Question: Explain . Q. Nos. 1-10 : Read the following 6. If interest payments are subtracted questions and choose the correct from gross fiscal deficit, the





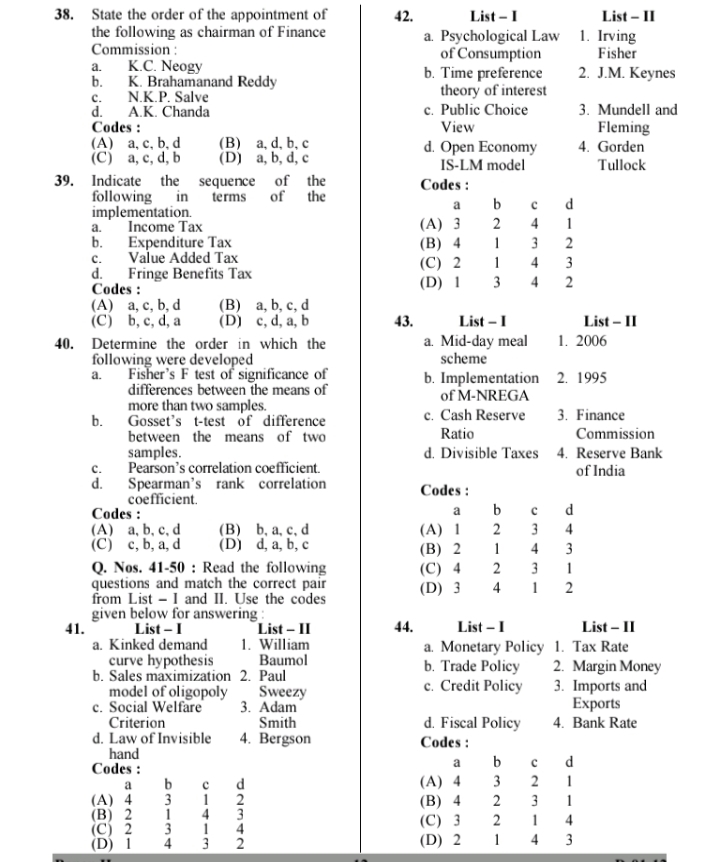

Explain .





