Question: Everything else constant, the international trade effect indicates that aggregate expenditures in the domestic economy fall when: A) domestic prices fall relative to foreign prices.


Everything else constant, the international trade effect indicates that aggregate expenditures in the domestic economy fall when:
A) domestic prices fall relative to foreign prices.
B) domestic interest rates fall relative to foreign interest rates.
C) domestic prices rise relative to foreign prices.
D) domestic purchasing power rises relative to foreign purchasing power.
E) domestic interest rates rise relative to foreign interest rates.
The aggregate demand curve shows:
A) how the equilibrium level of aggregate expenditure changes in response to changes in production.
B) the amount people spend at different real GDP levels.
C) the positive relationship between the price level and real GDP.
D) the negative relationship between aggregate expenditure and real GDP.
E) how the equilibrium level of aggregate expenditure changes as the price level changes.
Which of the following is associated with an increase in the average price level?
A) A decrease in the aggregate quantity demanded
B) An increase in the aggregate quantity demanded
C) A leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve
D) A rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve
E) Aggregate quantity demanded remains unchanged but the aggregate expenditures curve shifts leftward.
Suppose an appreciation of the French franc causes U.S. prices of French wine imports to rise sharply. On the other hand, Californian wine becomes relatively inexpensive to French consumers. Other things equal, this will result in:
A) an increase in U.S. aggregate expenditures and an increase in the aggregate quantity of U.S. goods and services demanded.
B) a decrease in U.S. aggregate expenditures and a decrease in the aggregate quantity of U.S. goods and services demanded.
C) an increase in U.S. aggregate expenditures and a decrease in the aggregate quantity of U.S. goods and services demanded.
D) no change in either U.S. aggregate expenditures or the aggregate quantity of U.S. goods and services demanded.
E) a decrease in U.S. aggregate expenditures and an increase in the aggregate quantity of U.S. goods and services demanded.
The Keynesian region of the aggregate supply curve is:
A) horizontal.
B) downward-sloping.
C) upward-sloping.
D) vertical.
E) a 45-degree line.
The Keynesian region of the aggregate supply curve explains the situation experienced during the Great Depression. Therefore, we can conclude that the Great Depression was characterized by:
A) high unemployment and low inflation.
B) low unemployment and low inflation.
C) low unemployment and high inflation.
D) high unemployment and high inflation.
E) excess capacity but no unemployment or inflation.
When total planned expenditures are more than real GDP, there will be inventory accumulation.
A) True
B) False
If total planned expenditures exceed real GDP, the economy will contract, causing production of goods and services to decrease and unplanned inventories to rise.
A) True
B) False
When the aggregate expenditures function of a closed economy is plotted against real GDP, any point on the 45-degree line represents C + I + G = Y, where C = Consumption, I = Investment, G = Government spending, and Y = Real GDP.
A) True
B) False
Injections represent outflows of planned expenditures from the real GDP stream.
A) True
B) False
Injections to the economy include consumption, investment, and government spending.
A) True
B) False
Leakages are greater than injections when total planned expenditures exceed real GDP.
A) True
B) False
Other things equal, a reduction in personal income taxes will decrease consumption and will have an expansionary effect on real GDP.
A) True
B) False
Suppose for an economy, investment = $40; saving = $50, government spending + exports = 100; and taxes + imports = $110. Then for this economy, total leakages exceed total injections by $20, so there will be pressure for the economy to contract.
A) True
B) False
The paradox of thrift explains that increased savings by households could actually lower savings for the economy as a whole.
A) True
B) False
A marginal propensity to consume of 0.75 and a marginal propensity to import of 0.05 are associated with an open-economy spending multiplier of 3.33.
A) True
B) False
In general, autonomous spending increases have a lower multiplier effect on real GDP when the economy is open to international trade.
A) True
B) False
If the MPS equals 0.25 and the MPI is 0.15, then an initial change in investment spending of $250 million will result in a total change in equilibrium real GDP of $625 million.
A) True
B) False
Given a constant GDP gap, the higher the spending multiplier, the smaller will be the recessionary gap.
A) True
B) False
The recessionary gap is given by the difference between potential GDP and real GDP.
A) True
B) False
If the spending multiplier equals 6 and equilibrium real GDP is $32 billion below potential real GDP, then total planned expenditures need to decrease by approximately $5.33 billion to close the recessionary gap.
A) True
B) False
Foreign repercussions of changes in domestic imports cause the true domestic spending multiplier to be less than 1/(MPS+MPI)
A) True
B) False
Suppose the multiplier effect for Japan is 0.8 for any $1 billion change in U.S. government purchases. Therefore, Japanese real GDP will rise by $8 billion when U.S. government spending rises by $10 billion.
A) True
B) False
In reality, the simple spending multiplier [1/(MPS+MPI)] is applicable only to countries whose imports are a substantial fraction of income in foreign countries.
A) True
B) False
An increase in U.S. imports from Mexico will cause a decrease in income for Mexican individuals and businesses.
A) True
B) False
If German imports of French products are very important in determining the volume of German exports to France, we would expect the actual German spending multiplier to be larger than 1/(marginal propensity to save +marginal propensity to import).
A) True
B) False
The Keynesian aggregate expenditures model assumes that price level is constant.
A) True
B) False
A change in the price level in an economy will be depicted by a movement along the AE curve and not by a leftward or rightward movement of the curve.
A) True
B) False
Wealth is considered to be a nonincome determinant of consumption.
