Question: Embedded system lab homework, i will give thumbs up for the answers Embedded Systems Lab 4. PWM Generation Purposes Understanding the basic concepts of PWM.

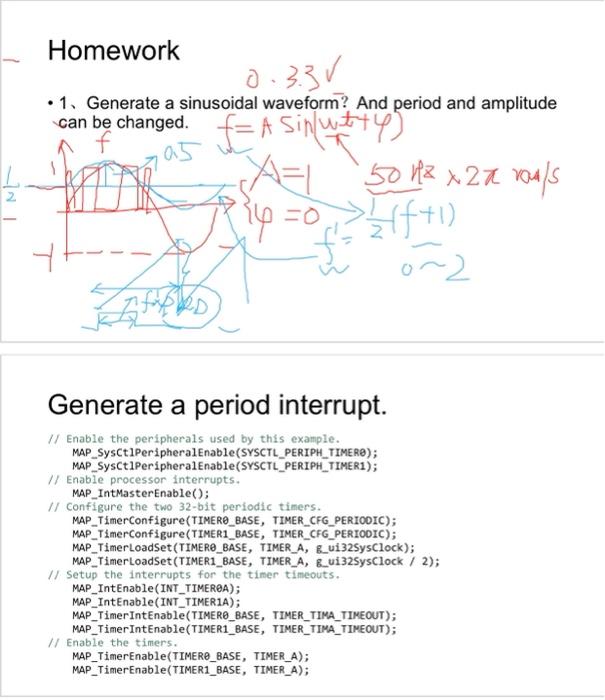
Embedded Systems Lab 4. PWM Generation Purposes Understanding the basic concepts of PWM. Learning Series Cortex-M4 PWM working principle. Learning the use of PWM related library functions. Study on the PWM module output cycle and duty cycle settings. Task 1: 1. Change the period and duty of PWM. PWMValue=PWMDividedClk/PWMFrequency- 1 2 Set the deadtime of PWM waveform. ion1A - 1 Generate a sinusoidal waveform? And period and amplitude can be changed. Generate a period interrupt. II Enable the peripherals used by this example. MAP_SysCt1Periphera1Enable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_TIMER); MAP_SysCt1PeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_TIMER1); // Enable processor interrupts. MAP_IntMasterEnable(); 1/ Configure the two 32-bit periodic timers. MAP_TimerConfigure(TIMERO_BASE, TIMER_CFG_PERIOOIC); MAP_TimerConfigure(TIMER1_BASE, TIMER_CFG_PERIOOIC); MAP_TimerLoadSet(TIMERO_BASE, TIMER_A, G_ui325ysClock); MAP_TimerLoadSet(TIMER1_BASE, TIMER_A, B_ui32SysClock / 2); 1/ Setup the interrupts for the timer timeouts. MAP_IntEnable(INT_TIMEREA); MAP_IntEnable(INT_TIMER1A); MAP_TimerIntEnable(TIMERO_BASE, TIMER_TIMA_TIMEOUT); MAP_TimerIntEnable(TIMER1_BASE, TIMER_TIMA_TIMEOUT); 1/ Enable the timers. MAP_TimerEnable(TIMER_BASE, TIMER_A); MAP_TimerEnable(TIMER1_BASE, TIMER_A)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


