Question: during September of the current year, the controller was asked to perform variance analysis for August. The January operating data provided the standard prices, rates,
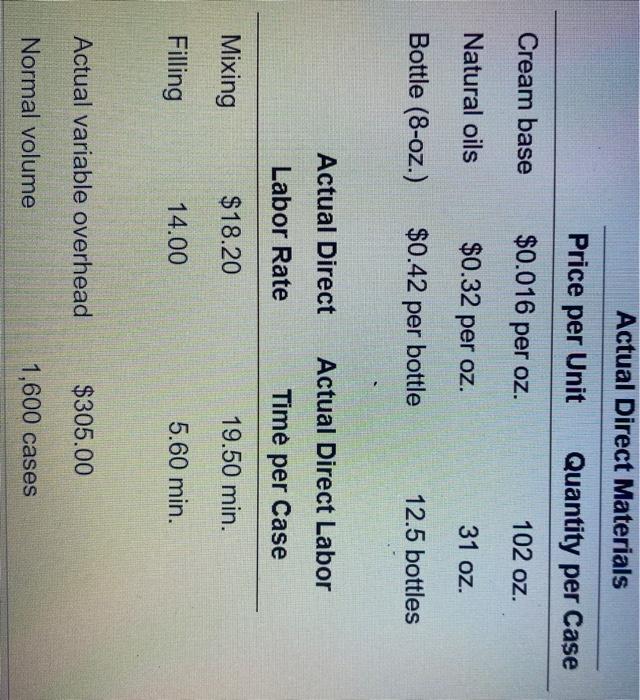
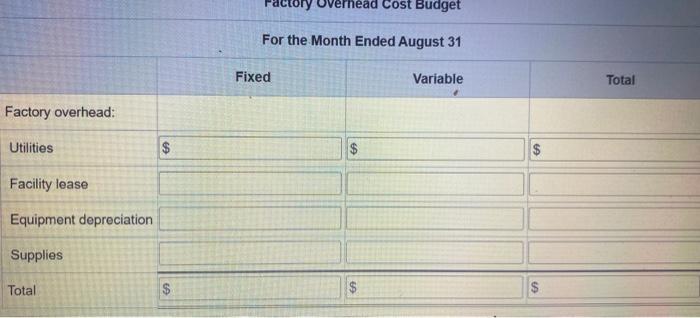
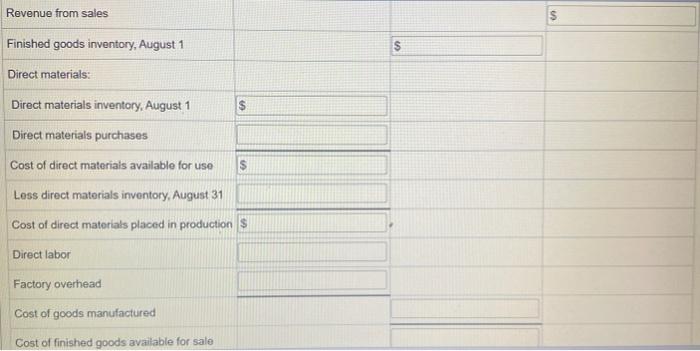
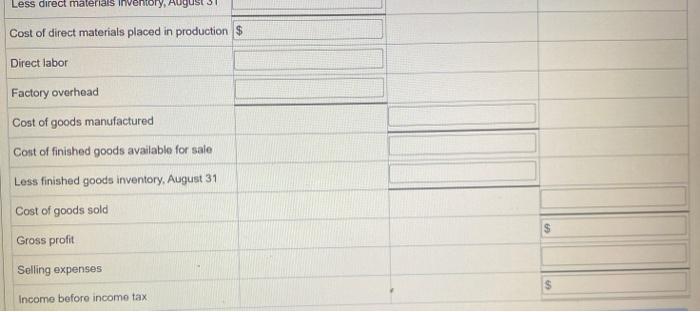
Actual Direct Materials Price per Unit Quantity per Case Cream base $0.016 per oz. 102 oz. Natural oils $0.32 per oz. 31 oz. Bottle (8-oz.) $0.42 per bottle 12.5 bottles Actual Direct Actual Direct Labor Labor Rate Time per Case Mixing $18.20 19.50 min. Filling 14.00 5.60 min. Actual variable overhead $305.00 Normal volume 1,600 cases Verhead cost Budget For the Month Ended August 31 Fixed Variable Total Factory overhead: Utilities $ $ $ $ Facility lease Equipment depreciation Supplies Total $ $ $ $ Revenue from sales Finished goods inventory, August 1 Direct materials: Direct materials inventory, August 1 Direct materials purchases Cost of direct materials available for use $ Less direct materials inventory, August 31 Cost of direct materials placed in production $ Direct labor Factory overhead Cost of goods manufactured Cost of finished goods available for sale Less direct materials inventory, AU Cost of direct materials placed in production $ Direct labor Factory overhead Cost of goods manufactured Cost of finished goods available for sale Less finished goods inventory, August 31 Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling expenses Income before income tax Actual Direct Materials Price per Unit Quantity per Case Cream base $0.016 per oz. 102 oz. Natural oils $0.32 per oz. 31 oz. Bottle (8-oz.) $0.42 per bottle 12.5 bottles Actual Direct Actual Direct Labor Labor Rate Time per Case Mixing $18.20 19.50 min. Filling 14.00 5.60 min. Actual variable overhead $305.00 Normal volume 1,600 cases Verhead cost Budget For the Month Ended August 31 Fixed Variable Total Factory overhead: Utilities $ $ $ $ Facility lease Equipment depreciation Supplies Total $ $ $ $ Revenue from sales Finished goods inventory, August 1 Direct materials: Direct materials inventory, August 1 Direct materials purchases Cost of direct materials available for use $ Less direct materials inventory, August 31 Cost of direct materials placed in production $ Direct labor Factory overhead Cost of goods manufactured Cost of finished goods available for sale Less direct materials inventory, AU Cost of direct materials placed in production $ Direct labor Factory overhead Cost of goods manufactured Cost of finished goods available for sale Less finished goods inventory, August 31 Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling expenses Income before income tax
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


