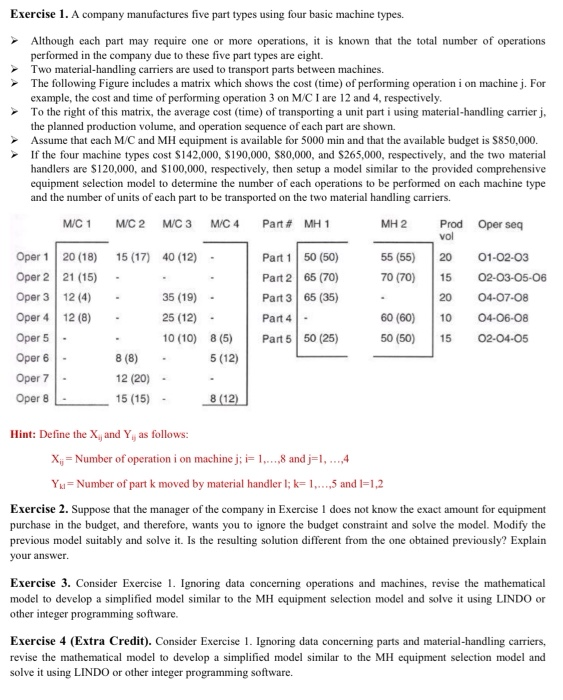
Question: Exercise 1. A company manufactures five part types using four basic machine types. Although each part may require one or more operations, it is known
Exercise 1. A company manufactures five part types using four basic machine types. Although each part may require one or more operations, it is known that the total number of operations performed in the company due to these five part types are eight. Two material handling carriers are used to transport parts between machines. The following Figure includes a matrix which shows the cost (time) of performing operation i on machine j. For example, the cost and time of performing operation 3 on M/C I are 12 and 4, respectively. To the right of this matrix, the average cost (time) of transporting a unit part i using material handling carrier j, the planned production volume, and operation sequence of each part are shown. Assume that each M/C and MH equipment is available for 5000 min and that the available budget is $850,000. If the four machine types cost $142,000, $190,000, 580,000, and $265,000, respectively, and the two material handlers are $120,000, and $100,000, respectively, then setup a model similar to the provided comprehensive equipment selection model to determine the number of each operations to be performed on each machine type and the number of units of each part to be transported on the two material handling carriers. MC 1 MC2 MC 4 Part # MH 1 MH 2 Prod Oper seg M/C 3 vol 20 01-02-03 55 (55) 70 (70) 15 02-03-05-06 Part 150 (50) Part 265 (70) Part 365 (35) Part 4 - Part 550 (25) 20 60 (60) Oper 1 20 (18) 15 (17) 40 (12) Oper 221 (15) Oper 3 12 (4) 35 (19) Oper 4 12 (8) 25 (12) Oper 5 10 (10) 8 (5) Oper 6 8 (8) 5 (12) Oper 7 12 (20) Oper 8 15 (15) 8 (12) 10 04-07-08 04-06-08 02-04-05 50 (50) 15 Hint: Define the X, and Y, as follows: X;= Number of operation i on machine j; i= 1,...,8 and j=1,...,4 Yu= Number of part k moved by material handler l; k= 1,...,5 and 1=1,2 Exercise 2. Suppose that the manager of the company in Exercise I does not know the exact amount for equipment purchase in the budget, and therefore, wants you to ignore the budget constraint and solve the model. Modify the previous model suitably and solve it. Is the resulting solution different from the one obtained previously? Explain your answer. Exercise 3. Consider Exercise 1. Ignoring data concerning operations and machines, revise the mathematical model to develop a simplified model similar to the MH equipment selection model and solve it using LINDO or other integer programming software. Exercise 4 (Extra Credit). Consider Exercise 1. Ignoring data concerning parts and material-handling carriers, revise the mathematical model to develop a simplified model similar to the MH equipment selection model and solve it using LINDO or other integer programming software. Bull doesn't NEED MORE INFO Exercise 1. A company manufactures five part types using four basic machine types. Although each part may require one or more operations, it is known that the total number of operations performed in the company due to these five part types are eight. Two material handling carriers are used to transport parts between machines. The following Figure includes a matrix which shows the cost (time) of performing operation i on machine j. For example, the cost and time of performing operation 3 on M/C I are 12 and 4, respectively. To the right of this matrix, the average cost (time) of transporting a unit part i using material handling carrier j, the planned production volume, and operation sequence of each part are shown. Assume that each M/C and MH equipment is available for 5000 min and that the available budget is $850,000. If the four machine types cost $142,000, $190,000, 580,000, and $265,000, respectively, and the two material handlers are $120,000, and $100,000, respectively, then setup a model similar to the provided comprehensive equipment selection model to determine the number of each operations to be performed on each machine type and the number of units of each part to be transported on the two material handling carriers. MC 1 MC2 MC 4 Part # MH 1 MH 2 Prod Oper seg M/C 3 vol 20 01-02-03 55 (55) 70 (70) 15 02-03-05-06 Part 150 (50) Part 265 (70) Part 365 (35) Part 4 - Part 550 (25) 20 60 (60) Oper 1 20 (18) 15 (17) 40 (12) Oper 221 (15) Oper 3 12 (4) 35 (19) Oper 4 12 (8) 25 (12) Oper 5 10 (10) 8 (5) Oper 6 8 (8) 5 (12) Oper 7 12 (20) Oper 8 15 (15) 8 (12) 10 04-07-08 04-06-08 02-04-05 50 (50) 15 Hint: Define the X, and Y, as follows: X;= Number of operation i on machine j; i= 1,...,8 and j=1,...,4 Yu= Number of part k moved by material handler l; k= 1,...,5 and 1=1,2 Exercise 2. Suppose that the manager of the company in Exercise I does not know the exact amount for equipment purchase in the budget, and therefore, wants you to ignore the budget constraint and solve the model. Modify the previous model suitably and solve it. Is the resulting solution different from the one obtained previously? Explain your answer. Exercise 3. Consider Exercise 1. Ignoring data concerning operations and machines, revise the mathematical model to develop a simplified model similar to the MH equipment selection model and solve it using LINDO or other integer programming software. Exercise 4 (Extra Credit). Consider Exercise 1. Ignoring data concerning parts and material-handling carriers, revise the mathematical model to develop a simplified model similar to the MH equipment selection model and solve it using LINDO or other integer programming software. Bull doesn't NEED MORE INFO