Question: Exercise In the next few labs, we will create a few classes to represent a Store Management system. A store has employees and customers in



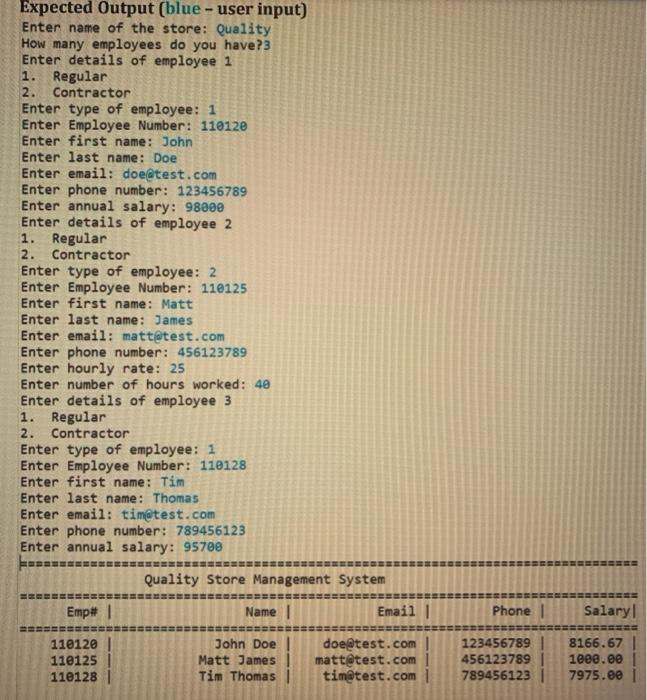
Exercise In the next few labs, we will create a few classes to represent a Store Management system. A store has employees and customers in their system. In this lab, we are creating a few classes namely Person, Employee, Regular, Contractor, Store. All personal attributes like first name, last name, email, phone number should be in Person class. Employee should have an employee number attribute and an Employee object named emp. As we know that the store has regular and contractor employees, we need to create two classes - Regular and Contractor, both extends Employee class. Regular class should have a salary attribute that represents the monthly salary. Contractor class should have attributes to represent hourly rate and number of hours worked. Store class will manipulate the store employees. More classes like Customer, different types of customer classes etc. will be added later. As the first step, you need to create the following classes: Person class Instance variables: firstName(String), lastName(String), email(String), phoneNumber (long). Constructor: as required Methods: getters that return name, email and phone number. Name should be returned as one string. If first name is "John" and last name is "Doe", getter should return "John Doe". . readPersonal Details(): Accepts nothing, returns nothing. Reads first name, last name, email and phone number and stores in corresponding variables. Employee class (extends Person) Instance variables: employeeNumber (int), emp (Person) Constructor: parameterized constructor that initializes an employee with employee number and all personal properties. As you have a parameterized constructor for Person class, use that to set personal properties (you need to create emp as a Person object from this constructor). Methods: 1. readEmployee (): accepts nothing, returns nothing. Reads all employee information. 2. print Employee (): accepts nothing, returns nothing. This method prints details of an employee using formatted output (use printf). Regular class (extends Employee) Instance variables: salary (double) Methods: 1. readEmployee(): accepts nothing, returns nothing. Make a call to the readEmployeel) method of the parent class. Then, reads annual salary from the user, converts it to monthly salary and store it in salary instance variable. 2. print Employee(): accepts nothing, returns nothing. Make a call to the print Employee of the parent class. Then, prints salary info (formatted output). Contractor class (extends Employee) Instance variables: hourlyRate (double), numHours (double) Methods: 1. readEmployee(): accepts nothing, returns nothing. Make a call to the readEmployeel) method of the parent class. Then, reads hourly rate and number of hours worked. 2. print Employee(): accepts nothing, returns nothing. Make a call to the printEmployee of the parent class. Then, prints salary, which is the product of hourly rate and the number of hours worked (formatted output). Store class Instance variables: an array of Employee named employees Constructor parameterized constructor that creates the array of employees with the given size (this size will be read in main(), and will be sent here when creating the Store object) Methods: 1. readEmployee Details: accepts nothing, returns nothing. In a for loop, read details of all employees. First, read the type of the employee. Based on the type of the employee, corresponding array object needs to be created (Polymorphism). Then, call readEmployee() method. 2. printEmployeeDetails(): accepts nothing, returns nothing. In a for loop, call printEmployee() to print details of all employees. 3. printLine(): static method that prints a line using "=" 4. printTitle(): static method that prints the title of the output. This method gets the name of the store as a parameter, which will be used in the formatted print statement.printLine() method will be called from this method to print lines. Lab3 class This is the driver class (test class), which means this class has the main method. Main method . . This method read the name of the store (example: "Quality") and the number of employees (stored in num). A Store object will be created with the 'num'. Call readEmployee Details() method to read details of all employees Print the title and the header row Call print Employee() method to print details of all employees. Format your code with proper indentation and formatting. Your code should be properly commented. Test plan and external documentation are not required for this exercise, but in future labs they will be required. Expected Output (blue - user input) Enter name of the store: Quality How many employees do you have?3 Enter details of employee 1 1. Regular 2. Contractor Enter type of employee: 1 Enter Employee Number: 110120 Enter first name: John Enter last name: Doe Enter email: doe@test.com Enter phone number: 123456789 Enter annual salary: 98000 Enter details of employee 2 1. Regular 2. Contractor Enter type of employee: 2 Enter Employee Number: 110125 Enter first name: Matt Enter last name: James Enter email: matt@test.com Enter phone number: 456123789 Enter hourly rate: 25 Enter number of hours worked: 40 Enter details of employee 3 1. Regular 2. Contractor Enter type of employee: 1 Enter Employee Number: 110128 Enter first name: Tim Enter last name: Thomas Enter email: tim@test.com Enter phone number: 789456123 Enter annual salary: 95708 Quality Store Management System Name Email Emp# 1 Phone | Salary 110120 110125 110128 John Doel Matt James Tim Thomas doe@test.com matt@test.com | tim@test.com 1 123456789 456123789 | 7894561231 8166.67 1eee.ee 7975.ee
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