A) True
B) False
A depreciation of the U.S. dollar will result in an increase in aggregate expenditures in the country.
A) True
B) False
When the price level in an economy falls, the demand for bonds and other nonmonetary financial assets rises.
A) True
B) False
The aggregate demand curve depicts a negative relationship between real GDP and the general price level.
A) True
B) False
Ceteris paribus, a decline in the general price level in the United States will make foreign-produced goods relatively more expensive to U.S. residents and increase the aggregate demand of domestic goods.
A) True
B) False
A decrease in the general price level is associated with an upward shift in the aggregate expenditures function.
A) True
B) False
If the equilibrium level of income is solely a function of aggregate supply, then the aggregate supply curve must be in the Keynesian region.
A) True
B) False
The portion of the aggregate supply curve that is a positive function of the general price level represents excess capacity and unemployed resources.
A) True
B) False
A horizontal aggregate supply curve indicates that equilibrium real GDP is determined by aggregate supply.
A) True
B) False
According to economists, the fixed-price model of macroeconomic equilibrium depicts the modern economy most closely because it assumes that aggregate supply is independent of price.
A) True
B) False
A major drawback of the Keynesian approach to macroeconomic equilibrium is the assumption that the supply of goods and services in the economy always adjusts to aggregate expenditures
A) True
B) False.


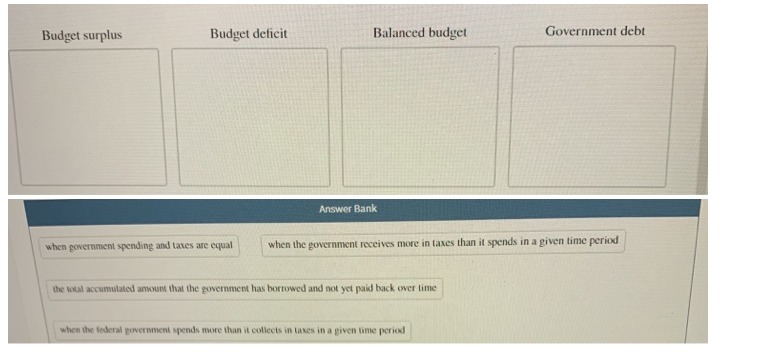
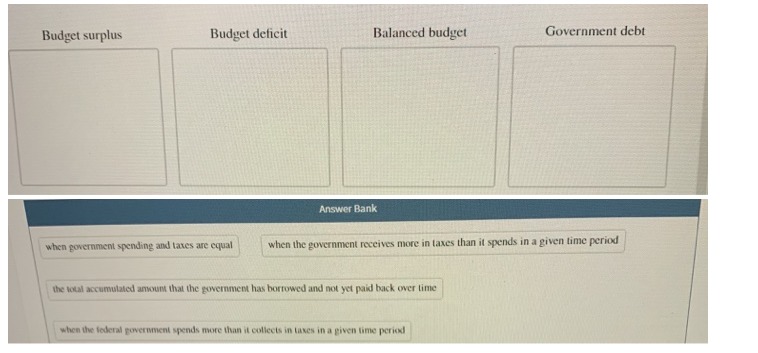
55. Suppose the price level is fixed, the MPC is .5, and the GDP gap is a negative $100 billion To achieve full-employment output (exactly), government should: A, increase government expenditures by $100 billion. B. increase government expenditures by $50 billion. C. reduce taxes by $50 billion. D. reduce taxes by $200 billion. 56. An effective expansionary fiscal policy will: A. reduce a cyclical deficit, but necessarily increase the actual deficit. B. reduce the cyclically-adjusted deficit. C. increase the cyclically-adjusted deficit but reduce the actual deficit. D. always result in a balanced actual budget once full-employment is achieved. 57. The Federal budget deficit is found by: A. subtracting government tax revenues plus government borrowing from government spending in a particular year. B. subtracting government tax revenues from government spending in a particular year. C. cumulative the differences between government spending and tax revenues over all years since the nation's founding. D. subtracting government revenues from the noninvestment-type government spending in a particular year. 58. The amount by which Federal tax revenues exceed Federal government expenditures during a particular year is the: A. Federal reserve. B. budget deficit. C. budget surplus. D. public debt. 59. The crowding-out effect of expansionary fiscal policy suggests that: A. government spending increases at the expense of private investment. B. imports replace domestic production. C. private investment increases at the expense of government spending D. saving increases at the expense of investment. 60. The public debt is the amount of money that: A, state and local governments owe to the Federal government. B. Americans owe to foreigners. C. the Federal government owes to holders of U.S. securities. D. the Federal government owes to taxpayers.If the economy were in a recession and even if the government did not make fiscal policy changes, we would expect government expenditure to be: high and tax revenues to be high, probably leading to a budget deficit. high and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget deficit. O low and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget surplus. O high and tax revenues to be low, probably leading to a budget surplus. QUESTION 2 Which of the following is considered expansionary fiscal policy? The government decreases the income tax rate. The government increases defense spending due to national security concerns. The government increases education subsidies for disadvantaged children to reduce inequality. A state (not federal) government cuts highway spending to balance its budget.Budget surplus Budget deficit Balanced budget Government debt Answer Bank when government spending and taxes are equal when the government receives more in taxes than it spends in a given time period the total accumulated amount that the government has borrowed and not yet paid back over time when the federal poverement spends more than it collects in taxes in a piven time period
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


