Question: execute the scripts within your Oracle environment by executing them in this order: midterm.sql, midterm-data.sql, insert-words.sql, insert-counts.sql. These scripts create and populate four tables (shown
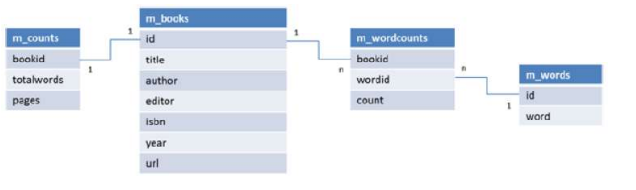
execute the scripts within your Oracle environment by executing them in this order: midterm.sql, midterm-data.sql, insert-words.sql, insert-counts.sql. These scripts create and populate four tables (shown in the database diagram below), i.e., m_books, m_counts, m_wordcounts, and m_words. The m_wordcounts table represents a many-to-many relationship between m_books and m_words, meaning that a given word in the m_words table may appear one or more times (as indicated by the m_wordcounts.count field) in one or more books.
General SQL Queries Write SQL queries to answer the questions below. Note that your SQL code should be as general-purpose as possible (i.e., assume that the sample tables could have many more rows than what has been provided). 1. How many unique words are there across all books? Note that to be unique, a word must only appear once. 2. How many unique words are there per book? Design your query to display the results ordered alphabetically by book title.
3. What are the top eight most frequently occurring words across all books? Design your query to display the results in order starting from the most frequently occurring word. 4. How many unique words are there per author? How many unique words are there per editor? Design your query to combine the above results and display the results ordered alphabetically by author/editor name. 5. What is the percentage of word counts to total unique words per book? For example, if a word occurs 47 times in a work that contains 4700 unique words, the percentage for this word is 1%.
SQL Queries to Handle Stopwords A "stopword" is a word that search engines often ignore. Typical stopwords include: the; of; and; to; or; not; that; there; and so on. From question 3 above, you probably found a lot of these stopwords. In this section, we will work further with stopwords to improve the query results of question 3. Write SQL creation scripts and queries as specified below. As above, your SQL code should be as general-purpose as possible. 6. Write a creation script for a new table called m_stopwords that has a unique id field and a foreign key wordid field that references the m_words table. 7. Write a single SQL query that inserts rows into the (assumed-to-be-empty) m_stopwords table by selecting the top 20 most frequently occurring words across all books. 8. Taking stopwords from the m_stopwords table into account, write an SQL query that selects the top 20 most frequently occurring words across all books, i.e., ignore stopwords. Be sure you do not delete or change any of the existing tables or their data (i.e, do not simply delete stopwords from m_wordcounts).
Oracle PL/SQL Functions and Procedures Write PL/SQL functions and procedures as specified below. 9. Create a PL/SQL function called generatePassword() that generates (and returns) a random password based on the words data. Generated passwords have the following general format:
m_counts bookid totalwords pages m_books id title author editor isbn m_wordcounts bookid wordid count m_words id word year url
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


