Question: excel formulas please! Step 3 : Production Cost Forecast Now that you have forecasted the production needs for the year, Highstorm Manufacturing needs you to
excel formulas please!
Step : Production Cost Forecast
Now that you have forecasted the production needs for the year, Highstorm Manufacturing needs you to forecast projected production costs for the year on a monthly basis. These costs should be based on the number of units being manufactured each month rather than the number of units being sold.
Production costs include Raw Materials, Labor, and Manufacturing Overhead. Your production volume forecast can be used to help determine the overall estimated cost of Raw Materials purchases. The purchasing department has recently locked in a contract with your suppliers for all of next year. So you know that each pound of Raw Materials purchased will be $
Variable labor costs per unit manufactured are $unit for Product A and $unit for Product B Variable Manufacturing Overhead costs are estimated to be $ unit for both products. Additionally, fixed labor costs related to production activities are expected to be $ for the year, and fixed overhead costs are projected at $ for the year. These fixed costs are spread across Product A and B
Use this information combined with your forecasted production and purchasing volume to populate Table below and compute a forecast of production costs for Highstorms Manufacturing.
Table Worth up to points B
Septemb
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
begintabularlllll
hline & & & &
hline December & & & &
hline
endtabular
Table Product A Worth up to points
begintabularlllll
hline begintabularll
hline multicolumncbegintabularc
Forecasted Units to Produce
Product A
endtabular & Projected Sales
endtabular & begintabularc
Projected Ending
Inventory
endtabular & begintabularc
Projected Beginning
Inventory
endtabular & Units to Produce
hline January & & & &
hline Febraury & & & &
hline March & & & &
hline April & & & &
hline May & & & &
hline June & & & &
hline July & & & &
hline August & & & &
hline September & & & &
hline October & & & &
hline November & & & &
hline December & & & &
hline
endtabular
Table Product B Worth up to
begintabularlllll
hline multicolumncbegintabularl
Forecasted Units to Produce
ProductA
endtabular & begintabularl
Projected Sales
endtabular & begintabularc
Projected Ending
Inventory
endtabular & begintabularc
Projected Beginning
Inventory
endtabular & multicolumnc Units to Produce
