Question: Exercise 4-17 (Static) Using activity-based costing to allocate overhead, compute product cost and gross profit LO P3 Ice Cool produces two different models of air
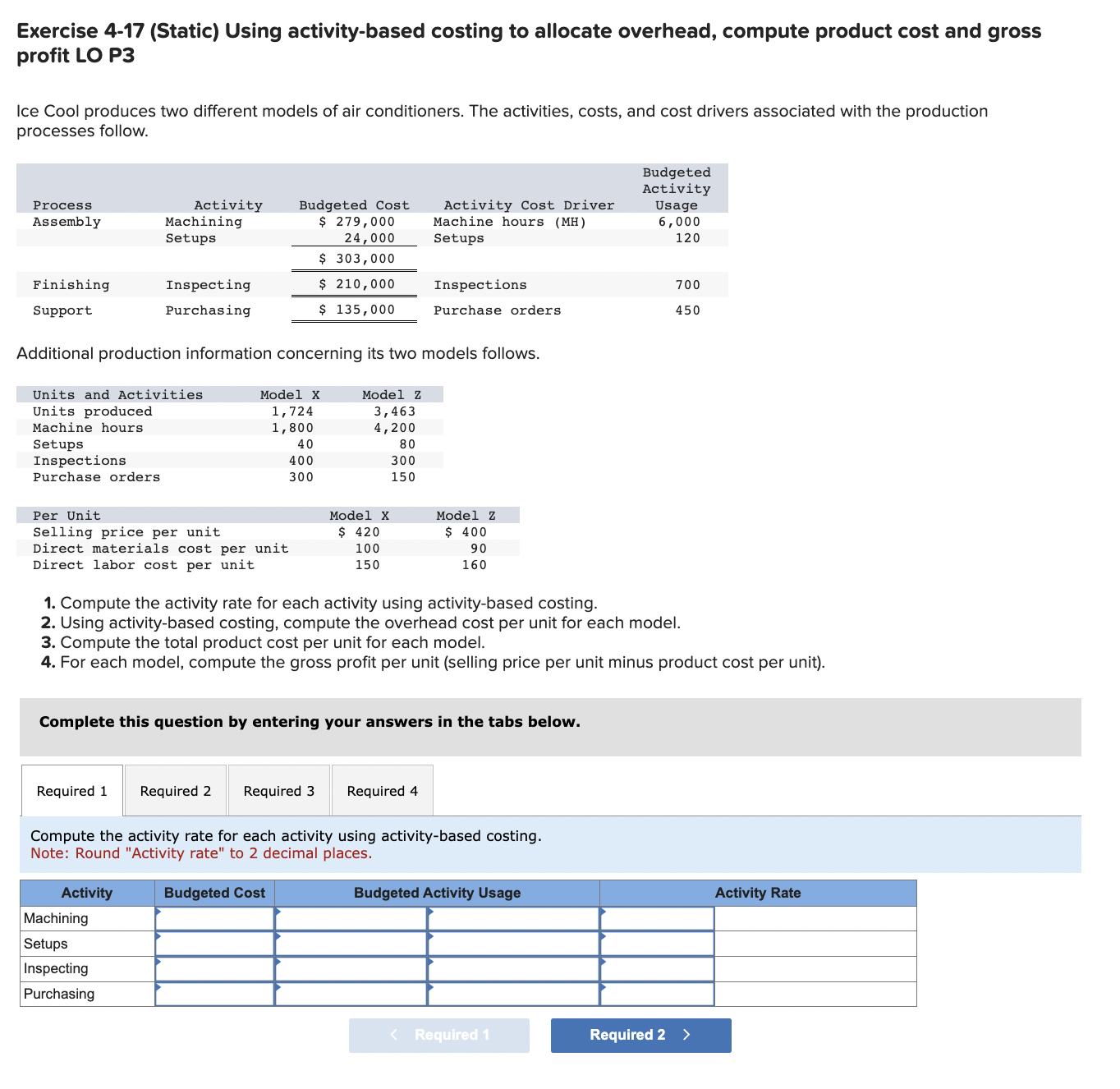
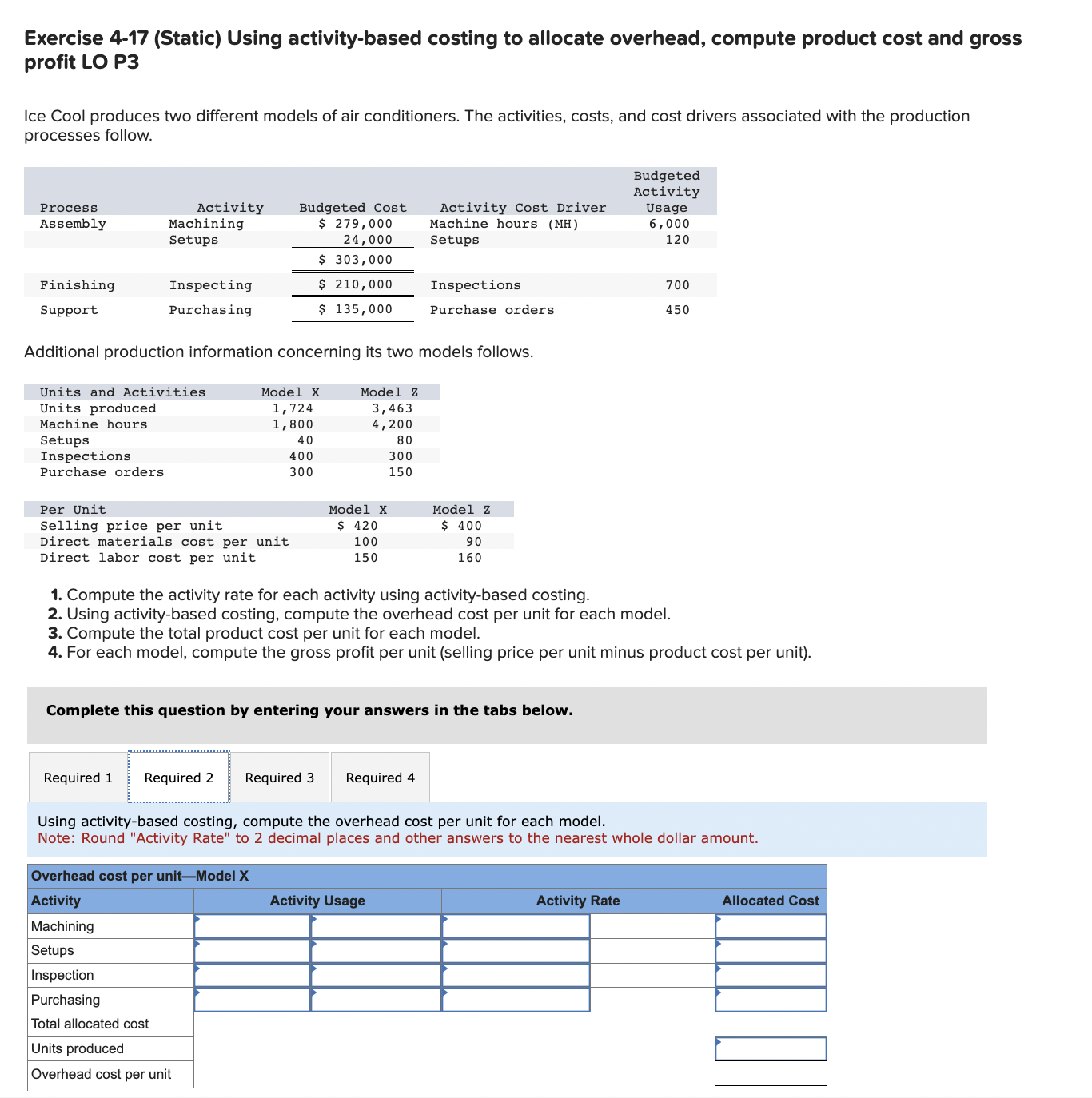
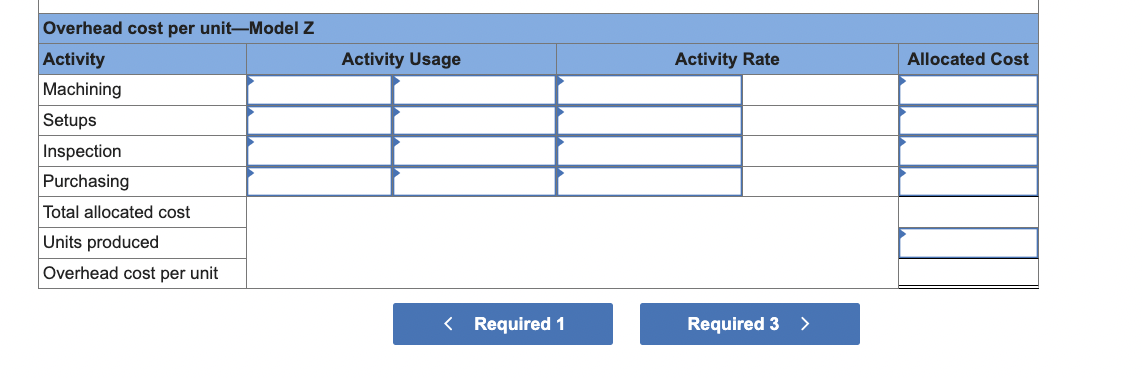
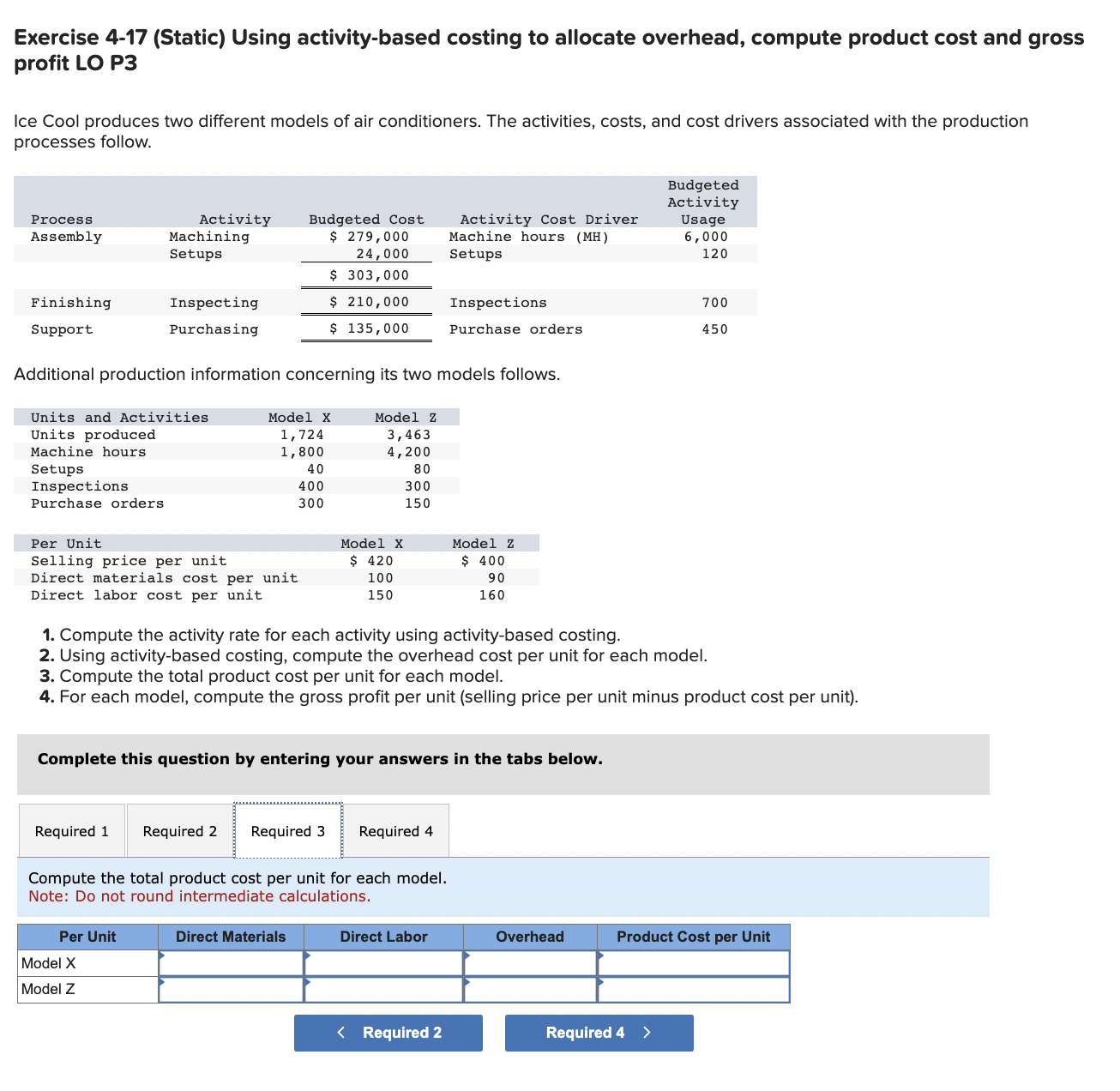
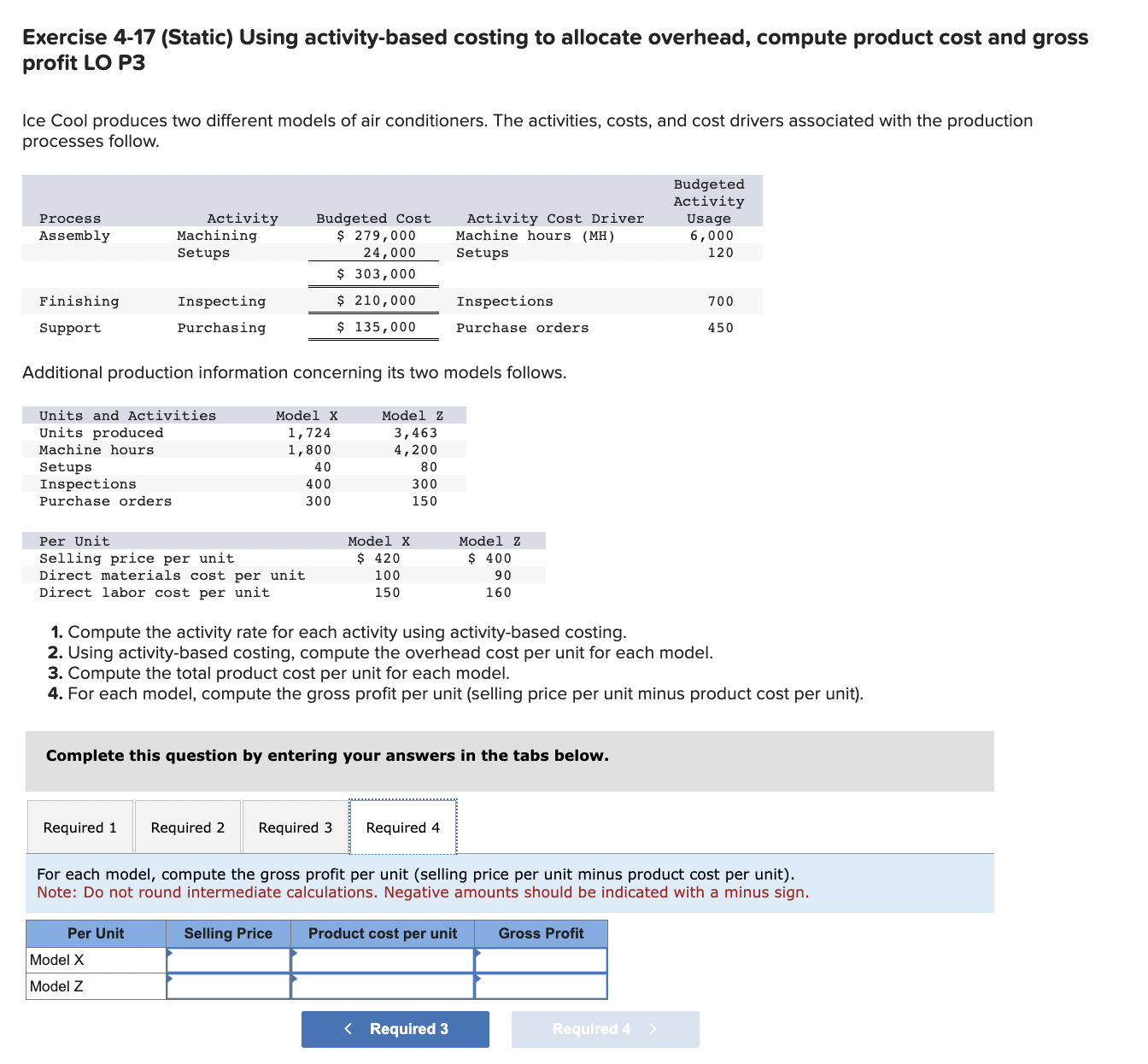
Exercise 4-17 (Static) Using activity-based costing to allocate overhead, compute product cost and gross profit LO P3 Ice Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The activities, costs, and cost drivers associated with the production processes follow. Additional production information concerning its two models follows. 