Question: Explain the output # Random Forest Model:# data selection is based on the top 6 variables positively correlated with the Target variable as shown abovedata
Explain the output
# Random Forest Model:# data selection is based on the top 6 variables positively correlated with the Target variable as shown abovedata |> select( Curricular.units.1st.sem..approved., Curricular.units.1st.sem..grade., Curricular.units.2nd.sem..approved., Curricular.units.2nd.sem..grade., Tuition.fees.up.to.date, Scholarship.holder, Target ) |> mutate( Target = ifelse(Target == "Dropout", 1, 0), across(where(is.character), as.factor) )preprocess_data mutate( across(where(is.numeric), ~ ifelse(is.na(.), median(., na.rm = TRUE), .)), across(where(is.factor), ~ ifelse(is.na(.), levels(.)[which.max(table(.))], .)) )}data_clean select(-Target), target = train_data$Target, K = 5, dup_size = 0)$data |> rename(Target = class)# Train Random Forest model: Trains a Random Forest model with 500 trees, which is useful for capturing complex interactions within the data. The importance parameter allows us to assess the contribution of each feature.rf_model % {data.frame( Student_ID = rownames(data_clean), Dropout_Probability = ., Predicted_Dropout = ifelse(. >= 0.5, "High Risk", "Low Risk"), Actual_Status = ifelse(data_clean$Target == 1, "Dropout", "Retained") )}# View important featuresvarImpPlot(rf_model, main = "Feature Importance Ranking")# Display prediction resultshead(final_predictions)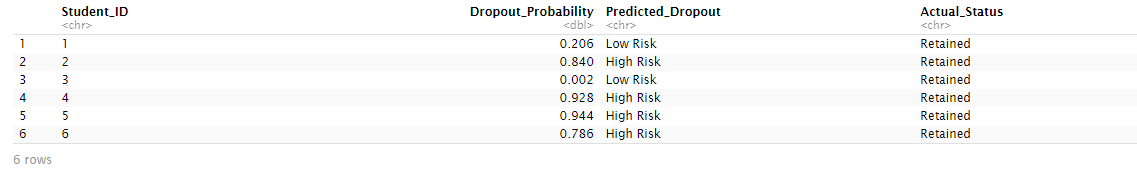
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


