Question: Engineering Problem 3: Carbon-Based Energy ACE533 Applied Chemical Engineering Il: Energy A hydrocracker is used after a fractionation column to split paraffins (long-chain alkanes) into
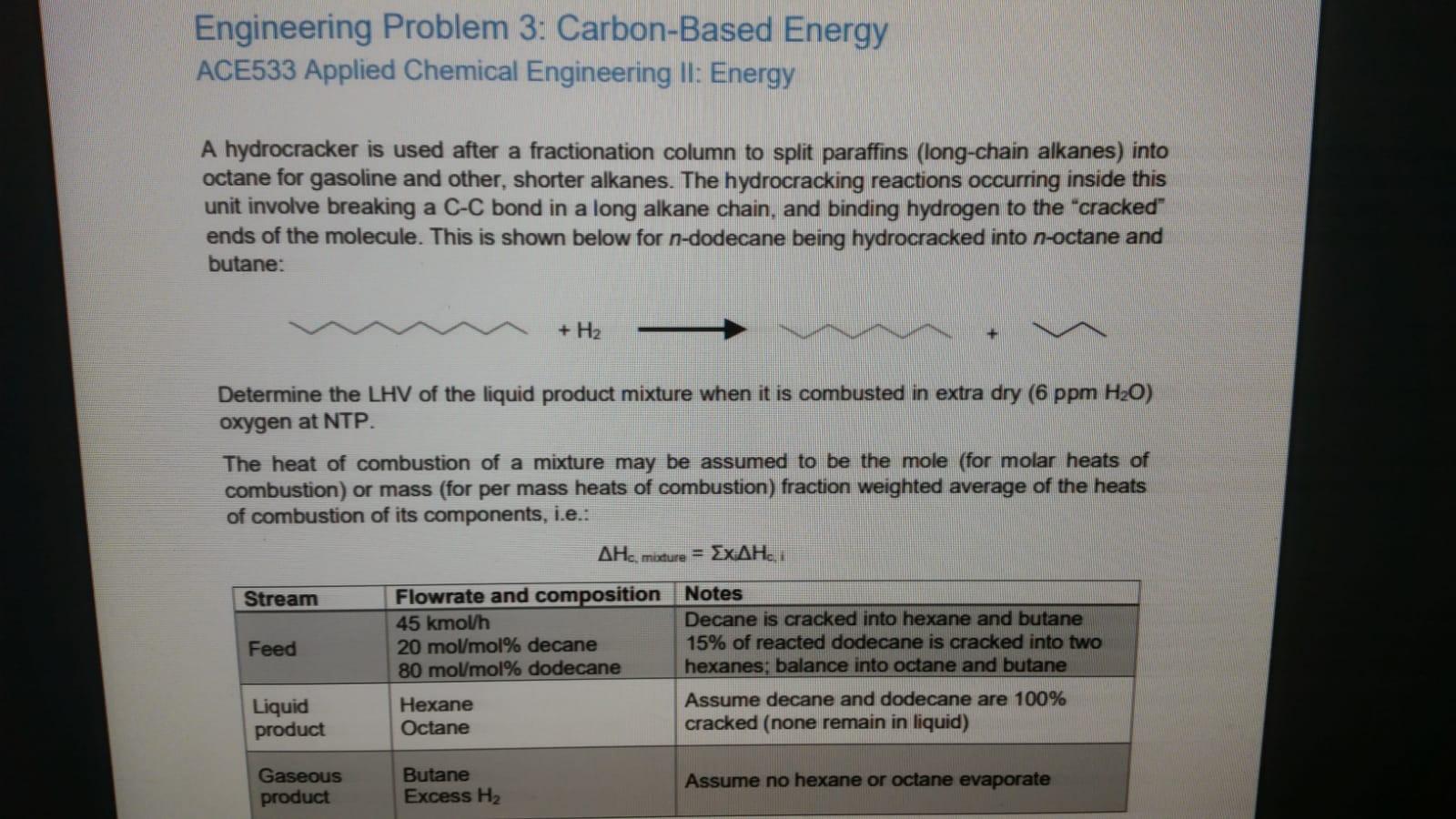
Engineering Problem 3: Carbon-Based Energy ACE533 Applied Chemical Engineering Il: Energy A hydrocracker is used after a fractionation column to split paraffins (long-chain alkanes) into octane for gasoline and other, shorter alkanes. The hydrocracking reactions occurring inside this unit involve breaking a C-C bond in a long alkane chain, and binding hydrogen to the "cracked" ends of the molecule. This is shown below for n-dodecane being hydrocracked into n-octane and butane: + H2 Determine the LHV of the liquid product mixture when it is combusted in extra dry (6 ppm H20) oxygen at NTP. The heat of combustion of a mixture may be assumed to be the mole (for molar heats of combustion) or mass (for per mass heats of combustion) fraction weighted average of the heats of combustion of its components, i.e.: AHC, mixture = ExAH. Stream Flowrate and composition Notes 45 kmolh Decane is cracked into hexane and butane Feed 20 mol/mol% decane 15% of reacted dodecane is cracked into two 80 mol/mol% dodecane hexanes, balance into octane and butane Liquid Hexane Assume decane and dodecane are 100% product Octane cracked (none remain in liquid) Gaseous product Butane Excess H2 Assume no hexane or octane evaporate Engineering Problem 3: Carbon-Based Energy ACE533 Applied Chemical Engineering Il: Energy A hydrocracker is used after a fractionation column to split paraffins (long-chain alkanes) into octane for gasoline and other, shorter alkanes. The hydrocracking reactions occurring inside this unit involve breaking a C-C bond in a long alkane chain, and binding hydrogen to the "cracked" ends of the molecule. This is shown below for n-dodecane being hydrocracked into n-octane and butane: + H2 Determine the LHV of the liquid product mixture when it is combusted in extra dry (6 ppm H20) oxygen at NTP. The heat of combustion of a mixture may be assumed to be the mole (for molar heats of combustion) or mass (for per mass heats of combustion) fraction weighted average of the heats of combustion of its components, i.e.: AHC, mixture = ExAH. Stream Flowrate and composition Notes 45 kmolh Decane is cracked into hexane and butane Feed 20 mol/mol% decane 15% of reacted dodecane is cracked into two 80 mol/mol% dodecane hexanes, balance into octane and butane Liquid Hexane Assume decane and dodecane are 100% product Octane cracked (none remain in liquid) Gaseous product Butane Excess H2 Assume no hexane or octane evaporate
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


