Question: Exercise 1: The Fibonacci numbers are defined as the sequence whose first two terms are equal to 1 and for which each subsequent term is


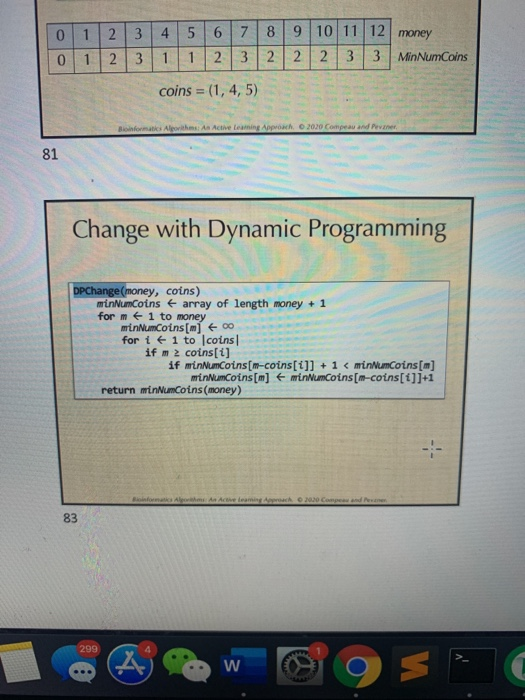

Exercise 1: The Fibonacci numbers are defined as the sequence whose first two terms are equal to 1 and for which each subsequent term is equal to the sum of the previous two terms; that is, the sequence (1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, ...). Explain why a recursive approach for computing the n-th Fibonacci number will be inefficient. Exercise 3: As money grows, the size of the array required by DPChange grows as well. Explain how this algorithm can be modified to still compute MinNumCoins(money, coins) while the array size required does not exceed the size of the largest coin denomination. 10 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 1 2 3 2 coins = (1,4,5) 9 10 11 12 2 2 3 3 money MinNumCoins Algorithms: An Active Learning Approach 2020 Compean and Change with Dynamic Programming DPChange (money, coins) minNumCoins array of length money + for me 1 to money minNumCoins[m] 00 - for it 1 to coins if m 2 coins[i] if minNumCoins[m-coins[i]] + 1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


