Question: e = ( ' * ' , 2 , ( ' + ' , ' x ' , 1 ) ) import math import random
e x
import math
import random
class IllegalOperatorException:
pass
def calcop left, right:
if op :
return left right
elif op :
return left right
elif op :
return left right
elif op :
return left right
else:
raise IllegalOperatorop
def computee:
if isinstancee tuple:
# We have an expression.
op l r e
# We compute the subexpressions.
ll computel
rr computer
# And on the basis of those, the whole expression.
return calcop ll rr
else:
# base expression; just return the number.
return e
from numbers import Number # The mother class of all numbers.
def isnumbere:
return isinstancee Number
def isvariablee:
return isinstancee str
def iscompositee:
return isinstancee tuple
def simplifye:
if isinstancee tuple:
op l r e
# We simplify the children expressions.
ll simplifyl
rr simplifyr
# We compute the expression if we can.
if isnumberll and isnumberrr:
return calcop ll rr
else:
return op ll rr
else:
# Leaf. No simplification is possible.
return e
varval x: y:
#@title Evaluating an expression with respect to a variable evaluation
def computee varval:
varval varval
if isnumbere:
return e
elif isvariablee:
if varval.gete None:
return varval.gete
else:
return e
else:
op l r e
ll computel varval
rr computer varval
if isnumberll and isnumberrr:
return calcop ll rr
else:
return op ll rr
#@title Exercise: define variables
def variablese l None:
if l is None:
l set
if isvariablee:
ladde
elif iscompositee:
op l r e
variablesl l
variablesr l
return setl
#@title Exercise: implementation of value equality
def valueequalitye f numsamples tolerancee:
Return True if the two expressions self and other are numerically
equivalent. Equivalence is tested by generating
numsamples assignments, and checking that equality holds
for all of them. Equality is checked up to tolerance, that is
the values of the two expressions have to be closer than tolerance.
It can be done in less than lines of code."""
vars variablese variablesf
for i in rangenumsamples:
map
for a in vars:
mapa random.gauss
if abscomputee map computef map tolerance:
return True
return False
#@title Derivation of a leaf expression
def derivateleafe x:
This function takes as input an expression e and a variable x
and returns the symbolic derivative of e wrt x as an expression."""
return if e x else
#@title Implement derivate
def derivatee x:
Returns the derivative of e wrt x
It can be done in less than lines of code."""
if iscompositee:
op l r e
if op or op :
return op derivatel x derivater x
elif op :
return op derivatel x rop l derivater x
elif op :
return op derivatel x r l derivater x r r
else:
return derivateleafe x
def derivateapproxf x varval, delta:
Computes the derivative of f with respect to x for a given delta,
using the fx delta fx delta method.
# This is fx
fx computef varvalvarval
varvaldelta dictvarval
varvaldeltax delta
# This is fx delta
fxplusdelta computef varvalvarvaldelta
return fxplusdelta fx delta
def similarx y epsilon:
if x and y :
# If they are negative, max and min play opposite roles.
return similarxy epsilon
if absx y epsilon:
return True
else:
return maxx yminx y epsilon epsilon
#@title Implementation of testderivative
def testderivativef df x delta tolerance numtests:
Tests if the derivative of f with respect to x is approximately equal to df
Returns True if the test passes for all randomly generated inputs, False otherwise."""
## YOUR SOLUTION HERE
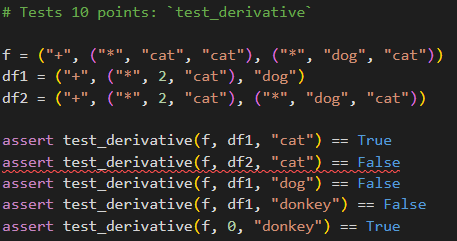
Please implement def testderivativef df x delta tolerance numtests You cannot import anything new or createdelete any existing methods. This method must pass the following test in picture:
# Tests points: 'testderivative'
cat, cat dog, cat
cat dog
cat dog, cat
assert testst:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


