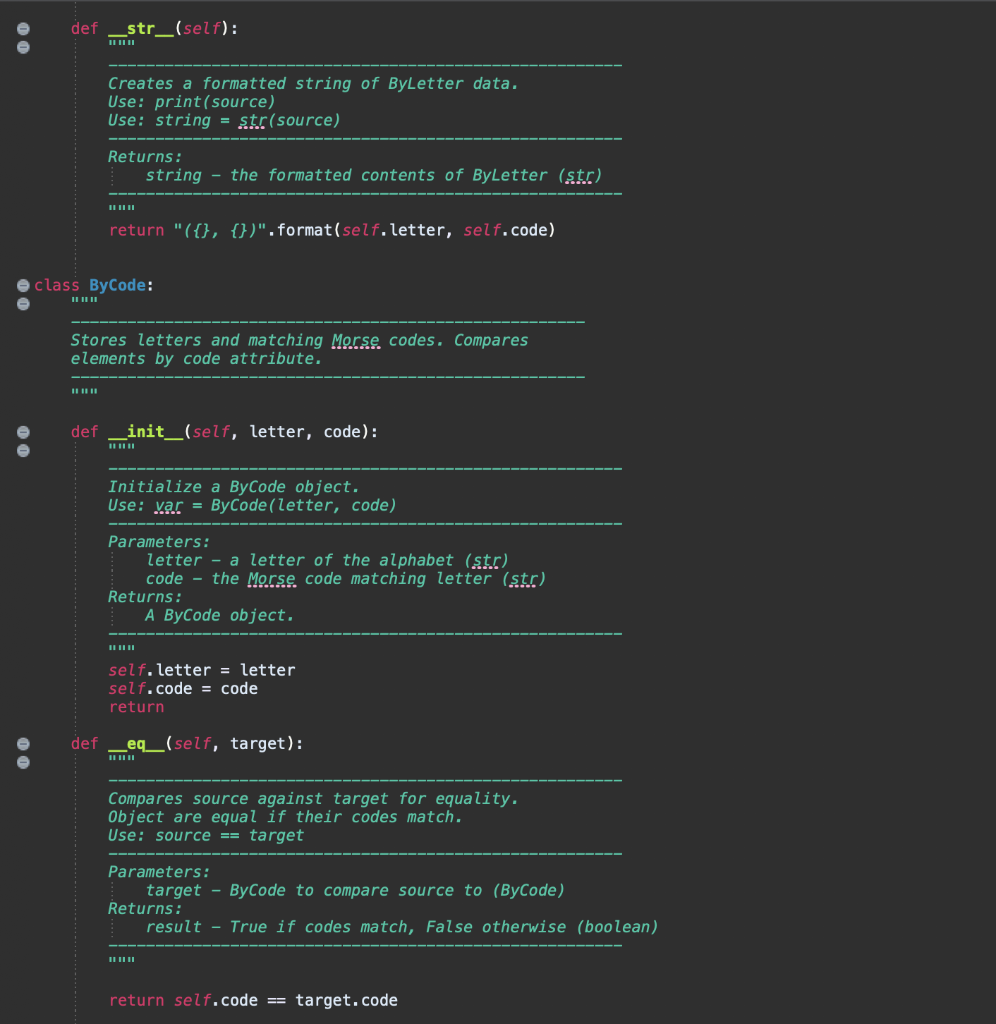
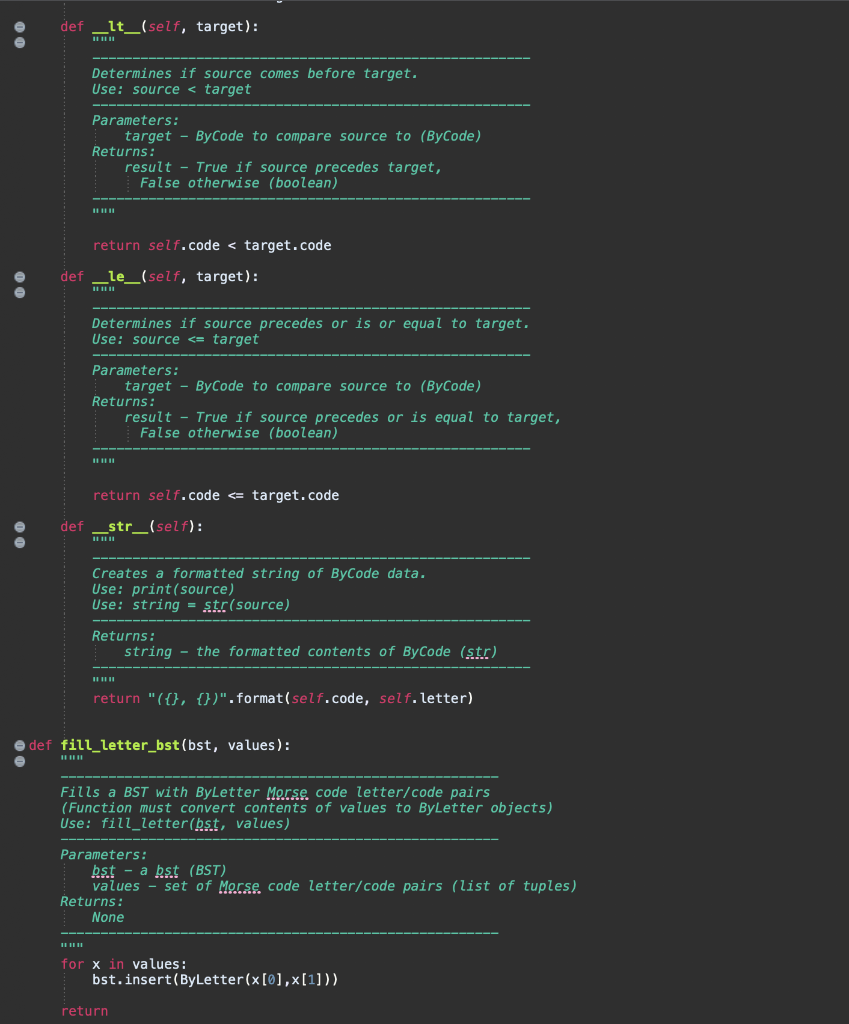
,) datal = (('A', ('D', ('G' (' ('M', ('P', ('s', (V ('Y' -'), ('B', ...'), ('C '), ('E', .'), ('F '), ('H', '), ('K' '), ('N', '), ('0' '), ('o' '), ('U '), ('W .--'), '), ('Z', '--..')) ('W', # In order by splitting. data2 = (('M', '--'), ('F', '..-.'), ('I', '-'), ('C', '-.-.'), ('J', ---'), ('P ('A' ), ('D', ('H', '), ('K -'), ('N' '), ('U', --'), ('yi -...'), ('E', '.'), ('I' ('G', '), ('l', ('0', '), ('s', ('x', -'), ('z', -..')). ('R', ('B', # In order by popularity. data3 = (('E','','), ('T', '-'), ('A', ('0', '---'), ('I', '..'), ('N', ('s', '), ('H', ..'), ('R', ('D', ), ('l' '), ('U' ('C', '), ('M ('p', ('F' ('G' '), ('B' ('K' '), ('j ('z', '), ('0' class By Letter: Stores letters and matching Morse codes. Compares elements by letter attribute. def _init__(self, letter, code): Initialize a ByLetter object. Use: var = ByLetter(letter, code) Parameters: letter - a letter of the alphabet (str) code - the Morse code matching letter (str) Returns: A ByLetter object. self.letter = letter self.code = code def eq__(self, target): Compares source against target for equality. Object are equal if their letters match. Use: source == target Parameters: target - ByLetter to compare source to (ByLetter) Returns: result - True if letters match, False otherwise (boolean) if self.letter == target. letter: result = True else: result = False return result def _it__(self, target): Determines if source comes before target. Use: source
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


