Question: Exhibit 4.5: The following questions are based on this problem and accompanying Solver sensitivity report. The Byte computer company produces two models of computers, Plain
-
-
Exhibit 4.5: The following questions are based on this problem and accompanying Solver sensitivity report.
The Byte computer company produces two models of computers, Plain and Fancy. It wants to plan how many computers to produce next month to maximize profits. Producing these computers requires wiring, assembly and inspection time. Each computer produces a certain level of profits but faces only a limited demand. There are also a limited number of wiring, assembly and inspection hours available in each month. The data for this problem is summarized in the following table.
In the provided blank, insert the letter that corresponds with the correct answer. For example, if the correct answer is "a. 2.5", insert "a" as the correct answer.
Computer
Profit per
Maximum demand for
Wiring Hours
Assembly Hours
Inspection Hours
Model
Model ($)
product
Required
Required
Required
Plain
40
80
.4
.5
.2
Fancy
35
90
.5
.4
.2
Hours Available
60
50
30
Let X1 = Number of Plain computers to produce
X2 = Number of Fancy computers to produce
The LP model for the problem is
MAX: 40 X1 + 35 X2
Subject to: .4 X1 + .5 X2 60 (wiring hours)
.5 X1 + .4 X2 50 (assembly hours)
.2 X1 + .2 X2 30 (inspection hours)
X1 80 (Plain computers demand)
X2 90 (Fancy computers demand)
X1, X2 0
Quiz 3 Exhibit 4.5 Image.png
-
I. Refer to Exhibit 4.5. What is maximum possible profit?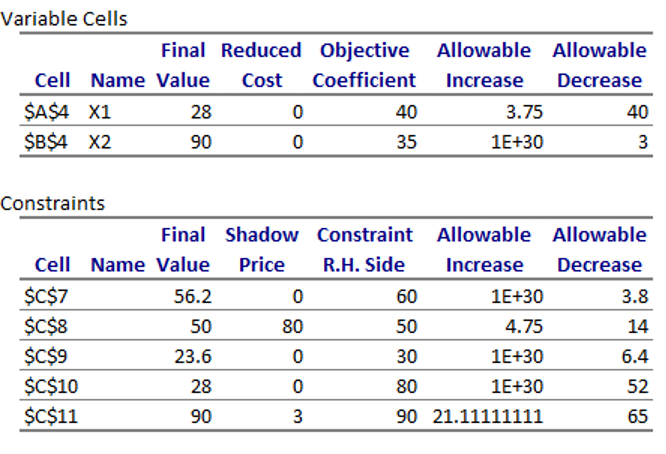
Blank 1
a. 4270
b. 4720
c. 4300
d. none of these
II. Refer to Exhibit 4.5. What happen to the optimal solution if the objective function coefficient of decision variable X1 is now equal to $45? Blank 2
a. cannot tell because there is not enough information
b. optimal solution is not going to change
c. optimal solution is going to change
d. the problem becomes infeasible
III. Refer to Exhibit 4.5. What is the value of the objective function if the objective function coefficient of decision variable X2 is now equal to $40? Blank 3
a. cannot tell because there is not enough information
b. 4270
c. 4720
d. 4300
IV. Refer to Exhibit 4.5. If the right-hand side of constraint associated with demand of fancy computers change from 90 to 100 computers, what is the value of the objective function? Blank 4
a. 4270
b. 4720
c. 4300
d. none of these
V. Refer to Exhibit 4.5. If you have to eliminate 5 hours to the right hand side of the constraint associated to the assembly department, what will be the value of the objective function equal to? Blank 5
a. cannot tell because there is not enough information
b. 3870
c. 4250
d. 4670
- Blank 1
- Blank 2
- Blank 3
- Blank 4
- Blank 5
-
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


