Question: Drop down options 1) (YES / NO / INSUFFICIENT INFORMATION) Number 1 is incorrect for the 2nd and 3rd part; for feedback on why its

Drop down options
1) (YES / NO / INSUFFICIENT INFORMATION)
Number 1 is incorrect for the 2nd and 3rd part; for feedback on why its wrong the application says to

Please help, thank you in advance!
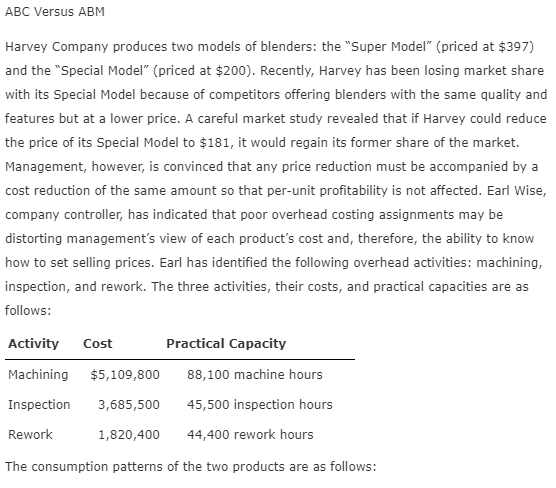
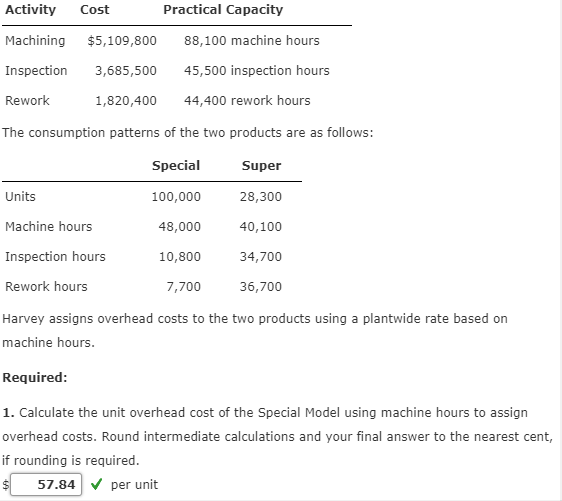
ABC Versus ABM Harvey Company produces two models of blenders: the "Super Model" (priced at $397) and the "Special Model" (priced at $200). Recently, Harvey has been losing market share with its Special Model because of competitors offering blenders with the same quality and features but at a lower price. A careful market study revealed that if Harvey could reduce the price of its Special Model to $181, it would regain its former share of the market. Management, however, is convinced that any price reduction must be accompanied by a cost reduction of the same amount so that per-unit profitability is not affected. Earl Wise, company controller, has indicated that poor overhead costing assignments may be distorting management's view of each product's cost and, therefore, the ability to know how to set selling prices. Earl has identified the following overhead activities: machining, inspection, and rework. The three activities, their costs, and practical capacities are as follows: Activity Cost Machining $5,109,800 Practical Capacity 88,100 machine hours 45,500 inspection hours 44,400 rework hours Inspection 3,685,500 Rework 1,820,400 The consumption patterns of the two products are as follows: Activity Cost Practical Capacity Machining $5,109,800 88,100 machine hours Inspection 3,685,500 45,500 inspection hours Rework 1,820,400 44,400 rework hours The consumption patterns of the two products are as follows: Special Super Units 100,000 28,300 Machine hours 48,000 40,100 Inspection hours 10,800 34,700 Rework hours 7,700 36,700 Harvey assigns overhead costs to the two products using a plantwide rate based on machine hours. Required: 1. Calculate the unit overhead cost of the Special Model using machine hours to assign overhead costs. Round intermediate calculations and your final answer to the nearest cent, if rounding is required. 57.84 per unit Now, repeat the calculation using ABC to assign overhead costs. Round intermediate calculations and your final answer to the nearest cent, if rounding is required. 39.75 X per unit Did improving the accuracy of cost assignments solve Harvey's competitive problem? Yes X 2. Now, assume that in addition to improving the accuracy of cost assignments, Earl observes that defective supplier components are the root cause of both the inspection and rework activities. Suppose further that Harvey has found a new supplier that provides higher-quality components such that inspection and rework costs are reduced by 50 percent. Now, calculate the cost of the Special Model (assuming that inspection and rework times are also reduced by 50 percent) using ABC. The relative consumption patterns also remain the same. Round intermediate calculations and your final answer to the nearest cent, if rounding is required. 33.79 per unit Comment on the difference between ABC and ABM. ABM is concerned with cost reduction as well as cost assignment, and it has allow 1. Remember if you are not using ABC to assign overhead, then a plantwide rate is needed. There will be two calculations. Discuss the outcome
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


