Question: Exercise 2 . 5 6 . ( * * * * * * * * * ) The definite integral of a function f ,
Exercise
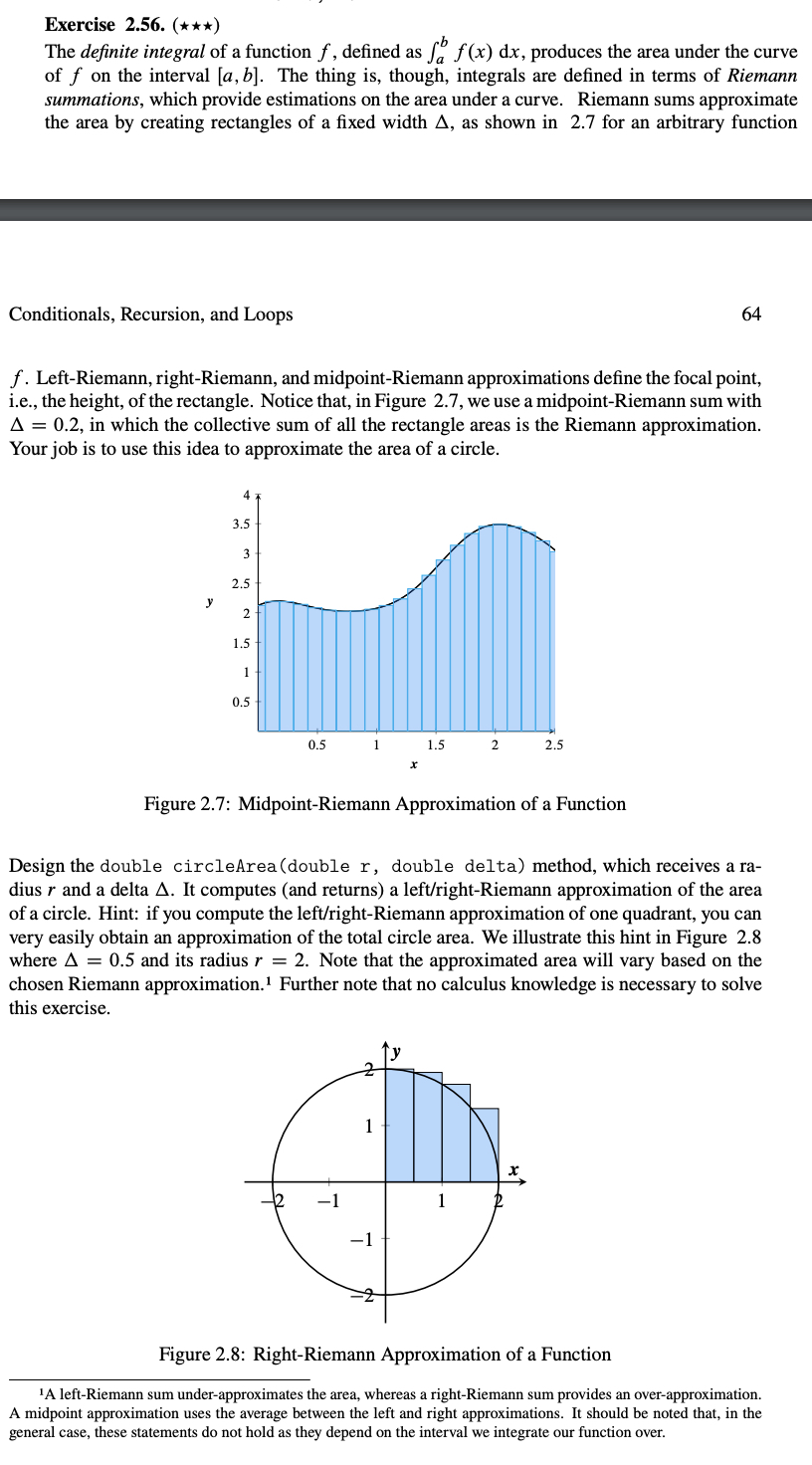
The definite integral of a function defined as produces the area under the curve of on the interval The thing is though, integrals are defined in terms of Riemann summations, which provide estimations on the area under a curve. Riemann sums approximate the area by creating rectangles of a fixed width as shown in for an arbitrary function
Conditionals, Recursion, and Loops
LeftRiemann, rightRiemann, and midpointRiemann approximations define the focal point, ie the height, of the rectangle. Notice that, in Figure we use a midpointRiemann sum with in which the collective sum of all the rectangle areas is the Riemann approximation. Your job is to use this idea to approximate the area of a circle.
Figure : MidpointRiemann Approximation of a Function
Design the double circleAreadouble double delta method, which receives a radius and a delta It computes and returns a leftrightRiemann approximation of the area of a circle. Hint: if you compute the leftrightRiemann approximation of one quadrant, you can very easily obtain an approximation of the total circle area. We illustrate this hint in Figure where and its radius Note that the approximated area will vary based on the chosen Riemann approximation. Further note that no calculus knowledge is necessary to solve this exercise.
Figure : RightRiemann Approximation of a Function
A leftRiemann sum underapproximates the area, whereas a rightRiemann sum provides an overapproximation. A midpoint approximation uses the average between the left and right approximations. It should be noted that, in the general case, these statements do not hold as they depend on the interval we integrate our function over.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