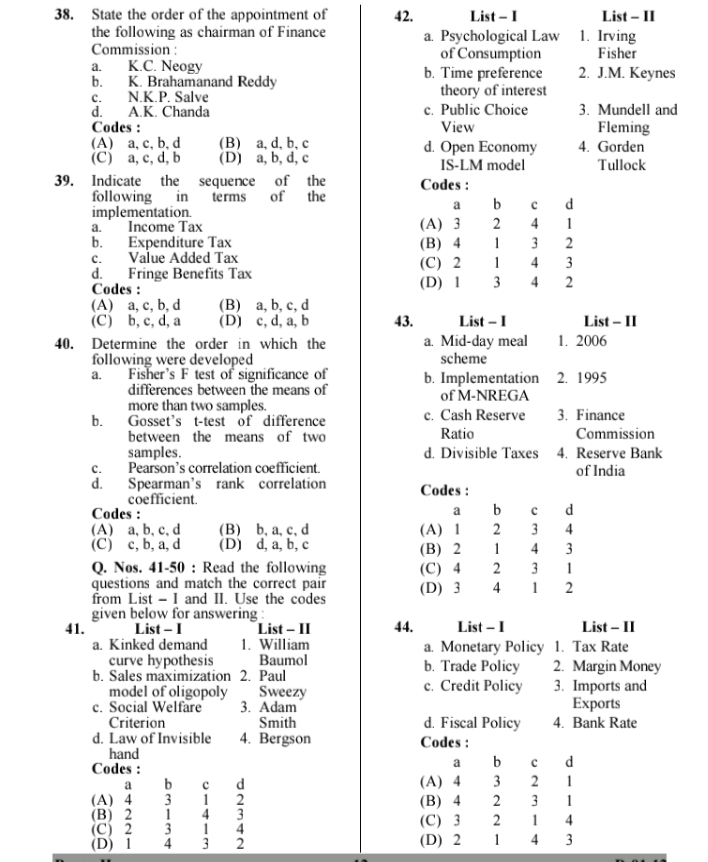

Q. Nos. 1-10 : Read the following 6. If interest payments are subtracted questions and choose the correct from gross fiscal deficit, the answer from the options given below remainder will be these questions. (A) revenue deficit 1. For downward movement along the B) gross primary deficit iso-quant, MRTS of Labour per unit (C) capital deficit of capital (MRTS, ) is given by (D) budgetary deficit (A) - dK/dL (B) dK/dL 7. Which of the following measures of (C) dL/dK central tendency will be the most (D) - dL/dK appropriate to use if the data relate to rates, proportions and ratios ? 2. Charging a different price in different (A) Arithmetic mean markets is called (A) price discrimination (B) Median (B) second degree price (C) Harmonic mean discrimination (D) Geometric mean (C) third degree price discrimination 8. Opportunity cost version of (D) perfect price discrimination comparative cost advantage doctrine was introduced by 3. Which of the following is the most significant in stabilization policy ? (A) J.M. Keynes (A) Private investment Kindleberger (B) Inventory investment C) Haberler (C) Autonomous investment (D) Karl Marx (D) Public investment 9. The most popular definition of 4. The concept of vicious circle of sustainable development is given by poverty is associated with (A) Kindleberger (A) World Development Report ) Schumpeter (B) UNDP Report (C) Ragnar Frish (C) Brundtland (D) Gunnar Myrdal (D) IMF Report 5. Solow built his model as an alternative to 10. During the planning period, highest (A) Kaldor's model of growth growth rate was achieved during (B) Ranis-Fei model of growth (A) eighth plan (C) Harrod-Domar model of (B) tenth plan growth (C) ninth plan (D) Meade's model of growth (D) seventh planQ. Nos. 11-20 : Read the questions 14. Human Development Index (HDI) is and select the correct option for the constructed with reference to answer from the list given below : a. Life expectancy at birth, real GDP per capita, gross 11. Labour theory of value was enrolment ratio, adult literacy propounded by rate. a. Adam Smith b Life expectancy at birth, real b. David Ricardo GDP per capita, combined C. Ragnar Nurkse, Gunnar gross enrolment ratio, adult Myrdal, R.M. Solow literacy rate. C. Fei-Rani's, Ragnar Nurkse Life expectancy, GDP per d. capita, infant mortality rate, Codes : literacy rate. (A) a and b (B) a and c d. GDP per capita, infant (C) a, b, c (D) a, b, c, d mortality rate, literacy rate Codes : 12. The features of the classical system (A) a and b (B) a and c are (C) c (D) a, b, d a. Monetary factors determine output and employment. 15. The unbalanced growth model was b. Self adjusting mechanism of propounded first by the economy. a. Albert O. Hirschman C. State action to direct b. H.S. Singer and Raul Prebisch development. C. Kindelberger and Ragnar d. Optimization through market in Nurkse the absence of state control. d. W.W. Rostow and Paul Codes : Streeten Codes : (A) a and b (B) a, b, c (A) a and b (B) a and c (C) b and d (D) a, b, d (C) a and d (D) a 13. Concepts of displacement and 16. Harrod-Domar model of growth is concentration effect in public based on the concepts of and their expenditure are attributed to equality a. A.C. Pigou and J.K. Mehta a. Population and productivity b. Alan T. Peacock and Jack growth. Wiseman b Investment and average growth C. Kenneth Arrow and Paul A rate of income. Samuelson C. Actual, warranted and natural d. A.R. Prest and I.M.D. Little growth rate. Codes : d. Productivity growth and (A) a and b (B) b investment growth. Codes : (C) a, b, c (D) a, b, c, d (A) a and c (B) a and d (C) c (D) a, b, c17. Factor endowment theory is also Q. Nos. 21-30 : Read the following known as questions and select the right a. Modern theory of international combination of Assertion (A) and Reason (R) from the codes given trade. below : b. Classical theory of 21. Assertion (A) : There is a natural international trade tendency to collude under Reciprocal demand theory. oligopoly. Factor proportions theory of Reason (R) : Inter-dependence of international trade. firms in oligopolistic markets. Codes : Codes : (A) a and b (B) band c (A) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation (C) a and d (D) c and d of (A). 18. Most important theory of increasing (B) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and public expenditure is associated with (R) is the correct explanation of (A). a. Adolph Wagner's hypothesis (C) (A) is correct, but (R) is b. Critical limit hypothesis incorrect. C. Administrative efficiency (D) (A) is incorrect, but (R) is hypothesis correct. d. Stability of income hypothesis 22. Assertion (A) : In short run, the Codes : marginal cost of output is the cost (A) a and b (B) a and c of additional labour and materials (C) a (D) c and d used in production. Reason (R) : Materials and labour 19. Under the Brettonwood system, the used in production alone vary in long term development assistance short run. was to be provided by Codes : a. IBRD (A) (A) is correct and (R) is incorrect. b. IDA (B) (A) is incorrect, but (R) is C. IMF correct. d. All the above (C) Both (A) and (R) are correct Codes : and (R) is the correct (A) a and b (B) a, b, c explanation of (A) (C) b and c (D) d (D) Both (A) and (R) are incorrect. 20. The Planning Commission of India 23. Assertion (A) : Post reform liberal trade policies have stimulated has recently announced the poverty India's growth. line as Reason (R) : Private enterprise got a. 7 42 per day per person for opportunities to contribute to urban area. growth of Indian manufacturing b. 7 26 per person per day for industries. rural areas. Codes : (A) Both (A) and (R) are correct, and C.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


