Question: Example: simulation of a multiserver queuing system Let us simulate one day, from 8 am till 10 pm, of a queuing system that has four
Example: simulation of a multiserver queuing system
Let us simulate one day, from 8 am till 10 pm, of a queuing system that has
four servers; Gamma distributed service times with parameters given in the table,
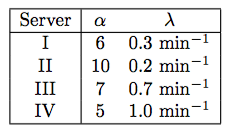
a Poisson process of arrivals with the rate of 1 arrival every 4 min, independent of service times;
random assignment of servers, when more than 1 server is available.
In addition, suppose that after 15 minutes of waiting, jobs withdraw from a queue if their service has not started.
For an ordinary day of work of this system, we are interested to estimate the expected values of:
the total time each server is busy with jobs;
the total number of jobs served by each server;
the average waiting time;
the longest waiting time;
the number of withdrawn jobs;
the number of times a server was available immediately (this is also the number of jobs with no waiting time);
the number of jobs remaining in the system at 10 pm. We start by entering parameters of the system.

Then we initialize variables and start keeping track of arriving jobs. These are empty arrays so far. They get filled with each arriving job.

The queuing system is ready to work! We start a while-loop over the number of arriving jobs. It will run until the end of the day, when arrival time T reaches 14 hours, or 840 minutes. The length of this loop, the total number of arrived jobs, is random.

Generated in accordance with Example 5.10 on p. 108, the arrival time T is obtained by incrementing the previous arrival time by an Exponential interarrival time. Generated within this while-loop, the last job actually arrives after 10 pm. You may either accept it or delete it.
Next, we need to assign the new job j to a server, following the rule of random assignment. There are two cases here: either all servers are busy at the arrival time T , or some servers are available.

The server (u) for the new job (j) is determined. We can now generate its service time S from the suitable Gamma distribution and update our records.

Rewrite this program in Python (or Java), except that on this line " " use library functions to generate a normal distribution.
" use library functions to generate a normal distribution.
Server | I 6 0.3 min-I II 10 0.2 min-1 III 7 0.7 min-1 IV 5 1.0 min-1 Server | I 6 0.3 min-I II 10 0.2 min-1 III 7 0.7 min-1 IV 5 1.0 min-1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


