Question: ....................... Factorial.java : public class Factorial { /** * Returns the factorial of the given integer. * * @param n * an integer * @return
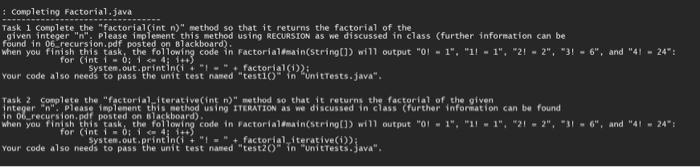
.......................
Factorial.java :
public class Factorial {
/**
* Returns the factorial of the given integer.
*
* @param n
* an integer
* @return the factorial of the given integer
*/
public static int factorial(int n) {
return 0;
}
/**
* Returns the factorial of the given integer.
*
* @param n
* an integer
* @return the factorial of the given integer
*/
public static int factorial_iterative(int n) {
return 0;
}
/**
* The main method of the {@code Factorial} class.
*
* @param args
* the program arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i
System.out.println(i + "! = " + factorial(i));
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i
System.out.println(i + "! = " + factorial_iterative(i));
}
}
.................................
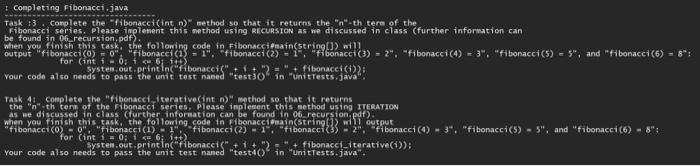
Fibonacci.java :
public class Fibonacci {
/**
* Returns the specified term in the Fibonacci series.
*
* @param n
* the index of the term in the Fibonacci series
* @return the specified term in the Fibonacci series
*/
public static int fibonacci(int n) {
return 0;
}
/**
* Returns the specified term in the Fibonacci series.
*
* @param n
* the index of the term in the Fibonacci series
* @return the specified term in the Fibonacci series
*/
public static int fibonacci_iterative(int n) {
return 0;
}
/**
* Returns the specified term in the Fibonacci series.
*
* @param n
* the index of the term in the Fibonacci series
* @param solutions
* an {@code int} array holding finbonacci terms calculated previously
* @return the specified term in the Fibonacci series
*/
public static int fibonacci_dp(int n, int[] solutions) {
return 0;
}
/**
* The main method of the {@code Fibonacci} class.
*
* @param args
* the program arguments
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i
System.out.println("fibonacci(" + i + ") = " + fibonacci(i));
System.out.println();
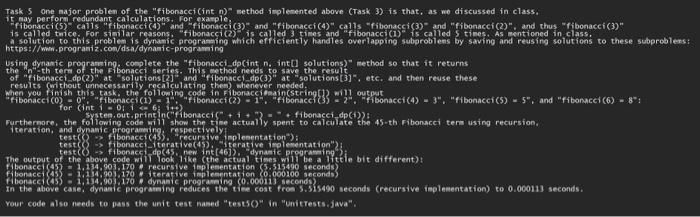
for (int i = 0; i Conpleting Factorial,java rask 1 complete the "factorial(int n )" method so that it returns the factorial of the given integer "n". Please inpleaent this method using ReCursion as ne discussed in class (further information can be ound in 06 recursion.pdf posted on Blackboard): rour code also needs to pass the unit test named "test10 " in "initrests. Java". rask 2 Conplete the "factorial_fterative(int n) " method so that it returns the factorial of the given nteger "n", Please implenent this method using ITERATIoN as we discussed in class (further information can be found in ob_recursion, pde posted on Blackboard). for (int i=0;i=4ji++)="+ factorial { terative(i)): t Conpleting fibonacci, java Task i3 Conplete the "fibonacci(int n ) " method so that it returns the " n th term of the Fibonacci sepies. Please inplenent this method using Ricuesion as ne discussed in class (further information can be found in of recursion, pdf . when you finish this task. the following code in fibonacciomain(string[]) wil1 vour code also needs to pass the unit test naked "test 302 in "Unittests, java." Task 41 Conplete the "fibonacei iterative (intn)" method so that it returns the " n "- th tere of the Fibonacci series, Pl ease inplenent this method using IIEATION as ne discussed in class (further information can be found in o6-recursionapde). vour code also needs to pass the unit test naned "testuO) in "Unitests. java. Task 5 one najor problen of the "fibonacei(int n )" sethod implenented above (Task 3 ) is that, as we discussed in class, it fay pertory redundant calculations. For exarple, is called taice. For similar reasons, fibonacci(2) is called 3 times and "fibonacci (1) is called 5 times. As anentioned in class. an solution to this problem is dynamic