Question: estion: Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for PDI. E/V80.00% Cost of equity9.40% Risk-free rate 3.00% Beta 1.28 Market equity risk premium 5.00%
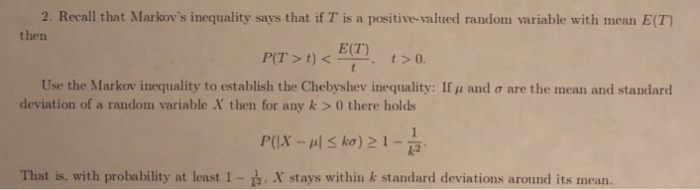
estion:
Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) for PDI.
E/V80.00%
Cost of equity9.40%
Risk-free rate 3.00%
Beta 1.28
Market equity risk premium 5.00%
D/V20.00%
Cost of debt4.00%
Corporate tax rate40.00%
WACC 80% x 9.40%) + [20% x 4% x (1 - 40%)]= 8.00% WACC = (E/V x Re) + ((D/V x Rd) x (1 - T))
*Cost of equityRisk free rate of return + (Beta * Risk premium) = 3% + (1.28 x 5%) 0.094
Givend the above, I cannot get the following:
Sum of FCF PV =?
Terminal value =?
Present value of terminal value =?
Total value of PDI =?
Assumptions
Discount rate ?
Terminal value ?

![+ [20% x 4% x (1 - 40%)]= 8.00% WACC = (E/V](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/667a87442fa1d_051667a8743dd3d6.jpg)
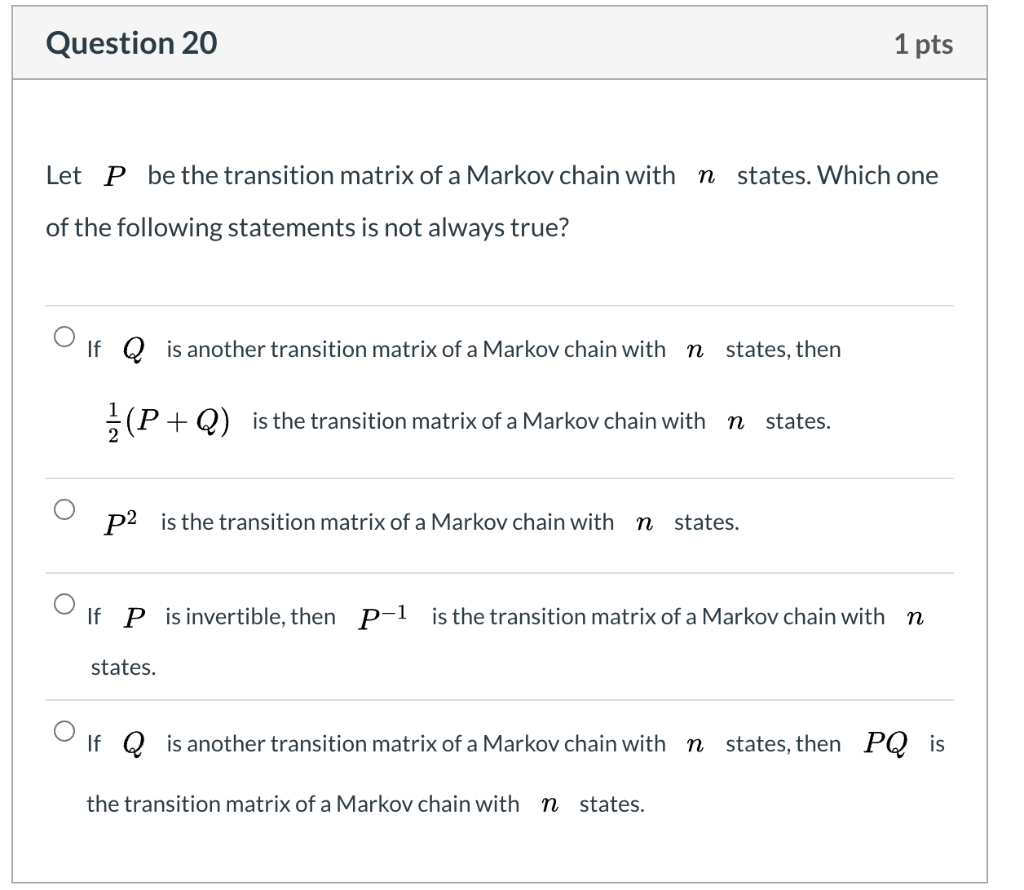
Let P be the transition matrix of a Markov chain with 7 states. Which one of the following statements is not always true? O p2 is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with 72 states. If O is another transition matrix of a Markov chain with 72 states, then PQ is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with 72 states. O If ) is another transition matrix of a Markov chain with 72 states, then *(P + Q) is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with 7, states. If P is invertible, then p-1 is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with 71, states.Question 20 1 pts Let P be the transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states. Which one of the following statements is not always true? If Q is another transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states, then =(P + Q) is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states. O P2 is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states. If P is invertible, then p-1 is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states. If Q is another transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states, then PQ is the transition matrix of a Markov chain with n states.2. Recall that Markov's inequality says that if T' is a positive-valued random variable with mean E(T) then E(T) P(T > 1 ) 0 there holds P(1X - #| Ska) 21 - 1 That is. with probability at least 1 - 2. X stays within & standard deviations around its mean
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


