Question: Every mechanical engineer needs to have a working knowledge of steel in the context of the iron carbon phase diagram. For questions below discuss

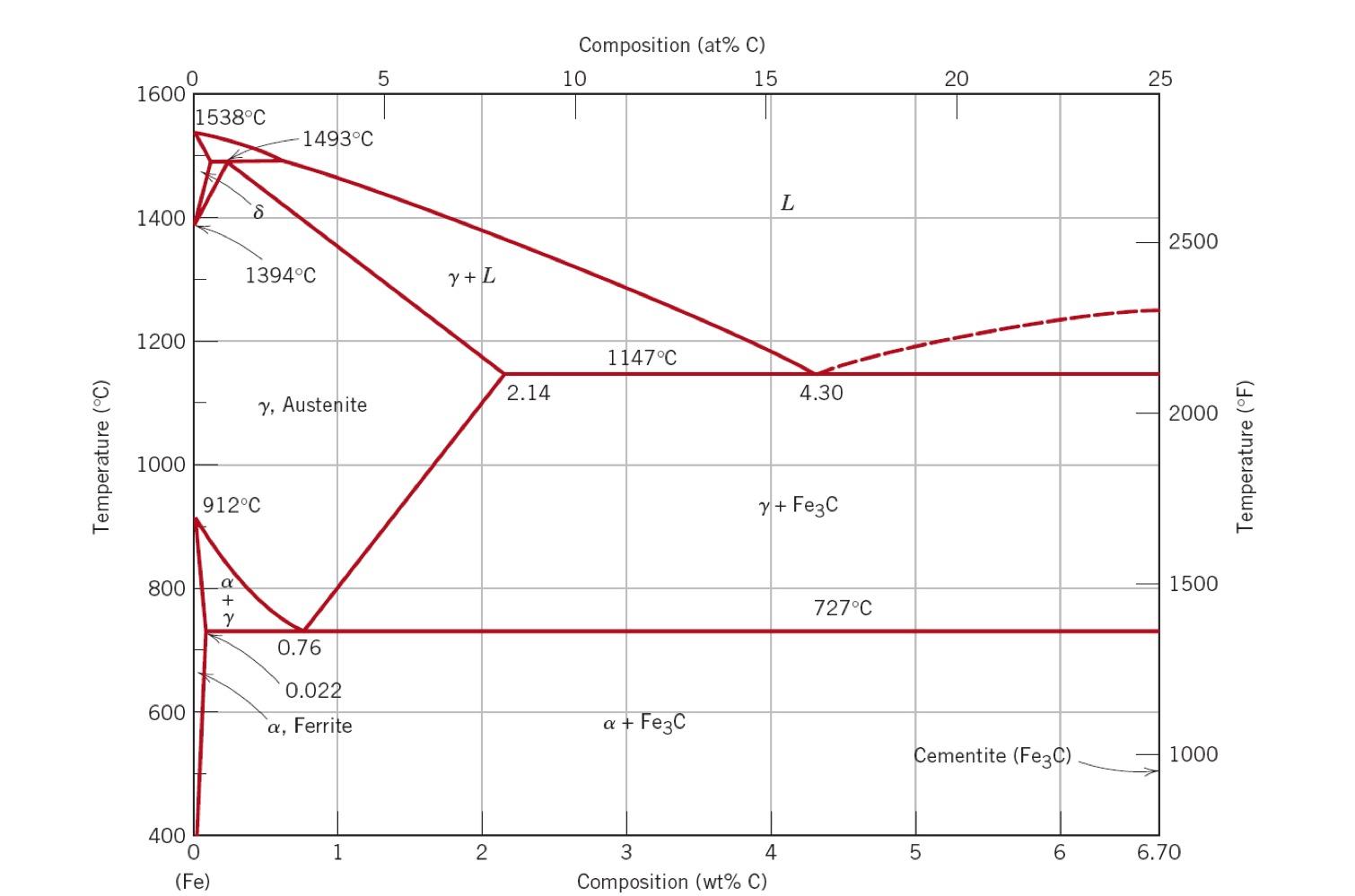

Every mechanical engineer needs to have a working knowledge of steel in the context of the iron carbon phase diagram. For questions below discuss the answer in terms of the material properties in the context of the phase diagram, composition, crystal structure, bonding, microstructure, and material composition. Use words, equations and diagrams as you see fit. Temperature (C) 1600 1400 1200 1000 1538C 600 800 + Y 400 O 8 (Fe) 912C 1493C 1394C y, Austenite 0.76 0.022 a, Ferrite 1 5 Y + L 2 2.14 Composition (at% C) 15 10 1147C a + Fe3C L 3 4 Composition (wt% C) 4.30 y+ Fe3C 727C 20 Cementite (Fe3C) 5 6 25 2500 2000 1500 1000 6.70 Temperature (F) a) What is the distinction between steels and cast irons? Explain in terms of material composition, properties, and microstructure. b) There is a type of steel microstructure known as 'pearlite'. What is the carbon concentration of this material and what are the phases present? Sketch the microstructure of pearlite in the box (clearly labeling the phases) below. c) For a 1050 steel alloy: Identify and illustrate (sketch draw a box and sketch the microstructure) the phases (grains) present at 850C and 726C. Clearly label the phases in your sketch. Calculate the percentage of pearlite in this alloy at 726C.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


