Question: ENGG 6 8 2 , Applied Heat Transfer Design Problem # Fall 2 0 2 4 Crude oil is to be transported overland in Alaska.
ENGG Applied Heat Transfer
Design Problem #
Fall
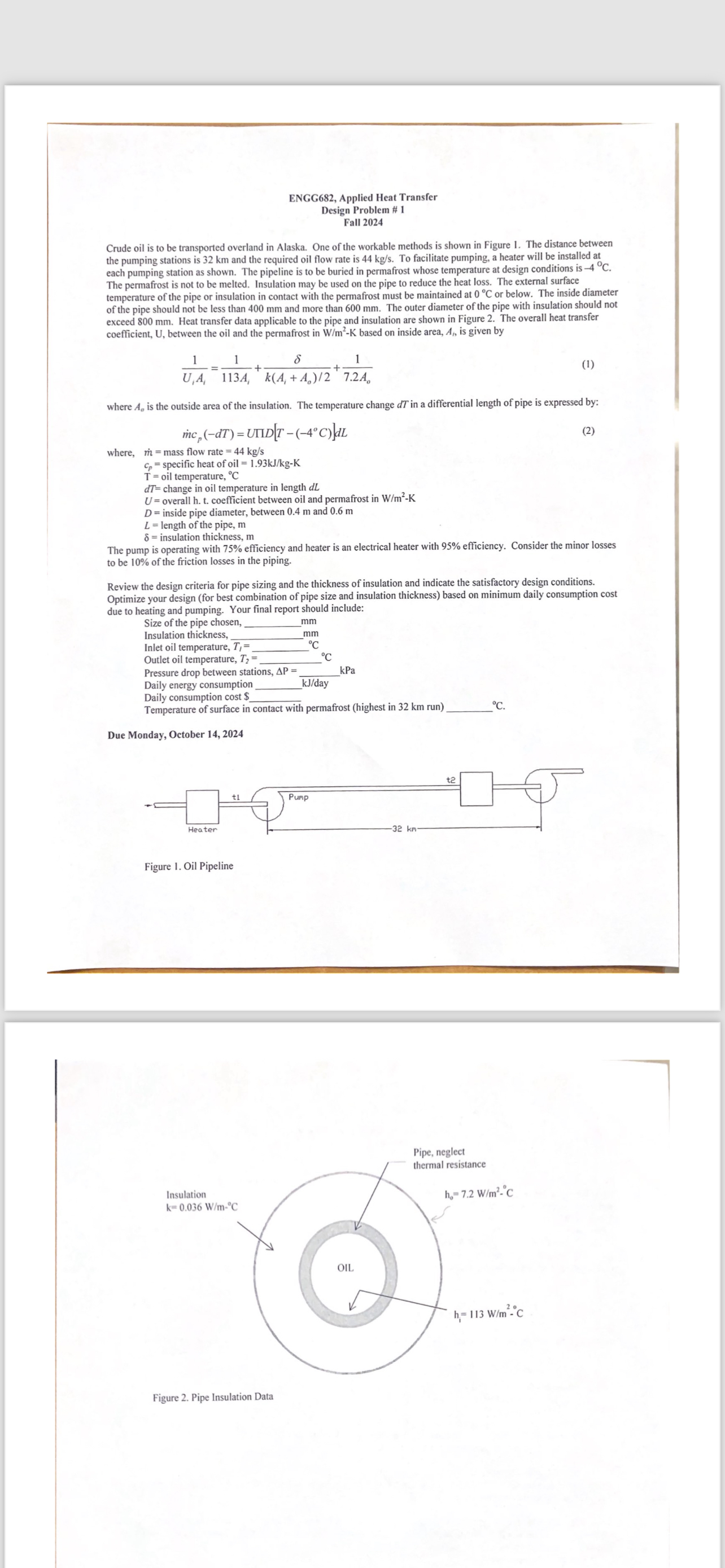
Crude oil is to be transported overland in Alaska. One of the workable methods is shown in Figure The distance between
the pumping stations is km and the required oil flow rate is To facilitate pumping, a heater will be installed at
The permafrost is not to be melted. Insulation may be used on the pipe to reduce the heat loss. The external surface
temperature of the pipe or insulation in contact with the permafrost must be maintained at or below. The inside diameter
of the pipe should not be less than mm and more than mm The outer diameter of the pipe with insulation should not
exceed mm Heat transfer data applicable to the pipe and insulation are shown in Figure The overall heat transfer
coefficient, U between the oil and the permafrost in based on inside area, is given by
where is the outside area of the insulation. The temperature change in a differential length of pipe is expressed by:
where, mass flow rate
specific heat of oil
change in oil temperature in length
overall h t coefficient between oil and permafrost in
inside pipe diameter, between m and m
length of the pipe,
insulation thickness,
The pump is operating with efficiency and heater is an electrical heater with efficiency. Consider the minor losses
to be of the friction losses in the piping.
Review the design criteria for pipe sizing and the thickness of insulation and indicate the satisfactory design conditions.
Optimize your design for best combination of pipe size and insulation thickness based on minimum daily consumption cost
due to heating and pumping. Your final report should include:
Size of the pipe chosen,
mm
Insulation thickness,
Inlet oil temperature,
Outlet oil temperature,
Pressure drop between stations,
Daily energy consumption
Daily consumption cost $
day
Temperature of surface in contact with permafrost highest in km run
Due Monday, October
Figure Oil Pipeline
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


