Question: Exercise 11.9 - Fig. 50 shows a half-wave rectifier circuit. This circuit converts an alternating current voltage source u(t) into an approximately constant voltage source.
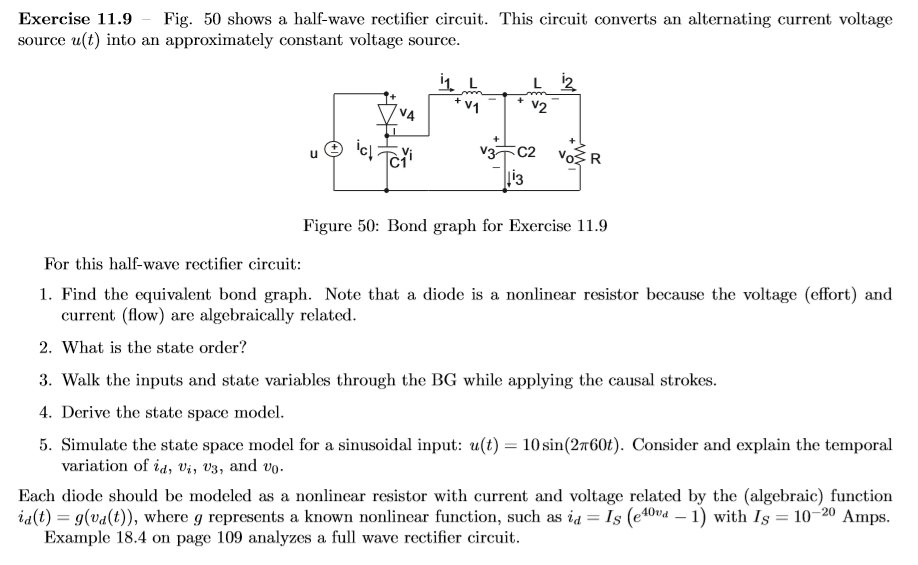
Exercise 11.9 - Fig. 50 shows a half-wave rectifier circuit. This circuit converts an alternating current voltage source u(t) into an approximately constant voltage source. u letei V302 VOER Figure 50: Bond graph for Exercise 11.9 For this half-wave rectifier circuit: 1. Find the equivalent bond graph. Note that a diode is a nonlinear resistor because the voltage (effort) and current (flow) are algebraically related. 2. What is the state order? 3. Walk the inputs and state variables through the BG while applying the causal strokes. 4. Derive the state space model. 5. Simulate the state space model for a sinusoidal input: u(t) = 10 sin(260t). Consider and explain the temporal variation of id, Vi, U3, and vo. Each diode should be modeled as a nonlinear resistor with current and voltage related by the (algebraic) function id(t) = g(va(t)), where g represents a known nonlinear function, such as id = Is (e40vd 1) with Is = 10-20 Amps. Example 18.4 on page 109 analyzes a full wave rectifier circuit. Exercise 11.9 - Fig. 50 shows a half-wave rectifier circuit. This circuit converts an alternating current voltage source u(t) into an approximately constant voltage source. u letei V302 VOER Figure 50: Bond graph for Exercise 11.9 For this half-wave rectifier circuit: 1. Find the equivalent bond graph. Note that a diode is a nonlinear resistor because the voltage (effort) and current (flow) are algebraically related. 2. What is the state order? 3. Walk the inputs and state variables through the BG while applying the causal strokes. 4. Derive the state space model. 5. Simulate the state space model for a sinusoidal input: u(t) = 10 sin(260t). Consider and explain the temporal variation of id, Vi, U3, and vo. Each diode should be modeled as a nonlinear resistor with current and voltage related by the (algebraic) function id(t) = g(va(t)), where g represents a known nonlinear function, such as id = Is (e40vd 1) with Is = 10-20 Amps. Example 18.4 on page 109 analyzes a full wave rectifier circuit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


