Question: Encode the following 16-bit data with a Hamming error code: 0b1100011110001110. Now A 16-bit number was encoded with a Hamming error code; later, we access
-
Encode the following 16-bit data with a Hamming error code: 0b1100011110001110.
Now A 16-bit number was encoded with a Hamming error code; later, we access the resulting 21-bit codeword as 0b100000101011111011100.
Q2: We notice that one bit was corrupted. Which bit was corrupted? Since we are working with Hamming codes, use the convention that the MSB is bit position 1, the second MSB is bit position 2, etc.
Q 3: What is the correct 16-bit data?
Now each bit gets stored 3 times in a row.
As an example, if the data bits were 1110, the code word would be 111111111000.
Q4 : For 8-bit data values, what is the fraction of code words that are valid?
How many possible data can you write using 8 bits? Now, apply the coding scheme, how many possible combinations do you have? What fraction of that are valid code words following the described coding scheme? 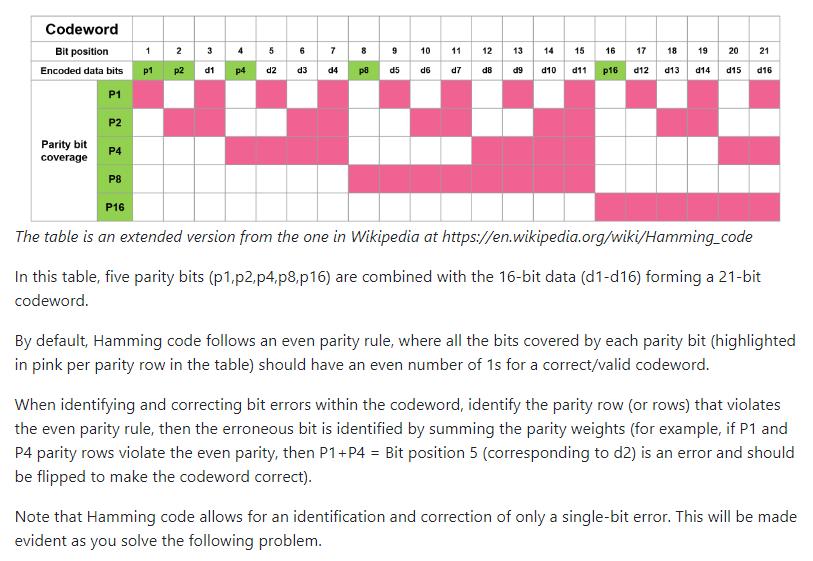
Codeword Bit position Encoded data bits P1 P2 Parity bit coverage P4 1 2 p1 p2 3 4 d1 p4 d2 d3 d4 8 p8 9 10 11 d6 d7 d5 12 13 d8 d9 14 d10 15 d11 16 p16 17 d12 18 19 20 21 d14 d15 d16 d13 P8 P16 The table is an extended version from the one in Wikipedia at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hamming_code In this table, five parity bits (p1,p2,p4, p8, p16) are combined with the 16-bit data (d1-d16) forming a 21-bit codeword. By default, Hamming code follows an even parity rule, where all the bits covered by each parity bit (highlighted in pink per parity row in the table) should have an even number of 1s for a correct/valid codeword. When identifying and correcting bit errors within the codeword, identify the parity row (or rows) that violates the even parity rule, then the erroneous bit is identified by summing the parity weights (for example, if P1 and P4 parity rows violate the even parity, then P1+P4 = Bit position 5 (corresponding to d2) is an error and should be flipped to make the codeword correct). Note that Hamming code allows for an identification and correction of only a single-bit error. This will be made evident as you solve the following problem.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Q1 Encoding the 16bit data 0b1100011110001110 with a Hamming error code The Hamming code adds extra ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