prograting which efficientiy hand les overlapping subproblens by saving and reusing solutions to these subproblens: using dynanic programing conplete the "fibonacei dp(int n, int[] solutions)" method so that it returns the n nth tem of the Fibonace sefies. This pethod needs to save the result results (without unnecessarify recalculating then) whenever needed. Furthermore, the following code mili shom the time actually spent to calculate the 45 -th fibonacei tera using recursion, iteration, and drnaanic programing; respectively. test( fibonacei(4), "recursive implesentation ); test { fibonacc (iterative (45) ifterative inplesentation" 2} The output of the above code wili look, like (the actual tiges wili be andite bile bit different) t tibonacei (45)=1,134,903,170 ? recursive inplesentation (5.515490 seconds) fibonacci(43)=1,13,903,170 dynanie prograning (0.000113 seconds). In the above case, dynasic programing reduces the tike cost fros S.5is490 seconds (recursive feplementation) to 0.000133 seconds. vour code also needs to pass the unit test nased "testsO" in "Unitrests.java
System.out.println("fibonacci(" + i + ") = " + fibonacci_iterative(i));
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i
System.out.println("fibonacci(" + i + ") = " + fibonacci_dp(i, new int[i + 1]));
System.out.println();
test(() -> fibonacci(45), "recursive implementation");
test(() -> fibonacci_iterative(45), "iterative implementation");
test(() -> fibonacci_dp(45, new int[46]), "dynamic programming");
}
/**
* Tests the specified {@code IntMethod}.
*
* @param method
* an {@code IntMethod}
* @param label
* a string representing the {@code IntMethod} to test
*/
private static void test(IntMethod method, String label) {
long t = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("fibonacci(45) = " + String.format("%,d", method.run())
+ String.format(" # " + label + " (%.6f seconds)", 1e-9 * (System.nanoTime() - t)));
}
/**
* An {@code IntMethod} represents a method returning an {@code int} value.
*
* @author Jeong-Hyon Hwang (jhh@cs.albany.edu)
*
*/
static interface IntMethod {
/**
* Returns an {@code int} value.
*
* @return an {@code int} value
*/
int run();
}
}
.............................................
UnitTests.java :
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.Test;
public class UnitTests {
/**
* Tests the Task 1 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
assertEquals(1, Factorial.factorial(0));
assertEquals(6, Factorial.factorial(3));
assertEquals(24, Factorial.factorial(4));
}
/**
* Tests the Task 2 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
assertEquals(1, Factorial.factorial_iterative(0));
assertEquals(6, Factorial.factorial_iterative(3));
assertEquals(24, Factorial.factorial_iterative(4));
}
/**
* Tests the Task 3 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
assertEquals(0, Fibonacci.fibonacci(0));
assertEquals(5, Fibonacci.fibonacci(5));
assertEquals(8, Fibonacci.fibonacci(6));
assertEquals(13, Fibonacci.fibonacci(7));
}
/**
* Tests the Task 4 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
assertEquals(0, Fibonacci.fibonacci_iterative(0));
assertEquals(5, Fibonacci.fibonacci_iterative(5));
assertEquals(8, Fibonacci.fibonacci_iterative(6));
assertEquals(13, Fibonacci.fibonacci_iterative(7));
}
/**
* Tests the Task 5 implementation.
*
* @throws Exception
* if an error occurs
*/
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception {
assertEquals(0, Fibonacci.fibonacci_dp(0, new int[1]));
assertEquals(5, Fibonacci.fibonacci_dp(5, new int[6]));
assertEquals(8, Fibonacci.fibonacci_dp(6, new int[7]));
assertEquals(13, Fibonacci.fibonacci_dp(7, new int[8]));
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
assertEquals(1134903170, Fibonacci.fibonacci_dp(45, new int[46]));
assertTrue(System.currentTimeMillis() - t
}
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


