Question: Exercise 5 . 2 A three - dof spatial robot arm is shown in the figure below. The robot has three revolute joints that allow
Exercise
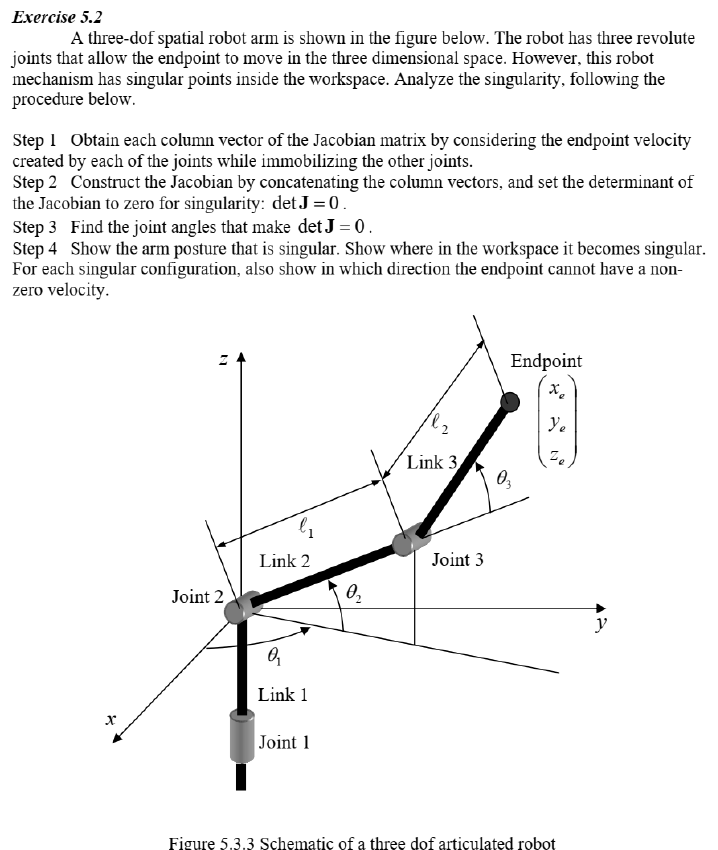
A threedof spatial robot arm is shown in the figure below. The robot has three revolute joints that allow the endpoint to move in the three dimensional space. However, this robot mechanism has singular points inside the workspace. Analyze the singularity following the procedure below.
Step I Obtain each column vector of the Jacobian matrix by considering the endpoint velocity created by each of the joints while immobilizing the other joints.
Step Construct the Jacobian by concatenating the column vectors, and set the determinant of the Jacobian to zero for singularity: operatornamedetmathbfJ
Step Find the joint angles that make operatornamedetmathbfJ
Step Show the arm posture that is singular. Show where in the workspace it becomes singular. For each singular configuration, also show in which direction the endpoint cannot have a nonzero velocity.
Figure Schematic of a three dof articulated robot
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


