Question: f3. Use any method to prove the statement. 1) For eyery integer n, if n2 is odd. then n is odd. 3. Write what you
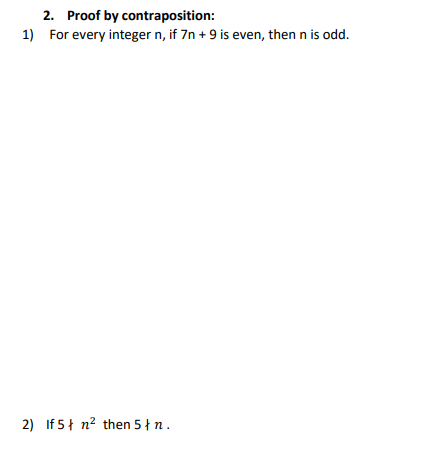
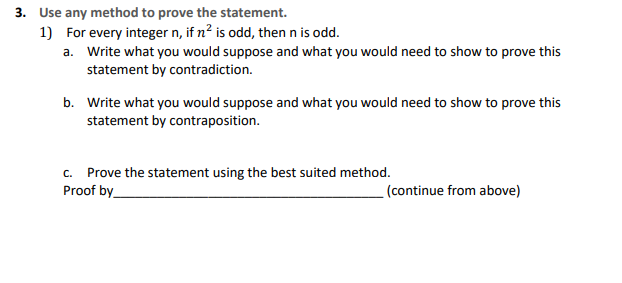





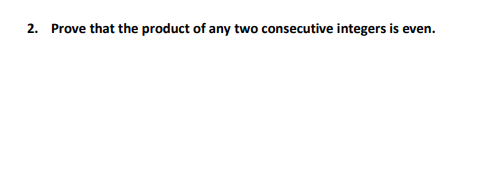

\f3. Use any method to prove the statement. 1) For eyery integer n, if n2 is odd. then n is odd. 3. Write what you would suppose and what you would need to show to prove this statement by contradiction. b. Write what you would suppose and what you would need to show to prove this statement by contraposition. c. Prove the statement using the best suited method. Proof by {continue from above} \f\f\f\fWorksheetl- Direct Proof and Disprool by Counterexample Marne: Determine which of the statements are true and which are false. Proye each true statement directly from the definition, and giye a counterexample for each false statement. If you need more space, please solye problems in the separate paper. ' True or False. The sum of any two odd integers is eyen. ' True or False. If a is any odd integer and b is any eyen integer, then 2a + 3b is eyen. ' True or False. For all nonnegatiye real numbers a and b, ' True or False. The product of two perfect squares is a perfect square. ' True or False. The sum of four consecutiye integers is diyisible by 2. ' True or False. The product of two irrationals is irrational. ' True orFalse. lfaEZand amod9=2,then mod3=1 ' True or False. If a; EZ and a mod 5 =4, then mod 5 = ' True or False. For all integers, a, b, and c, if and , then ' True or False. For all integers, a, b, and c, if and , then 2. Prove that the product of any two consecutive integers is even.Worksheet 1: Pro-of by cases Name: template the following pro-of. 1. Claim: For any intqern, n2 + 11 + 3 is always add. Proof)";I Let n. be an integer. [We wish to show that n2 + TI + 3 is odd.] We know that either ft is even or it is odd. So there are two cases to consider. [case 1} Suppose that n is even. [We need to show that n2 + rt + 3 is odd.] Since n is even we may write n = where it E E. Nowobsewethatn2+n+3=| ]2+| ]+3 =4k2+2k+2+1=1t 1+1. Since the integers are closed under multiplication and addition, we see that is an integer. This means that in2 + R + 3 is odd by denition of odd in this case. [easel] Suppose that n is odd. [We need to show that n 2 + n + 3 is odd.] Since n. is odd we may write in. = where ll: E E. Nowohsertrethatn2+n+3 =[ ]2+[ 1+3 = 2 {} + 1. Since the integers are closed under multiplication and addition, we see that is an integer. This means that n.2 + rt + 3 is odd by denition of odd in this case. In both cases we showed that for any integer n, n2 + rt + 3 is always add
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


