Question: Example 2.1.3 Let's calculate the adjacency matrix for the graph from Example 1.7.1 drawn again. below. We consider the vertices in alphabetical order. Since
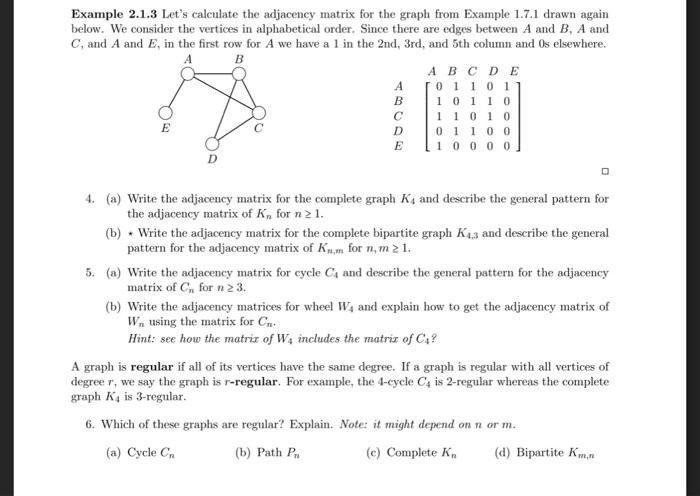
Example 2.1.3 Let's calculate the adjacency matrix for the graph from Example 1.7.1 drawn again. below. We consider the vertices in alphabetical order. Since there are edges between A and B, A and C, and A and E, in the first row for A we have a 1 in the 2nd, 3rd, and 5th column and Os elsewhere. B E D A B C D E ABCDE 011011 101 10 1 10 10 01100 10000 4. (a) Write the adjacency matrix for the complete graph K, and describe the general pattern for the adjacency matrix of K, for n 2 1. (b). Write the adjacency matrix for the complete bipartite graph K3 and describe the general pattern for the adjacency matrix of Km for n. m 2 1. 5. (a) Write the adjacency matrix for cycle C and describe the general pattern for the adjacency matrix of C for n 2 3. (b) Write the adjacency matrices for wheel W, and explain how to get the adjacency matrix of W, using the matrix for Cn. Hint: see how the matrix of W4 includes the matriz of C? A graph is regular if all of its vertices have the same degree. If a graph is regular with all vertices of degree r, we say the graph is r-regular. For example, the 4-cycle C4 is 2-regular whereas the complete graph K4 is 3-regular. 6. Which of these graphs are regular? Explain. Note: it might depend on n or m. (a) Cycle Cn (b) Path P (c) Complete Kn (d) Bipartite Km,n
Step by Step Solution
3.26 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Let G be a graph with n vertices V 1 V 2 V n The adjacency mat... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


