Question: esign 1. Write a class called Process which stores the ID, arrival time, and CPU burst length of a process, all are integers. You can

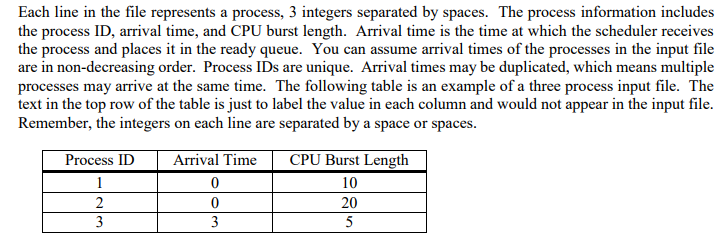

esign 1. Write a class called Process which stores the ID, arrival time, and CPU burst length of a process, all are integers. You can also add data members to keep track of information in order to compute the statistics about the process such as its wait time, response time, and turnaround time. The methods of the Process class are the get and set methods for each data member, the constructor for the class, and any method needed to compute the statistics for that process 2. Write a class called Scheduler to simulate a CPU scheduler for an operating system. The scheduler contains the ready queue and the ready queue is a circular linked list. You'll use the circular linked list you implemented for assignment 1. The only operations the scheduler performs is add and remove. The add operation adds a process into the ready queue into its appropriate spot within the ready queue according to the CPU scheduling algorithm implemented. Th according to the CPU scheduling algorithm implemented. You'll implement the CPU scheduling algorithms First Come First Serve, Shortest Remaining Time First which is the preemptive version of Shortest Job First, and Round Robin. Here is a perfect use of inheritance. If needed, you can add an additional method to the circular linked list class to help in the use of the ready queue for a particular CPU scheduling algorithm. e remove operation removes a process from the ready queue 3. Create a driver class and make the name of the driver class Assignment2 and it should only contain only one method public static void main (String args]. The main method receives, via the command line arguments, the name of the CPU scheduler that your simulator program will execute. If Round Robin is the CPU scheduler chosen then the time quantum value is also received via a command line argument. The main method opens the file assignment2.txt reading in the entire set of processes and initiates execution of the simulator program. Assume there is only a single processor with only one core. The main method itself should be fairly short. The command to launch your program using First Come First Serve scheduling: java Assignment2 FCFS The command to launch your program using Shortest Remaining Time First scheduling: java Assignment2 SRTF The command to launch your program using Round Robin scheduling with a time quantum of 10 java Assignment2 RR 10 4. The input to your program will be read from a plain text file called assignment2.txt. This is the statement you'll use to open the file FileInputStream fstream new FileInputStream ("assignment2.txt"); Assuming you're using Eclipse to create your project, you will store the input file assignment2.txt in the parent directory of your source code (.java files) which happens to be the main directory of your project in Eclipse. If you're using some other development environment, you will have to figure out where to store the input file esign 1. Write a class called Process which stores the ID, arrival time, and CPU burst length of a process, all are integers. You can also add data members to keep track of information in order to compute the statistics about the process such as its wait time, response time, and turnaround time. The methods of the Process class are the get and set methods for each data member, the constructor for the class, and any method needed to compute the statistics for that process 2. Write a class called Scheduler to simulate a CPU scheduler for an operating system. The scheduler contains the ready queue and the ready queue is a circular linked list. You'll use the circular linked list you implemented for assignment 1. The only operations the scheduler performs is add and remove. The add operation adds a process into the ready queue into its appropriate spot within the ready queue according to the CPU scheduling algorithm implemented. Th according to the CPU scheduling algorithm implemented. You'll implement the CPU scheduling algorithms First Come First Serve, Shortest Remaining Time First which is the preemptive version of Shortest Job First, and Round Robin. Here is a perfect use of inheritance. If needed, you can add an additional method to the circular linked list class to help in the use of the ready queue for a particular CPU scheduling algorithm. e remove operation removes a process from the ready queue 3. Create a driver class and make the name of the driver class Assignment2 and it should only contain only one method public static void main (String args]. The main method receives, via the command line arguments, the name of the CPU scheduler that your simulator program will execute. If Round Robin is the CPU scheduler chosen then the time quantum value is also received via a command line argument. The main method opens the file assignment2.txt reading in the entire set of processes and initiates execution of the simulator program. Assume there is only a single processor with only one core. The main method itself should be fairly short. The command to launch your program using First Come First Serve scheduling: java Assignment2 FCFS The command to launch your program using Shortest Remaining Time First scheduling: java Assignment2 SRTF The command to launch your program using Round Robin scheduling with a time quantum of 10 java Assignment2 RR 10 4. The input to your program will be read from a plain text file called assignment2.txt. This is the statement you'll use to open the file FileInputStream fstream new FileInputStream ("assignment2.txt"); Assuming you're using Eclipse to create your project, you will store the input file assignment2.txt in the parent directory of your source code (.java files) which happens to be the main directory of your project in Eclipse. If you're using some other development environment, you will have to figure out where to store the input file
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


