Question: Example: ho =850k(g)/(m^(3)) An incompressible viscous fluid flows between two horizontal parallel plates as shown. The plates are spaced 0.5cm apart and are
Example:\
\\\ ho =850k(g)/(m^(3))\ An incompressible viscous fluid flows between two horizontal parallel plates as shown. The plates are spaced
0.5cmapart and are very wide perpendicular to page. Flow is laminar and velocity profile at any cross section is given by,\
u=-(Y^(2))/(2\\\\mu )((\\\\Delta P)/(L))[1-((y)/(Y))^(2)]\ where
\\\\Delta Pis the pressure change that occurs in length
L. Calculate average mechanical energy loss
h_(1)between the pressure gages. Then show that mechanical energy loss also satisfies the equations\
gh_(l)=(\\\\int_(CV) \\\\mu ((delu)/(dely))^(2)dAA)/((m^())), and ,gh_(l)=Re((L)/(Y))((/bar (V)^(2))/(2))\ where\
Re=(\\\ ho (/bar (V))Y)/(\\\\mu ) 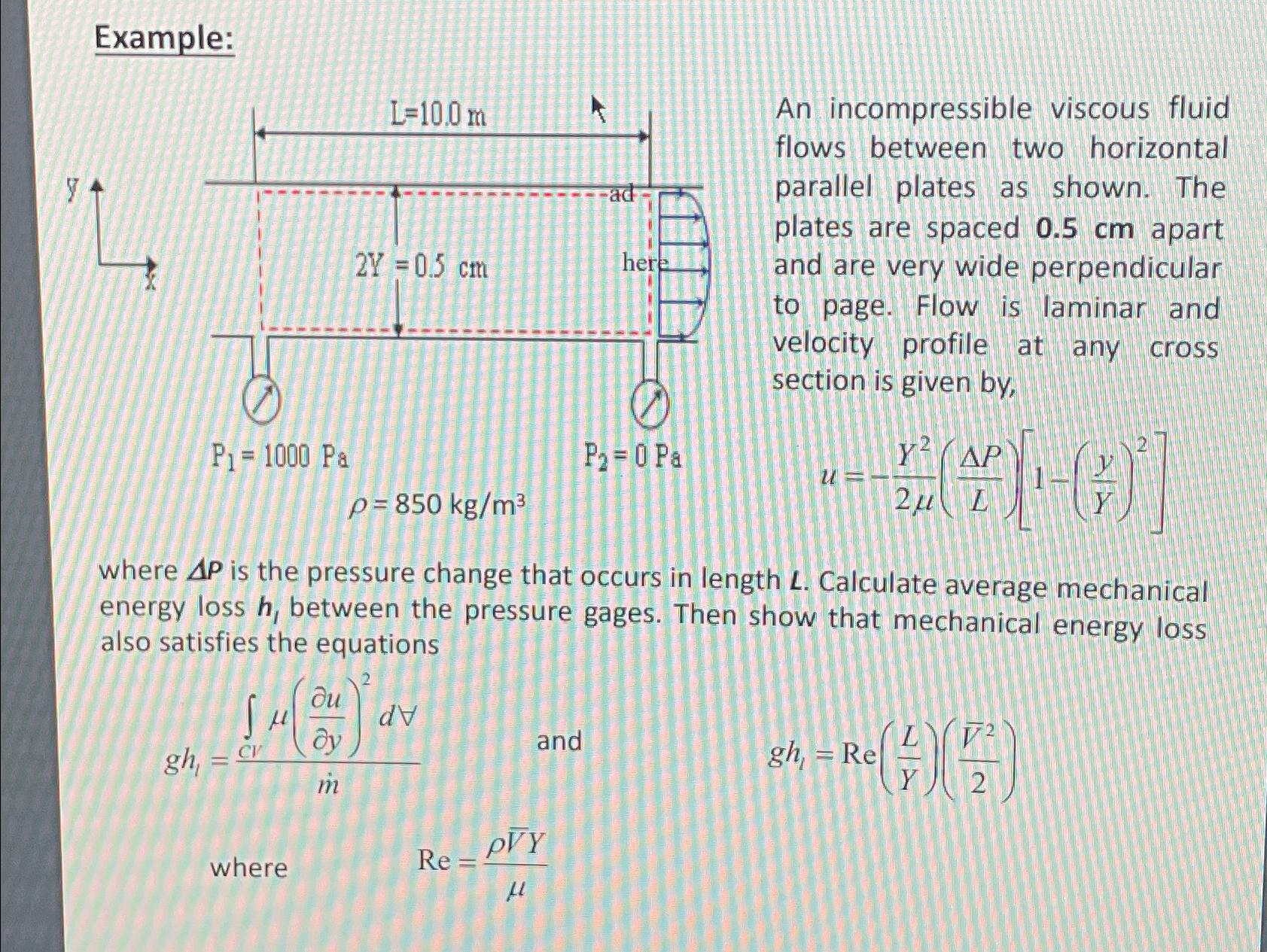
Example: An incompressible viscous fluid flows between two horizontal parallel plates as shown. The plates are spaced 0.5cm apart and are very wide perpendicular to page. Flow is laminar and velocity profile at any cross section is given by, u=2Y2(LP)[1(Yy)2] where P is the pressure change that occurs in length L. Calculate average mechanical energy loss h, between the pressure gages. Then show that mechanical energy loss also satisfies the equations where Re=VY
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


