Question: Exercise 6-25 Your answer is partially correct. Try again. Concord Construction Consultants performs cement core tests in its Greenville laboratory. The following standard costs for
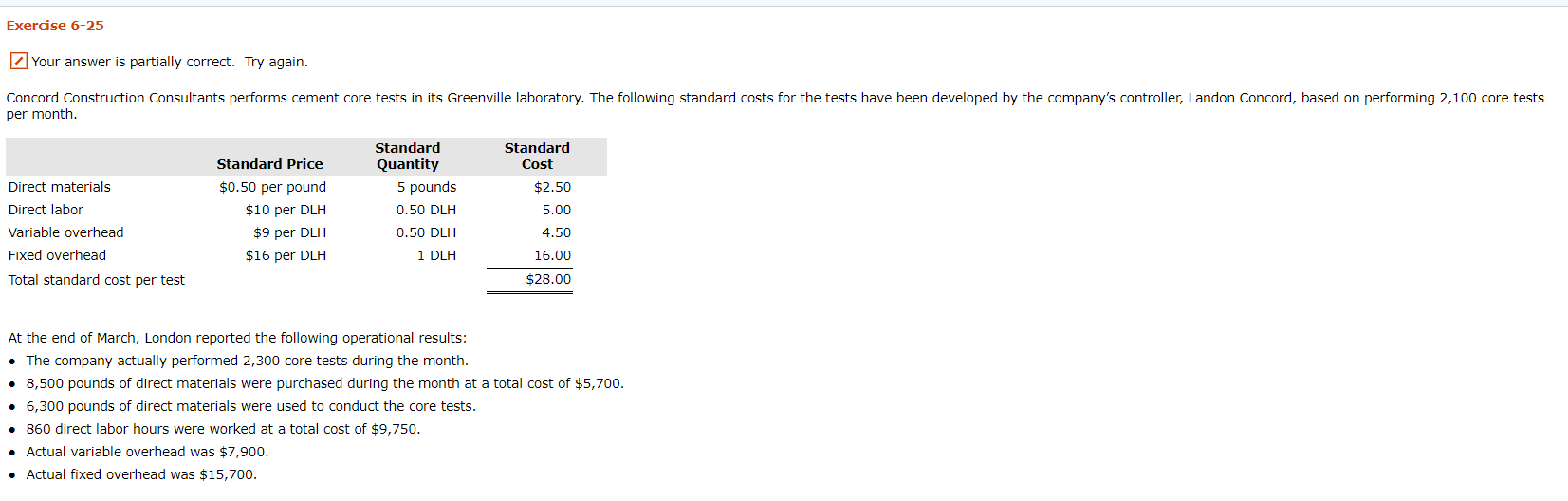
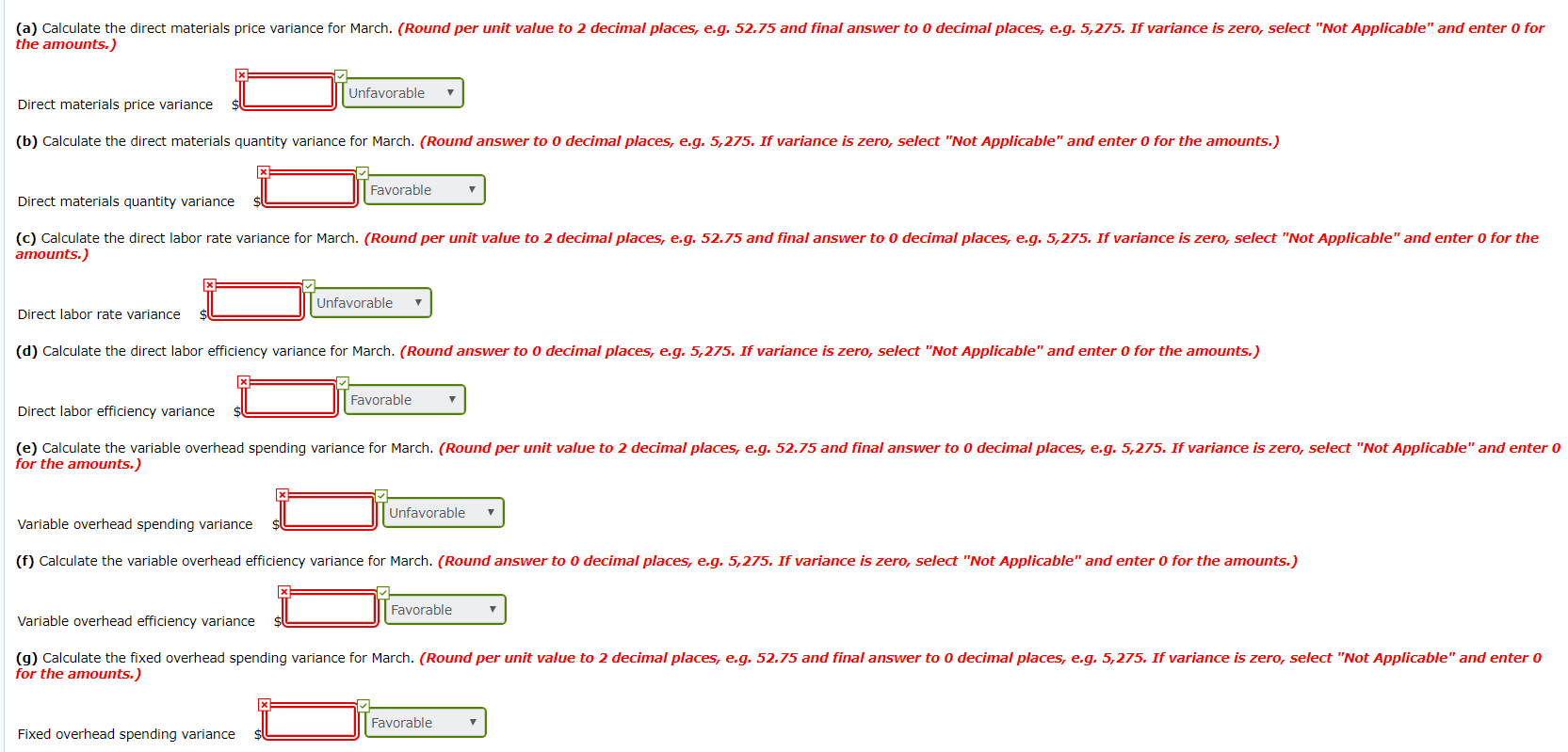
Exercise 6-25 Your answer is partially correct. Try again. Concord Construction Consultants performs cement core tests in its Greenville laboratory. The following standard costs for the tests have been developed by the company's controller, Landon Concord, based on performing 2,100 core tests per month. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Total standard cost per test Standard Price $0.50 per pound $10 per DLH $9 per DLH $16 per DLH Standard Quantity 5 pounds 0.50 DLH 0.50 DLH 1 DLH Standard Cost $2.50 5.00 4.50 16.00 $28.00 At the end of March, London reported the following operational results: The company actually performed 2,300 core tests during the month. 8,500 pounds of direct materials were purchased during the month at a total cost of $5,700. 6,300 pounds of direct materials were used to conduct the core tests. 860 direct labor hours were worked at a total cost of $9,750. Actual variable overhead was $7,900. Actual fixed overhead was $15,700. (a) Calculate the direct materials price variance for March. (Round per unit value to 2 decimal places, e.g. 52.75 and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter o for the amounts.) Unfavorable Direct materials price variance (b) Calculate the direct materials quantity variance for March. (Round answer to o decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter o for the amounts.) Favorable Direct materials quantity variance (c) Calculate the direct labor rate variance for March. (Round per unit value to 2 decimal places, e.g. 52.75 and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter o for the amounts.) Unfavorable Direct labor rate variance (d) Calculate the direct labor efficiency variance for March. (Round answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter o for the amounts.) Favorable Direct labor efficiency variance (e) Calculate the variable overhead spending variance for March. (Round per unit value to 2 decimal places, e.g. 52.75 and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter 0 for the amounts.) e J u Unfavorable ntavorable Variable overhead spending variance (f) Calculate the variable overhead efficiency variance for March. (Round answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter o for the amounts.) Favorable Variable overhead efficiency variance su (9) Calculate the fixed overhead spending variance for March. (Round per unit value to 2 decimal places, e.g. 52.75 and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 5,275. If variance is zero, select "Not Applicable" and enter 0 for the amounts.) Favorable Fixed overhead spending variance su
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


