Question: Exercise 6 : Rigid body buckling When finding the critical load ( buckling load ) of a rigid member, we have to imagine that the
Exercise : Rigid body buckling
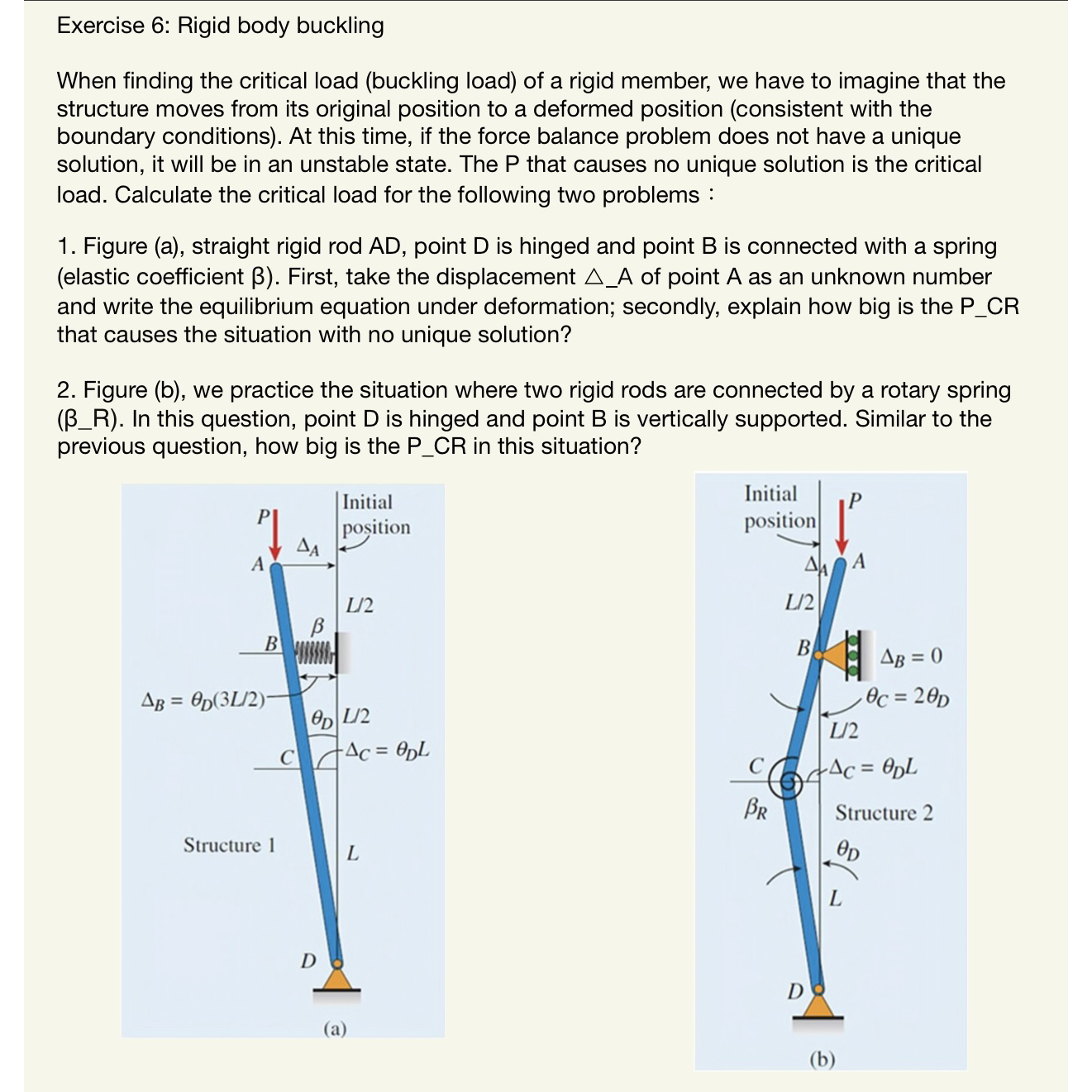
When finding the critical load buckling load of a rigid member, we have to imagine that the structure moves from its original position to a deformed position consistent with the boundary conditions At this time, if the force balance problem does not have a unique solution, it will be in an unstable state. The that causes no unique solution is the critical load. Calculate the critical load for the following two problems :
Figure a straight rigid rod point is hinged and point is connected with a spring elastic coefficient First, take the displacement of point as an unknown number and write the equilibrium equation under deformation; secondly explain how big is the PCR that causes the situation with no unique solution?
Figure b we practice the situation where two rigid rods are connected by a rotary spring In this question, point is hinged and point is vertically supported. Similar to the previous question, how big is the PCR in this situation?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