hline January & & & &
hline February & & & &
hline March & & & &
hline April & & & &
hline May & & & &
hline June & & & &
hline July & & & &
hline August & & & &
hline September & & & &
hline October & & & &
hline November & & & &
hline December & & & &
hline
endtabular
Step : Production Cost Forecast
Now that you have forecasted the production needs for the year, Highstorm Manufacturing needs you to forecast projected production costs for the year on a monthly basis. These costs should be based on the number of units being manufactured each month rather than the number of units being sold.
Production costs include Raw Materials, Labor, and Manufacturing Overhead. Your production volume forecast can be used to help determine the overall estimated cost of Raw Materials purchases. The purchasing department has recently locked in a contract with your suppliers for all of
Project Overview
Project Inputs
F Accessibility: Investigate
Step : Forecast Production Volume
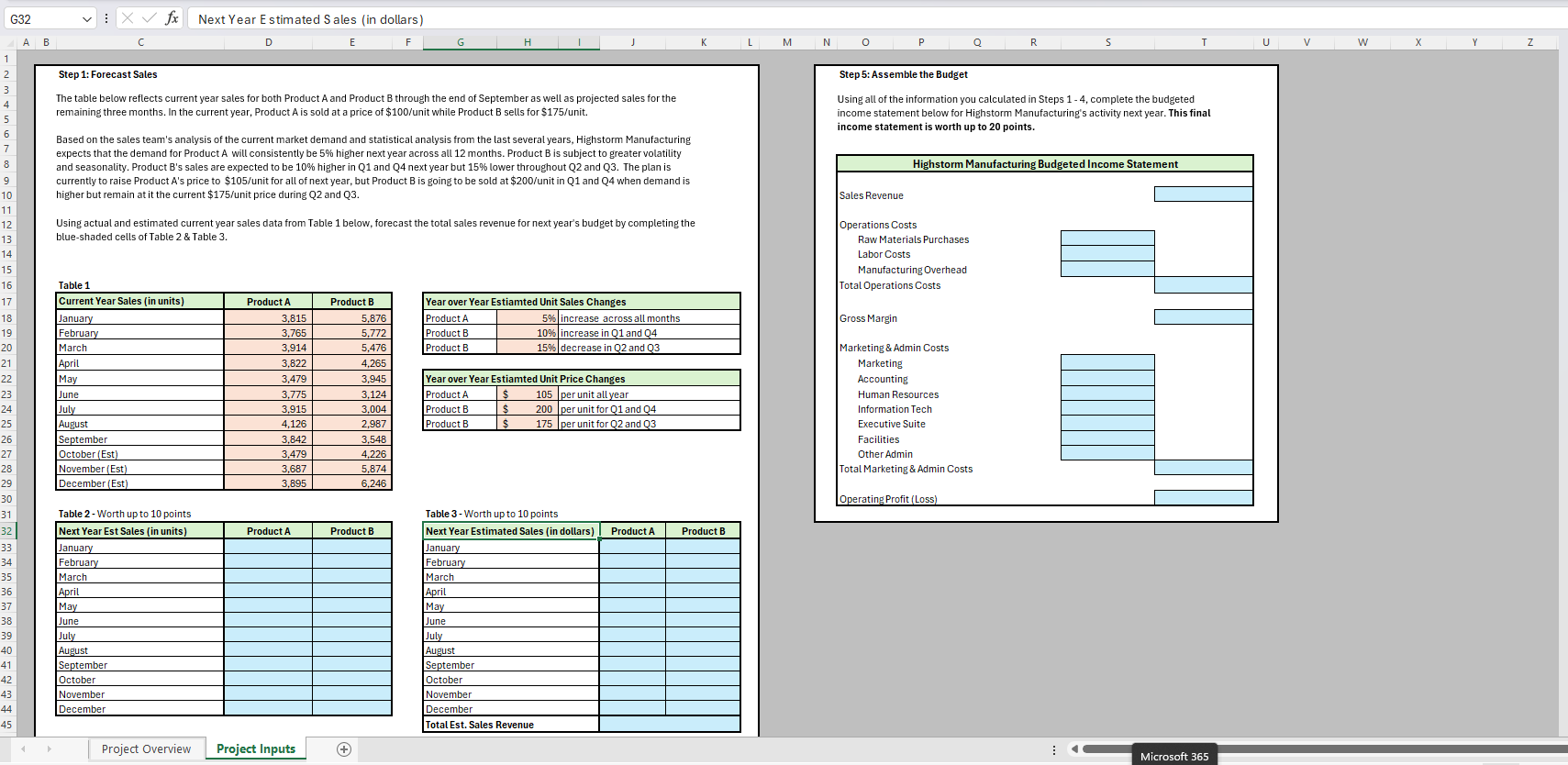
Using the forecasted sales you've calculated for next year, Highstorm Manufacturing needs you to forecast their production unit volume on a monthly basis for both Product A and Product B next year. In Table below, you have been provided the projected year end Materials and Finished Goods inventory at the end of this year for both Product A and Product B
Product A and B both use the same raw materials. Product A uses lbs of Raw Materials and Product B uses lbs of raw materials per unit.
The company would also like to adopt a policy beginning next year where Materials inventory at the end of each month is equal to of the anticipated needs for the following two months while Finished Goods inventory at the end of each month should be kept at of the anticipated unit sales for the following two months.
Since the company currently has no estimated for January or February sales two years from now, ending Materials inventory for those two months should be targeted as of next year's projected November & December needs, while Finished Goods Inventory should be targeted as of projected November and December's anticipated sales.
Using this information, use Tables & below to forecast Highstorm Manufacturing's monthly materials purchases and production volume for Product A and Product B Assume all units produced are started and completed in the same month No WIP inventory
Table
Table Worth up to points
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