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing. 2. Using activity-based costing, compute the overhead cost per unit for each model. 3. Compute the total product cost per unit for each model. 4. For each model, compute the gross profit per unit (selling price per unit minus product cost per unit). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing. Note: Round "Activity rate" to 2 decimal places. Exercise 4-17 (Static) Using activity-based costing to allocate overhead, compute product cost and gross profit LO P3 Ice Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The activities, costs, and cost drivers associated with the production processes follow. Additional production information concerning its two models follows. 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing. 2. Using activity-based costing, compute the overhead cost per unit for each model. 3. Compute the total product cost per unit for each model. 4. For each model, compute the gross profit per unit (selling price per unit minus product cost per unit). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using activity-based costing, compute the overhead cost per unit for each model. Note: Round "Activity Rate" to 2 decimal places and other answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. Required 1 Required 3> Exercise 4-17 (Static) Using activity-based costing to allocate overhead, compute product cost and gross profit LO P3 Ice Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The activities, costs, and cost drivers associated with the production processes follow. Additional production information concerning its two models follows. 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing. 2. Using activity-based costing, compute the overhead cost per unit for each model. 3. Compute the total product cost per unit for each model. 4. For each model, compute the gross profit per unit (selling price per unit minus product cost per unit). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the total product cost per unit for each model. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Exercise 4-17 (Static) Using activity-based costing to allocate overhead, compute product cost and gross profit LO P3 Ice Cool produces two different models of air conditioners. The activities, costs, and cost drivers associated with the production processes follow. Additional production information concerning its two models follows. 1. Compute the activity rate for each activity using activity-based costing. 2. Using activity-based costing, compute the overhead cost per unit for each model. 3. Compute the total product cost per unit for each model. 4. For each model, compute the gross profit per unit (selling price per unit minus product cost per unit). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. For each model, compute the gross profit per unit (selling price per unit minus product cost per unit). Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Negative amounts should be indicated with a minus sign
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


