Question: fa) Show that if A + ip is an eigenvalue of A and z = r + zy is a corresponding eigenvector, then / =
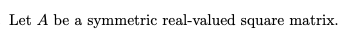
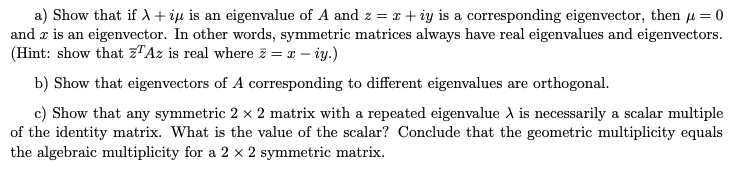
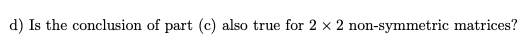
\fa) Show that if A + ip is an eigenvalue of A and z = r + zy is a corresponding eigenvector, then / = 0 and r is an eigenvector. In other words, symmetric matrices always have real eigenvalues and eigenvectors. (Hint: show that 2"Az is real where z = x - iy.) b) Show that eigenvectors of A corresponding to different eigenvalues are orthogonal. c) Show that any symmetric 2 x 2 matrix with a repeated eigenvalue ) is necessarily a scalar multiple of the identity matrix. What is the value of the scalar? Conclude that the geometric multiplicity equals the algebraic multiplicity for a 2 x 2 symmetric matrix.\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


