Question: EMBEDDED SYSTEM CHAPTER 1 1.10 What are the two basic classifications of numbers with which we are concerned in an embedded application? 1.14 What do
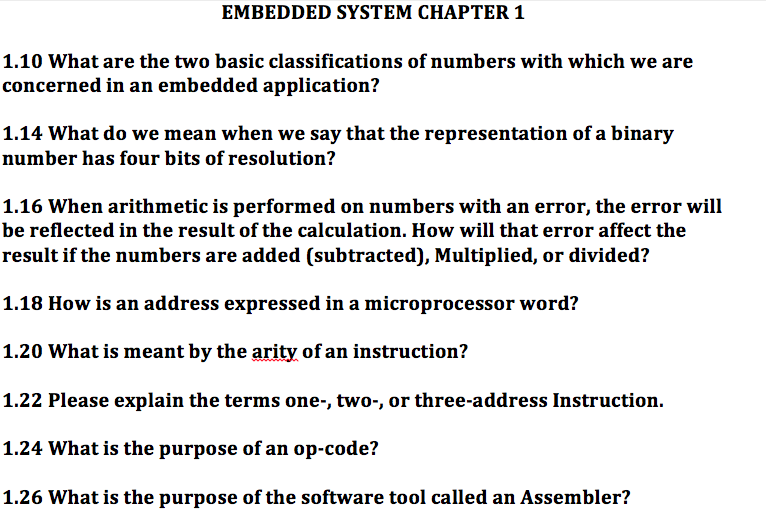
EMBEDDED SYSTEM CHAPTER 1 1.10 What are the two basic classifications of numbers with which we are concerned in an embedded application? 1.14 What do we mean when we say that the representation of a binary number has four bits of resolution? 1.16 When arithmetic is performed on numbers with an error, the error will be reflected in the result of the calculation. How will that error affect the result if the numbers are added (subtracted), Multiplied, or divided? 1.18 How is an address expressed in a microprocessor word? 1.20 What is meant by the arity of an instruction? 1.22 Please explain the terms one-, two-, or three-address Instruction. 1.24 What is the purpose of an op-code? 1.26 What is the purpose of the software tool called an Assembler? EMBEDDED SYSTEM CHAPTER 1 1.10 What are the two basic classifications of numbers with which we are concerned in an embedded application? 1.14 What do we mean when we say that the representation of a binary number has four bits of resolution? 1.16 When arithmetic is performed on numbers with an error, the error will be reflected in the result of the calculation. How will that error affect the result if the numbers are added (subtracted), Multiplied, or divided? 1.18 How is an address expressed in a microprocessor word? 1.20 What is meant by the arity of an instruction? 1.22 Please explain the terms one-, two-, or three-address Instruction. 1.24 What is the purpose of an op-code? 1.26 What is the purpose of the software tool called an Assembler
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


