Question: Droinet Me 5 1 Random sequence of bits ( long sequences of equal - probable bits ) . Transmitter a ) Use the given signal
Droinet
Me
Random sequence of bits long sequences of equalprobable bits
Transmitter
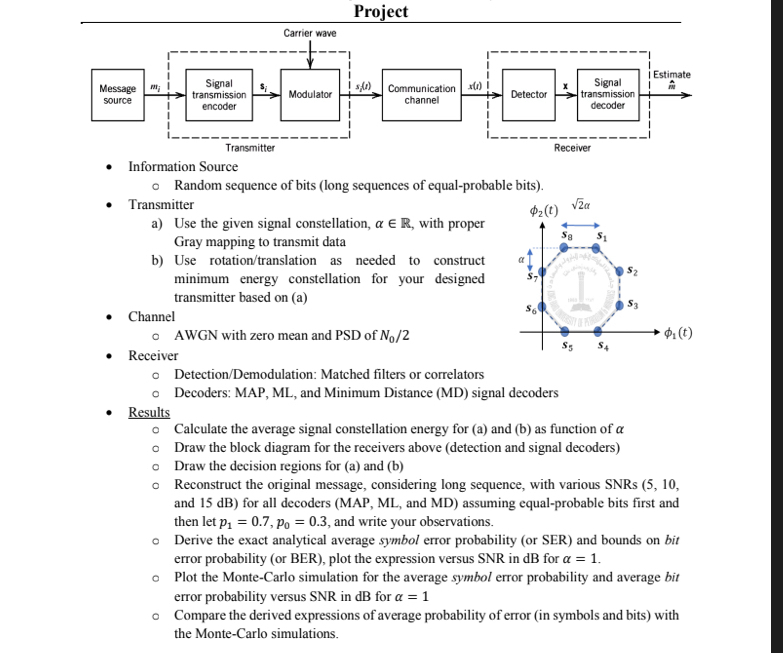
a Use the given signal constellation, with proper Gray mapping to transmit data
b Use rotationtranslation as needed to construct minimum energy constellation for your designed transmitter based on a
Channel
AWGN with zero mean and PSD of
Receiver
DetectionDemodulation: Matched filters or correlators
Decoders: MAP, ML and Minimum Distance MD signal decoders
Results
Calculate the average signal constellation energy for a and b as function of
Draw the block diagram for the receivers above detection and signal decoders
Draw the decision regions for a and b
Reconstruct the original message, considering long sequence, with various SNRs and dB for all decoders MAP ML and MD assuming equalprobable bits first and then let and write your observations.
Derive the exact analytical average symbol error probability or SER and bounds on bit error probability or BER plot the expression versus SNR in dB for
Plot the MonteCarlo simulation for the average symbol error probability and average bit error probability versus SNR in dB for
Compare the derived expressions of average probability of error in symbols and bits with the MonteCarlo simulations.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


