Question: economic programming Exercise 3 Return to the labor supply decision in the first part of the Household and Asset Pricing notes. In class we used
economic programming
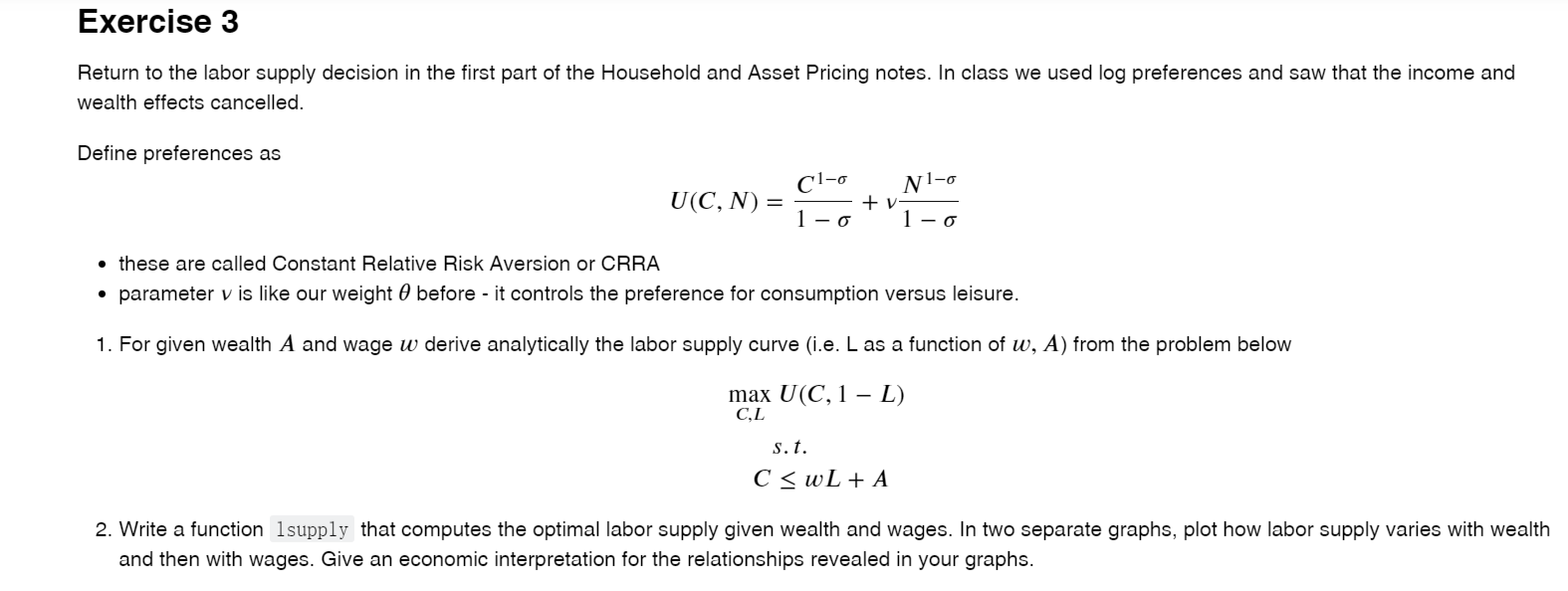
Exercise 3 Return to the labor supply decision in the first part of the Household and Asset Pricing notes. In class we used log preferences and saw that the income and wealth effects cancelled. Define preferences as Nl-o Cl-o U(C, N) = +v 1-0 1-0 these are called Constant Relative Risk Aversion or CRRA parameter v is like our weight before - it controls the preference for consumption versus leisure. 1. For given wealth A and wage w derive analytically the labor supply curve (i.e. L as a function of w, A) from the problem below max U(C, 1 - - L) CL S.t. C
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


