Question: fClaim: (LHS) = (RHS) Proof: We use combinatorial proof. We count...( Explanation of What We Are Counting)... (1st Counting): The left-hand side is... ...( Explanation
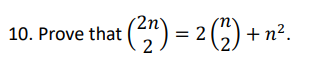


\fClaim: (LHS) = (RHS) Proof: We use combinatorial proof. We count...( Explanation of What We Are Counting)... (1st Counting): The left-hand side is... ...( Explanation of How We Are Counting)... 0 (2nd Counting): Now, let's count this a different way... ...( Explanation of How We Are Counting the Same Thing a Different Way)... ...Which is the right-hand side. 0 In summary, we've counted ( What We Counted) with two methods. One method gives (LHS), and the other gives (RHS). Therefore, (LHS) = (RHS)Try to break it into parts. a. What does (22\") count? b. What does (2\") count? What are there two of? Why might that mean we need to addfmultiply to get 2 (at)? c. What might 112 account for? Remember that n2 = n x n and it might be helpful to think about when we use the product principle
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


