Question: Exercise 15-19 (Algorithmic) (LU. 3, 4) Henry, a freelance driver, finds customers using various platforms such as Uber and Grubhub. He is single and has
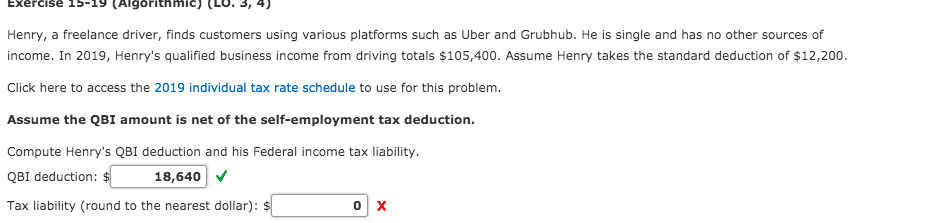
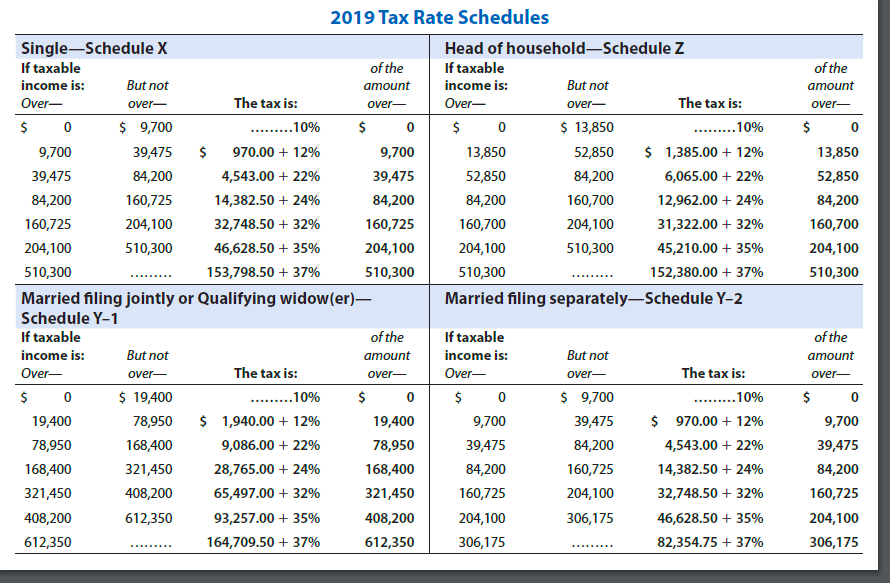
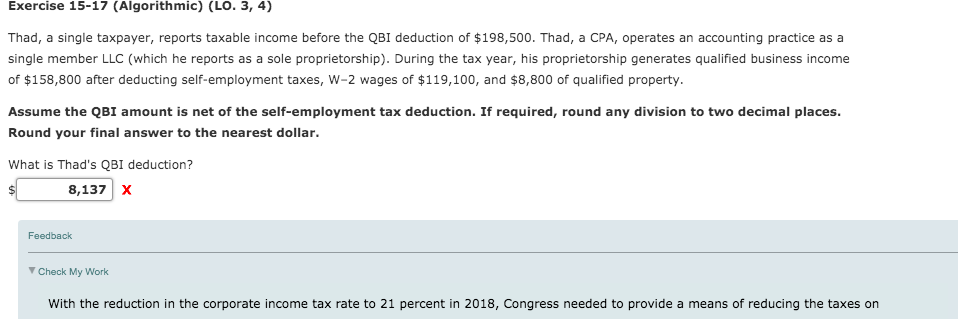
Exercise 15-19 (Algorithmic) (LU. 3, 4) Henry, a freelance driver, finds customers using various platforms such as Uber and Grubhub. He is single and has no other sources of income. In 2019, Henry's qualified business income from driving totals $105,400. Assume Henry takes the standard deduction of $12,200. Click here to access the 2019 individual tax rate schedule to use for this problem. Assume the QBI amount is net of the self-employment tax deduction. Compute Henry's QBI deduction and his Federal income tax liability. QBI deduction: $ 18,640 Tax liability (round to the nearest dollar): $ of the amount over- 0 13,850 52,850 84,200 160,700 204,100 510,300 2019 Tax Rate Schedules Single-Schedule X Head of householdSchedule Z If taxable of the If taxable income is: But not amount income is: But not Over- over- The tax is: over Over- over- The tax is: $ 0 $ 9,700 ......... 10% 0 $ 0 $ 13,850 ......... 10% 9,700 39,475 $ 970.00 + 12% 9,700 13,850 52,850 $ 1,385.00 + 12% 39,475 84,200 4 ,543.00 + 22% 39,475 52,850 84,200 6,065.00 + 22% 84,200 160,725 14,382.50 + 24% 84,200 84,200 160,700 12,962.00 + 24% 160,725 204,100 32,748.50 + 32% 160,725 160,700 204,100 31,322.00 + 32% 204,100 510,300 46,628.50 + 35% 204,100 204,100 510,300 45,210.00 + 35% 510,300 ......... 153,798.50 + 37% 510,300 510,300 ......... 152,380.00 + 37% Married filing jointly or Qualifying widow(er) Married filing separatelySchedule Y-2 Schedule Y-1 If taxable of the If taxable income is: But not amount income is: But not Over- over- The tax is: over Over- over- The tax is: $ 0 $ 19,400 ......... 10% $ 0 $ 0 $ 9,700 .........10% 19,400 78,950 $ 1,940.00 + 12% 19,400 9,700 39,475 $ 970.00 + 12% 78,950 168,400 9,086.00 + 22% 78,950 39,475 84,200 4,543.00 + 22% 168,400 321,450 28,765.00 + 24% 168,400 84,200 160,725 14,382.50 +24% 321,450 408,200 65,497.00 + 32% 321,450 160,725 204,100 32,748.50 + 32% 408,200 612,350 93,257.00 + 35% 408,200 204,100 306,175 46,628.50 + 35% 612,350 164,709.50 + 37% 612,350 306,175 82,354.75 + 37% of the amount over- $ 0 9,700 39,475 84,200 160,725 204,100 306,175 Exercise 15-17 (Algorithmic) (LO. 3, 4) Thad, a single taxpayer, reports taxable income before the QBI deduction of $198,500. Thad, a CPA, operates an accounting practice as a single member LLC (which he reports as a sole proprietorship). During the tax year, his proprietorship generates qualified business income of $158,800 after deducting self-employment taxes, W-2 wages of $119,100, and $8,800 of qualified property. Assume the QBI amount is net of the self-employment tax deduction. If required, round any division to two decimal places. Round your final answer to the nearest dollar. What is Thad's QBI deduction? $ 8,137 X Feedback Check My Work With the reduction in the corporate income tax rate to 21 percent in 2018, Congress needed to provide a means of reducing the taxes on
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


